Abstract
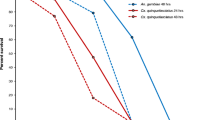
An ecological study was conducted in two pools, one temporary and one semi-permanent at the Kenya coast to determine the relationship between infection levels of Coelomomyces indicus Iyengar in larvae of Anopheles gambiae Giles, and the species and density of copepods found in these sites. Microcyclops minutus Claus, an intermediate host of Coelomomyces indicus, was the predominant species in both pools. Other species were, Mesocyclops leuckarti Claus, Mesocyclops leuckarti pilosa Kiefer, and Mesocyclops (Thermocyclops) decipiens Kiefer. Infections occurred during the periods when M. minutus densities were above 12 cyclops per 250 ml of water. A positive relationship was shown between M. minutus density and infection levels in An. gambiae with C. indicus. The r-value for this relationship in the temporary pool was 0.726, and in the semi-permanent pool, 0.639.
Résumé
On a dirigé un étude écologique dans deux flaques, l’une temporaire et l’autre quasi-permanent, au cote de Kenya pour que determine le rapport entre les niveaux d’infection par Coelomomyces indicus Iyengar dans les larves de Anopheles gambiae Giles, et les espèces de copepods et leur densité a ces sites. Microcyclops minutus Claus, un hote intermedaire de C. indicus, était l’espèce predominant dans les deux flaques. D’autres espèces étaient Mesocyclops leuckarti Claus, Mesocyclops leuckarti pilosa Kiefer, et Mesocyclops (Thermocyclops) decipiens Kiefer. Les infections ont existé pendant le temps que les densités de M. minutus était plus que 12 cyclops/250 ml d’eau. On a demonstré un rapport positiv entre le densité de M. minutus et les niveaux d’infection avec C. indicus dans les larves de A. gambiae. Le valeur r pour ce rapport dans le flaque temporaire a été 0.726 et dans le flaque quasi-permanent, le valeur a été 0.639.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Couch J. N. (1972) Mass production of Coelomomyces, a fungus that kills mosquitoes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science. USA 69, 2043–2047.
Couch J. N. and Umphlett C. J. (1963) Coelomomyces infections. In. E. A. Steinhaus (ed.), Insect pathology, an advanced treatise, Vol. 2, Academic Press, New York. pp. 149–188.
Chapman H. C. (1974) Biological control of mosquito larvae. A. Rev. Ent. 19, 33–59.
Chapman H. C. and Glen Jr. F. E. (1972) Incidence of the fungus Coelomomyces punctatus and C. dodgei in larval populations of the mosquito Anopheles crucians in 2 Louisiana ponds. J. Invertebr. Path. 19, 256–261.
Federici B. A. (1977) Coelomomyces punctatus: The effect of high intermediate copepod host density on larval mosquito infection rates. Proceedings and Papers of the California Control Association 45, 109.
Federici B. A. (1980) Production of the mosquito-parasitic fungus Coelomomyces dodgei through syncronized infection and growth of the intermediate copepod host Cyclops vernalis. Entomophaga 25, 209–217.
Federici B. A. and Chapman H. C. (1977) Coelomomyces dodgei: Establishment of an in vivo laboratory culture. J. Invertebr. Path. 30, 288–297.
Federici B. A. and Roberts D. W. (1976) Experimental laboratory infection of mosquito larvae with fungi of the genus Coelomomyces. II. Experiments with Coelomomyces punctatus in Anopheles quadrimaculatus. J. Invertebr. Path. 27, 333–341.
Harding J. F. and Smith W. A. (1974) A key to the British freshwater cyclopid and calanoid copepods. Freshwater Biological Association. Scientific Publication No. 18, 25–41.
Kiefer F. (1939) Crustacea. IV. Copepoda: Diaptomidae, cyclopidae. Mission Scientifique de L’Omo Tome V. Fascicule 56.
Muspratt J. (1946) Experimental infection of larvae of Anopheles gambiae (Diptera, Culicidae) with a Coelomomyces fungus. Nature 158, 202.
Muspratt J. (1963) Destruction of the larvae of Anopheles gambiae Giles by a Coelomomyces fungus. WHO Bulletin 29, 81–86.
Otieno W. A., Odindo M. O., Sabwa D. M. (1985) Occurrence of Coelomomyces indicus, a fungal pathogen of malaria mosquito vector, Anopheles gambiae complex along the Kenya coast. Insect Sci. Applic. 6(2), 199–204.
Pennak R. W. (1978) Freshwater invertebrates of the United States. John Wiley and Sons. Inc. New York. pp. 388–420.
Pillai J. A. (1971) Coelomomyces opifexi (Pillai and Smith) (Coelomomycetaceae: Blastocladiales) I. Its distribution and the ecology of infection in New Zealand. Hydrobiologia 38, 425–436.
Umphlett C. J. (1969) Infection levels of Coelomomyces punctatus, an aquatic fungus parasite, in a natural population of the common malaria mosquito, Anopheles quadrimaculatus. J. Invertebr. Path. 15, 299–305.
Walker A. J. (1938) Fungal infections of mosquitoes, especially Anopheles costalis. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 32, 231–244.
Whisler H. C., Zebold S. L. and Shemanchuk J. A. (1975) Life history of Coelomomyces psorophorae. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science U.S.A. Vol. 72(2), 693–696.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabwa, D.M., Otieno, W.A. & Odindo, M.O. Infection Levels of Coelomomyces indicus Iyengar in Larvae of Anopheles gambiae Giles, as Related to the Copepod Fauna in Breeding Sites at the Kenya Coast. Int J Trop Insect Sci 8, 29–32 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400006901
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400006901