Abstract
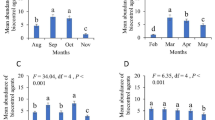
Surveys were conducted in two different ecological zones (semi-arid and arid) of Kenya to monitor egg, larval and pupal populations of the sorghum shootfly, Atherigona soccata, on a wild host, Sorghum arundinaceum. Populations were found to be usually higher on wild sorghum than on local varieties of Sorghum bicolor, the cultivated host. During dry periods, shootfly eggs and larvae were still found on wild sorghum, especially in moist areas such as beds of temporary streams or river banks. Population levels seem to be related primarily with the availability of susceptible stems, which in itself is determined by rainfall, soil conditions, density of other vegetation and by the phenology and the distribution of the host plant, Sorghum arundinaceum, being a pioneer species which colonizes recently disturbed areas and is subsequently replaced by other grass species. Since no evidence of the existence of an aestivation diapause has been found, it is reasonable to assume that Sorghum arundinaceum is a major reservoir for A. soccata, especially during the dry season.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry D. (1972) Notes on life history of a sorghum fly, Atherigona varia soccata. Ann. ent. Soc. Am. 65, 586–589.
Bleton C. A. and Fieuzet L. (1943) Sur la présence et la biologie au Maroc, d’Atherigona soccata Rondani, diptére parasite du sorgho cultivé. Bull. Soc. Hist. nat. Afr. N. 34, 112–117.
Blum A. (1972) Sorghum breeding for shootfly resistance in Israel. In Control of Sorghum Shootfly (Ed. by Jotwani M. G. and Young W. R.), pp. 180–191. Oxford & IBH, New Delhi.
Deeming J. C. (1971) Some species of Atherigona Rondani (Diptera:Muscidae) from Northern Nigeria, with special reference to those injurious to cereal crops. Bull. ent. Res. 61, 133–190.
Granados Y. (1972) The role of wild hosts on the population dynamics of the sorghum shootfly in Thailand. In Control of Sorghum Shootfly (Ed. by Jotwani M. G. and Young W. R.), pp. 112–118. Oxford & IBH, New Delhi.
Nye I. W. B. (1960) The Insect Pests of Graminaceous Crops of East Africa. Colonial Research Studies No. 31, HMSO, London.
Ogwaro K. (1979) Seasonal activity of the sorghum shootfly Atherigona soccata (Diptera:Anthomyiidae). Entomologia exp. appl. 26, 74–79.
Ram S., Handa D. P. and Gupta M. P. (1976) Effects of planting dates of fodder sorghum on the incidence of shootfly, Atherigona soccata Rond. Indian J. Ent. 38, 290–293.
Starks K. J. (1970) Increasing infestation of the sorghum shootfly in experimental plots. J. econ. Ent. 63, 1715–1716.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delobel, A.G.L., Unnithan, G.C. The Status of Sorghum Arundinaceum as a Host of Atherigona Soccata Rondani (Diptera:Muscidae) in Kenya. Int J Trop Insect Sci 2, 67–71 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400002186
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400002186