Abstract
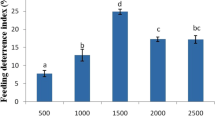
Feeding on Ricinus communis leaf treated with different concentrations (0.1, 0.3 and 0.5%) of ether extracts of Erithrina indica seed and Delonix regia flower against Ergolis merione, Porthesia scintillans and Spodoptera exigua resulted in high larval and pupal mortality. Food consumption, assimilation, conversion and fecundity decrease with increasing concentration. Larval mortality was 20 to 91 % and damage was decreased by 65% through the application of the highest concentration of each chemical.
Résumé
Se nouir en Ricinus communis furille treté avec des concentration différente (0,1, 0,3 et 0,5%) d’extraction d’ether de Erithrina indica de recine et de fleur Delonix regia contre Ergolis merione, Porthesia scintillans et Spodoptera exigua résulte en mortalité de chinille et de pupal élevé. La consommation de neurriture, assimulé, changé et fécondé diminue avec la concéntration montente. La mortalité des chenille était de 20 à 91% et la décroissance par 65% par là de là haute concentration de chaque produit application chemique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Applebaum S. W. and Birk Y. (1972) Natural mechanism of resistance to insects in legume seeds. In Insect and Mite Nutrition (Edited by Rodriguez J. C.), pp. 629–636. North Holland, Amsterdam.
Bernays E. A. and Chapman R. F. (1978) Plant chemistry and acridoid feeding behaviour. In Biochemical Aspects of Plant Animal Coevolulion (Edited by Harborne J. B.), pp. 99–141. Academic Press, New York.
Brattsten L. (1979) Biochemical defense mechanisms in herbivores against plant allelochemicals. In Herbivores: Their Interaction with Secondary Plant Metabolites (Edited by Rosenthal G. A. and Janzen D. H.) pp. 199–277. Academic Press, New York.
Chandrakantha J. (1985) Studies on seed-insect interaction: Bioenergetics and reproduction of Callosobruchus maculatus. Ph.D. thesis, Madurai Kamaraj University, Madurai, India.
Cates R. G. and Rhoades D. (1977) Pattern in production of antiherbivore chemical defense in plant communities. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 5, 185–193.
Feeny P. P. (1976) Plant apparency and chemical defense: Biochemical interaction between plants and insects. In Rev. Adv. Phytochem. (Edited by Wallace J. and Mansell R.), 10, 1–10.
Janzen D. H. (1977) Seed eaters versus seed size, number, toxicity and dispersal. Evolution 23, 1–27.
Koul O. (1982) Insect feeding deterrents in plants. Ind. Rev. Life Sci. 2, 97–125.
Mansour M. H. (1981) Efficiency of two allelochemics on the conversion of ingested and digested food into body tissues of Spodoptera littoralis. Z. Angew. Entomol. 92, 493–499.
Manuwoto S. and Scriber J. M. (1981) Consumption and utilization of three maize genotypes by the Southern armyworm Spodoptera eridania. J. econ. Entomol. 75, 163–167.
McDaniel C. N. and Berry S. J. (1974) Effects of caffeine - and aminophylline on adult development of Cecropia silk moth. J. Insect Physiol. 20, 245–252.
Muthukrishnan J. and Pandian T. J. (1987) Insecta. In Animal Energetics (Edited by Pandian T. J. and Vernberg F. J.), pp. 371–511. Academic Press, New York.
Muthukrishnan J. and Senthamizhselvan M. (1987) Use of Azadirachta indica and tannic acid as pesticides in the management of lepidopterous pests. Int. Conf. on Pesticides in Tropical Agriculture (in press).
Muthukrishnan J., Mathavan S. and Venkatasubbu K. (1979) Effects of caffeine and theophylline on food utilization and energetics of Danus chrysippus. Entomon 4, 307–312.
Rhoades D. F. and Cates R. G. (1976) Towards a general theory of plant antiherbivore chemistry: Biochemical interaction between plants and insects. Rev. Adv. Phytochem. 10, 168–213.
Rose A. F., Jones K. C., Haddon W. F. and Dreyer D.C. (1981) Frindelane diterpenoid acids from Grindelia humilis: feeding deterrency of diterpene acids towards aphids. Phytochemistry 20, 2249–2255.
Schoonhoven L. M. and Meerman J. (1978) Metabolic cost of changes in diet and neutralisation of allelochemicals. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 24, 689–693.
Scriber J. M. (1978) Cyanogenic glycosides in Lotus corniculatus. The effect upon growth, energy budget and nitrogen utilization of southern armyworm, Spodoptera eridania. Oecologia 34, 143–155.
Subbaratnam A. V. (1956) Chemical examination of the seeds of Erythrina indica. Ind. J. Sci. Res. 15, 210–212.
Waldbauer G. P. (1968) The consumption and utilization of food by insects. Adv. Insect Physiol. 5, 229–288.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senthamizhselvan, M., Muthukrishnan, J. Effect of Plant Chemicals on Food Consumption of Three Lepidopteran Larvae. Int J Trop Insect Sci 13, 429–434 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400013722
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400013722