Abstract
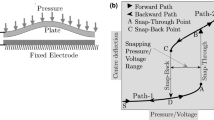
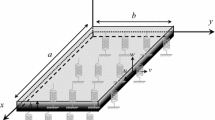
This article studies the stability of a functionally graded clamped-clamped microplate subjected to hydrostatic and electrostatic pressures. Equilibrium positions of the micro-plate are determined and shown in the state control space. To study the stability of the equilibrium positions, the motion trajectories are given for different initial conditions in the phase plane. Effects of the electrostatic and hydrostatic pressure changes on the deflection and stability of the micro-plate for some sample value of k are studied and values of the applied voltage and hydrostatic pressure leading system to unstable conditions by undergoing a saddle node and homoclinic bifurcations are determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koizumi, M., The concept of FGM. Ceramic Transactions, Functionally Gradient Materials, 1993, 34(1): 3–10.
Ferreira, A., Batra, R., Roque, C., Qian, C. and Martins, P., Static analysis of functionally graded plates using third order shear deformation theory and a meshless method. Composite Structures, 2005, 69: 449–457.
Bian, Z., Lim, C. and Chen, W., On functionally graded beams with integrated surface piezoelectric layers. Composite Structures, 2006, 72: 339–351.
Srinivas, S. and Rao, A., Bending vibration and buckling of simply supported thick orthotropic rectangular plates and laminates. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1970, 6: 1463–1481.
Zhang, D. and Zhou, Y., A theoretical analysis of FGM thin plates based on physical neutral surface. Computational Materials Science, 2008, 44: 716–720.
Vel, S. and Batra, R., Three-dimensional exact solution for the vibration of functionally graded rectangular plates. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2004, 272: 703–730.
Woo, J., Meguid, S. and Ong, L., Nonlinear free vibration behavior of functionally graded plates. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, 289: 595–611.
Vel, S. and Batra, R., Exact solution for thermoelastic deformations of functionally graded thick rectangular plates. AIAA Journal, 2002, 40: 1421–1433.
Vel, S. and Batra, R., Three-dimensional analysis of transient thermal stresses in functionally graded plates. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2003, 40: 7181–7196.
Kim, Y., Temperature dependent vibration analysis of functionally graded rectangular plates. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2005, 284: 531–549.
Rogers, T., Watson, P. and Spencer, A., Exact three-dimensional elasticity solutions for bending of moderately thick inhomogeneous and laminated strips under normal pressure. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1995, 32: 1659–1673.
Tarn, J. and Wang, Y., Asymptotic thermoelastic analysis of anisotropic inhomogeneous and laminated plates. Journal of Thermal Stresses, 1995, 18: 35–58.
Cheng, Z. and Batra, R., Three-dimensional thermoelastic deformations of a functionally graded elliptic plate. Composites Part B, 2000, 31: 97–106.
Reddy, J. and Cheng, Z., Three-dimensional solutions of smart functionally graded plates. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2001, 68: 234–241.
Wu, T., Shukla, K. and Huang, J.H., Post-buckling analysis of functionally graded rectangular plates. Composite Structures, 2007, 81: 1–10.
Ferreira, A., Batra, R., Roque, C., Qian, L. and Jorge, R., Natural frequencies of functionally graded plates by a meshless method. Composite Structures, 2006, 75: 593–600.
Batra, R. and Jin, J., Natural frequencies of a functionally graded anisotropic rectangular plate. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2005, 282: 509–516.
Yang, J., Liew, K. and Kitipornchai, S., Second-order statistics of the elastic buckling of functionally graded rectangular plates. Composites Science and Technology, 2005, 65: 1165–1175.
Abrate, S., Functionally graded plates behave like homogeneous plates. Composites Part B Engineering, 2008, 39: 151–158.
Matsunaga, H., Free vibration and stability of functionally graded plates according to a 2-D higher-order deformation theory. Composite Structures, 2008, 82: 499–512.
Qian, L., Batra, R. and Chen, L., Static and dynamic deformations of thick functionally graded elastic plate by using higher-order shear and normal deformable plate theory and meshless local Petrov-Galerkin method. Composites Part B Engineering, 2004, 35(6–8): 685–697.
Zhong, Z. and Yu, T., Vibration of a simply supported functionally graded piezoelectric rectangular plate. Smart Materials & Structures, 2006, 15: 1404–1412.
Roque, C., Ferreira, A. and Jorge, R., A radial basis function approach for the free vibration analysis of functionally graded plates using a refined theory. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2007, 300: 1048–1070.
Zhao, X., Lee, Y. and Liew, K., Free vibration analysis of functionally graded plates using the element-free kp-Ritz method. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2009, 319: 918–939.
Pradyumna, S. and Bandyopadhyay, J., Free vibration analysis of functionally graded curved panels using a higher-order finite element formulation. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 318: 176–192.
Chen, X. and Liew, K., Buckling of rectangular functionally graded material plates subjected to nonlinearly distributed in-plane edge loads. Smart Materials & Structures, 2004, 13: 1430–1437.
Batra, R. and Aimmanee, S., Vibrations of thick isotropic plates with higher order shear and normal deformable plate theories. Computers and Structures, 2005, 83: 934–955.
Woo, J. and Meguid, S., Nonlinear analysis of functionally graded plates and shallow shells. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2001, 38(42–43): 7409–7421.
Hao, Y., Chen, L., Zhang, W. and Lei, J., Nonlinear oscillations, bifurcations and chaos of functionally graded materials plate. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 312(4–5): 862–892.
Liew, K., Yang, J. and Kitipornchai, S., Postbuckling of Piezoelectric FGM plates subject to thermo-electromechanical loading. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2003, 40: 3869–3892. (doi:10.1016/S0020-7683(03)00096-9).
Shen, H., Post buckling of FGM plates with piezoelectric actuators under thermo-electro-mechanical loadings. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2005, 42: 6101–6121.
Zhang, Y., Ikehara, T., Lu, J., Kobayashi, T., Ichiki, M., Itoh, T., et al. Novel MEMS-based thermometer with low power consumption for health-monitoring network application. SPIE, 2008, 1: 6800.
Craciunescu, C. and Wuttig, M., New ferromagnetic and functionally grade shape memory alloys. Journal of Optoelectronics Advanced Materials, 2003, 5(1): 139–146.
Fu, Y., Du, H. and Zhang, S., Functionally graded TiN/TiNi shape memory alloy films. Journal of Materials Letters, 2003, 57(20): 2995–2999.
Fu, Y., Du, H., Huang, W., Zhang, S. and Hu, M., TiNi-based thin films in MEMS applications: a review. Sensors and Transducers Journal (A), 2004, 112(2–3): 395–408.
Witvrouw, A. and Mehta, A., The use of functionally graded poly-SiGe layers for MEMS applications. Journal of Functionally Graded Materials, 2005, (8): 492–493: 255–260.
Lee, Z., Ophus, C., Fischer, L., Nelson-Fitzpatrick, N., Westra, K., Evoy, S. et al., Metallic NEMS components fabricated from nano-composite Al-Mo films. Journal of Nanotechnology, 2006, 17(12): 3063–3070.
Rahaeifard, M., Kahrobaiyan, M. and Ahmadian, M., Sensitivity analysis of atomic force microscope cantilever made of functionally graded materials. In: DETC2009-86254, 3rd International Conference on Micro and Nano-Systems (MNS3) 2009, San Diego, CA, USA, 2009.
Mohammadi-Alasti, B., Rezazadeh, G, Borgheei, A., Minaei, S. and Habibifar, R., On the mechanical behavior of a functionally graded micro-beam subjected to a thermal moment and nonlinear electrostatic pressure. Composite Structures, 2011, 93: 1516–1525.
Zhou, M. et al., A novel capacitive pressure sensor based on sandwich structures. Journal of Micro Electro Mechanical System, 2005, 14:1272–1281.
Rajalingham, C. and Bhat, R., Influence of electric field on diaphragm stability and vibration in a condenser microphone. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1998, 211(5): 819–827.
Bay, J., Hansen, O. and Bouwstra, S., Micromachined double backplate differential capacitive microphone. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 1999, 9(1): 30–33.
Soleymani, P., Sadeghian, H., Tahmasebi, A. and Rezazadeh, G., Pull-in Instability Investigation of Circular Micro Pump Subjected to Nonlinear Electrostatic Force. Sensors & Transducers Journal, 2006, 69(7): 622–628.
Rezazadeh, G., Tayefe-Rezaei, S., Ghesmati, J. and Tahmasebi, A., Investigation of the pull-in phenomenon in drug delivery micropump using Galerkin method. Sensors and Transducers Journal, 2007, 78(4): 1098–107.
Zhang, Y. and Zhao, Y., Numerical and analytical study on the pull-in instability of microstructure under electrostatic loading. Journal of Sensors and Actuators (A) Physical, 2006, 127: 366–367.
Rezazadeh, G., Khatami, F. and Tahmasebi, A., Investigation of the torsion and bending effects on static stability of electrostatic torsional micromirrors. Microsystem Technologies, 2007, 13(7): 715–722.
Sazonova, V., A Tunable Carbon Nanotube Resonator. Ph.D. dissertation, university of Cornell, 2006.
Kao, P., Dai, C., Hsu, C. and Lee, C., Fabrication and characterization of a tunable in-plane resonator with low driving voltage. Sensors, 2009, 9: 2062–2075.
Dai, C. and Chen, Y., Modeling and manufacturing of micromechanical RF switch with inductors. Sensors, 2007, 7: 2660–2670.
Hasanyan, D., Batra, R. and Harutyunyan, S., Pull-in instabilities in functionally graded micro thermo electromechanical systems. Journal of Thermal Stresses, 2008, 31: 1006–1021.
Jia, X., Yang, J. and Kitipornchai, S., Characterization of FGM micro-switches under electrostatic and Casimir forces. Materials Science and Engineering, 2010, 10: 012178.
Talebian, S., Rezazadeh, G., Fathalilou, M. and Toosi, B., Effect of temperature on pull-in voltage and natural frequency of an electrostatically actuated microplate. Journal of Mechatronics, 2010, 20: 666–673.
Sadeghian, H., Rezazadeh, G. and Osterberg, P., Application of the generalized differential quadrature method to the study of pull-in phenomena of MEMS switches. IEEE/ASME Journal of Microelectromechanical System, 2007, 16(6): 1334–1340.
Rezazadeh, G., Tahmasebi, A. and Zubtsov, M., Application of piezoelectric layers in electrostatic MEM actuators: controlling of pull-in voltage. Microsystem Technologies, 2006, 12: 1163–1170.
Nabian, A., Rezazadeh, G., Haddad-derafshi, M. and Tahmasebi, A., Mechanical behavior of a circular micro plate subjected to uniform hydrostatic and non-uniform electrostatic pressure. Microsystem Technologies, 2008, 14: 235–240.
Nabian, A., Rezazadeh, G., Haddad-derafshi, M. and Tahmasebi, A., Investigation of pull-in phenomenon of rectangular micro-plate subjected to nonlinear electrostatic pressure. Sensors & Transducers Journal, 2006, 73(11): 810–818.
Azizi, S., Design of Micro Accelerometer to Use as Airbag Activator. MSc thesis, Mechanical Engineering Department, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran, 2008: 53–54.
Seydel, R., Practical Bifurcation and Stability Analysis, Third Edition. Springer, aDOI 10.1007/978-1-4419-1740-9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nabian, A., Rezazadeh, G., Almassi, M. et al. On the Stability of a Functionally Graded Rectangular Micro-Plate Subjected to Hydrostatic and Nonlinear Electrostatic Pressures. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 26, 205–220 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-9166(13)60020-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-9166(13)60020-8