Abstract
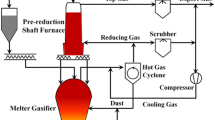
Based on the principles of the discrete element method (DEM), a scaled-down model was established to analyze burden descending behavior, including asymmetric phenomena, throughout an entire COREX shaft furnace (SF). The applicability of the DEM model was validated by determining its accordance with a previous experiment. The effects of discharge rate and abnormal conditions on solid flow were described in terms of solid flow pattern and microscopic analysis. Results confirmed that the solid flow of the COREX SF can be divided into four different flow regions; the largest normal force exists at the top of the man-made dead zone, and the weak force network exists in the funnel flow region. The basic solid flow profile was identified as a clear Flat→U→W type. Increasing the discharge rate decreased the quasi-stagnant zone size, but did not affect the macroscopic motion of particles or the shape of patterns above the bustle. For asymmetric conditions, in which particles were discharged at different rates, the solid flow patterns were asymmetric. Under an abnormal condition where no particles were discharged from the left outlet, a sizeable stagnant zone was formed opposite to the working outlet, and “motionless” particles located in the left stagnant zone showed potential to increase the period of static contacts and sticking effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. S. Zhou, Iron and Steel 40 (2005) No. 11, 1–8.
Y. X. Qu, Y. X. Yang, Z. S. Zou, C. Zeilstra, K. Meijer, R. Boom, ISIJ Int. 54 (2014) 2196–2205.
B. Anameric, S. K. Kawatra, Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 30 (2008) 1–51.
N. Wang, X. M. Xie, Z. S. Zou, L. Guo, W. R. Xu, Y. S. Zhou, Steel Res. Int. 79 (2008) 547–552.
Y. X. Qu, Z. S. Zou, Y. P. Xiao, ISIJ Int. 52 (2012) 2186–2193.
H. F. Li, Z. G. Luo, Z. S. Zou, J. J. Sun, L. H. Han, Z. X. Di, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 19 (2012) No. 9, 36–42.
J. J. Sun, Z. G. Luo, Z. S. Zou, Powder Technol. 281 (2015) 159–166.
L. H. Han, Z. G. Luo, X. L. Zhou, H. Zhou, Z. S. Zou, Y. Z. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20 (2013) No. 3, 30–35.
Q. Li, M. X. Feng, Z. S. Zou, ISIJ Int. 53 (2013) 1365–1371.
L. H. Han, Z. G. Luo, H. Zhou, Z. S. Zou, Y. Z. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 22 (2015) No. 4, 304–310.
Y. J. Lee, Powder Technol. 102 (1999) 194–201.
H. Zhou, Z. S. Zou, Z. G. Luo, T. Zhang, Y. You, H. F. Li, Ironmak. Steelmak. 42 (2015) 209–216.
M. Y. Kou, S. L. Wu, W. Shen, K. P. Du, L. H. Zhang, J. Sun, ISIJ Int. 53 (2013) 2080–2089.
Q. F. Hou, M. Samman, J. Li, A. B. Yu, ISIJ Int. 54 (2014) 1772–1780.
P. A. Cundall, O. D. L. Strack, Geotechnique 29 (1979) 47–65.
H. P. Zhu, Z. Y. Zhou, R. Y. Yang, A. B. Yu, Chem. Eng. Sci. 62 (2007) 3378–3396.
H. P. Zhu, Z. Y. Zhou, R. Y. Yang, A. B. Yu, Chem. Eng. Sci. 63 (2008) 5728–5770.
H. Takahashi, N. Komatsu, ISIJ Int. 33 (1993) 655–663.
B. Wright, P. Zulli, Z. Y. Zhou, A. B. Yu, Powder Technol. 208 (2011) 86–97.
Z. Y. Zhou, H. P. Zhu, B. Wright, A. B. Yu, P. Zulli, Powder Technol. 208 (2011) 72–85.
M. Shimizu, Y. Kimura, M. Isobe, C. R. Che, S. Inaba, Tetsu-to-Hagane 73 (1987) 194–201.
S. Natsui, S. Ueda, H. Nogami, J. Kano, R. Inoue, T. Ariyama, Steel Res. Int. 82 (2011) 964–971.
W. G. Li, Baosteel Technology (2008) No. 6, 11–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Key Technology Research and Development Program during 12th Five-year Plan of China (2011BAE04B02); National Natural Science Foundation of China (51174053)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Zg., Zhou, H., Zhang, T. et al. DEM Simulation of Solid Flow Including Asymmetric Phenomena in COREX Shaft Furnace. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 22, 1098–1106 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(15)30118-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(15)30118-7