Abstract
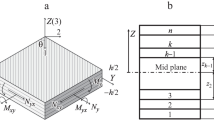
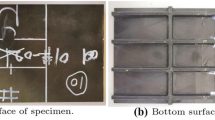
This study focused on the impact behavior of carbon-fiber-wrapped composite cylinders subjected to impact from flat-ended, hemispherical-nosed and conical-nosed impactors. Damage morphologies of the cylinders and mechanisms of the damage were analyzed. Change laws of the maximum impact forces, durations of impact processes and energies absorbed by the cylinders after impact with different impactors and impact energies were obtained. A finite element model was developed and the simulation results were in reasonable agreement with the tests. Finally, taking the flat-ended impactor as an example, stress distributions of the cylinders under pressurization and impact were discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Demir, O. Sayman, A. Dogan, V. Arikan, Y. Arman, The effects of repeated transverse impact load on the burst pressure of composite pressure vessel, Compos. Part B 68 (2015) 121–125.
Q. Tang, X.Y. Liao, Z. Gao, Stacking sequence optimization of laminated composite cylinder shell for maximal buckling load, Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 21 (4) (2008) 31–34.
Z.H. Xie, A.J. Vizzini, Q.R. Tang, On residual compressive strength prediction of composite sandwich panels after low-velocity impact damage, Acta Mech. Solida Sinica 19 (1) (2006) 9–17.
S. Agrawal, K.K. Singh, P.K. Sarkar, Impact damage on fibre-reinforced polymer matrix composite-a review, J. Compos. Mater. 48 (3) (2014) 317–332.
C.L. Zheng, M.F. Ren, W. Zhao, H.R. Chen, Delamination prediction of composite filament wound vessel with metal liner under low velocity impact, Compos. Struct. 75 (1–4) (2006) 387–392.
M.G. Han, S.H. Chang, Failure analysis of a Type III hydrogen pressure vessel under impact loading induced by free fall, Compos. Struct. 127 (2015) 288–297.
EN 12245-2002, Transportable gas cylinders-Fully wrapped composite cylinders.
ISO/TS 15869-2009, Gaseous hydrogen and hydrogen blends-Land vehicle fuel tanks.
ISO 11439-2013, Gas cylinders-high pressure cylinders for the on-board storage of natural gas as a fuel for automotive vehicles.
G. Perillo, F. Grytten, S. Sørbø, V. Delhaye, Numerical/experimental impact events on filament wound composite pressure vessel, Compos. Part B 69 (2015) 406–417.
P. Blanc-Vannet, Burst pressure reduction of various thermoset composite pressure vessels after impact on the cylindrical part, Compos. Struct. 160 (2017) 706–711.
K.L. Alderson, K.E. Evans, Low velocity transverse impact of filament-wound pipes. Part 1: damage due to static and impact loads, Compos. Struct. 20 (1) (1992) 37–45.
K.L. Alderson, K.E. Evans, Failure mechanisms during the transverse loading of filament-wound pipes under static and low velocity impact conditions, Composites 23 (3) (1992) 167–173.
J. Curtis, M.J. Hinton, S. Li, S.R. Reid, P.D. Soden, Damage, deformation and residual burst strength of filament-wound composite tubes subjected to impact or quasi-static indentation, Compos. Part B 31 (5) (2000) 419–433.
K. Lasn, N.P. Vedvik, A.T. Echtermeyer, The sensitivity of the burst performance of impact damaged pressure vessels to material strength properties, IOP Conf. Ser. 139 (1) (2016) 012029.
S.W. Kim, E.H. Kim, M.S. Jeong, I. Lee, Damage evaluation and strain monitoring for composite cylinders using tin-coated FBG sensors under low-velocity impacts, Compos. Part B 74 (2015) 13–22.
M. Tarfaoui, P.B. Gning, L. Hamitouche, Dynamic response and damage modeling of glass/epoxy tubular structures: numerical investigation, Compos. Part A 39 (1) (2008) 1–12.
C. Atas, B.M. Icten, M. Kucuk, Thickness effect on repeated impact response of woven fabric composite plates, Compos. Part B 49 (2013) 80–85.
Q.G. Wu, H.M. Wen, Y. Qin, S.H. Xin, Perforation of FRP laminates under impact by flat-ended projectiles, Compos. Part B 43 (2) (2012) 221–227.
S.H. Xin, H.M. Wen, Numerical study on the perforation of fiber reinforced plastic laminates struck by high velocity projectiles, J. Strain Anal. Eng. Des. 47 (7) (2012) 513–523.
J.R. Xiao, B.A. Gama, J.W. Gillespie, Progressive damage and delamination in plain weave S-2 glass/SC-15 composites under quasi-static punch-shear loading, Compos. Struct. 78 (2) (2007) 182–196.
P.F. Liu, L.J. Xing, J.Y. Zheng, Failure analysis of carbon/epoxy composite cylindrical laminates using explicit finite element method, Compos. Part B 56 (2014) 54–61.
A. Manes, D. Lumassi, L. Giudici, M. Giglio, An experimental-numerical investigation on aluminium tubes subjected to ballistic impact with soft core 7.62 ball projectiles, Thin-Walled Struct. 73 (2013) 68–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Q., Chen, X., Fan, Z. et al. Experimental and numerical studies of impact on filament-wound composite cylinder. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 30, 540–549 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camss.2017.09.001
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camss.2017.09.001