Abstract
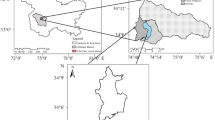
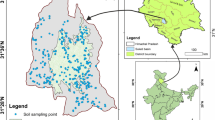
The research was carried out in Beni-Mousssa perimeter in the southern part of the Tadla plain, in Morocco. This study was performed using physicochemical analyses combined with statistical and geostatistical analysis to understand the spatial variability of soil quality in this agricultural area and to elaborate sustainable management of soil and environmental decision. The locations of sampling sites were defined by knowledge of the region’s farmers, on-site observations, and analyzed in the laboratory using the standard procedures for each soil property. A total of 67 soil samples were collected and analyzed in Geo-Resources and Environment Laboratories at the Faculty of Sciences and Techniques of Beni-Mellal, to identify physical and chemical soil properties especially pH, electrical conductivity (EC), organic carbon (OC), carbonate content (CaCO3), texture, exchangeable potassium (K), total phosphorus (P), total nitrogen (N), and cation exchange capacity (CEC). The soil presented an alkaline reaction. Other soil characteristics varied considerably in the overall study area. Pearson correlation among pH, soil OC, and CaCO3 were considered to be positive and significant (p < 0.05). Gaussian, exponential, spherical, and K-Bessel semivariogram models were selected, with weak to strong spatial dependency to be the better adjustment by using ordinary kriging techniques to estimate the spatial variability of soil characteristics. The obtained results revealed that the variation of soil characteristics in the study area depended on intrinsic and management soil factors. The detailed maps obtained in the framework of this type of study are very useful at international level in the selection of appropriate interventions, in particular with regard to the quantity of fertilizers, crop rotation, conservation and rehabilitation of deteriorated soils.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayoubi, S. H., Zamani, S. M., & Khormali, F. (2007). Spatial variability of some soil properties for site specific farming in northern Iran. Internat J Plant Prod. https://doi.org/10.22069/IJPP.2012.539.
Balmer, M. G. (1967). Principles of Statistics (2nd ed.). Edinburgh and London: Oliver and Boyd.
Barakat, A. (2020). Groundwater NO3 concentration and its potential health effects in Beni Moussa perimeter (Tadla plain concentration and its potential health effects in Beni Moussa perimeter (Tadla plain. Morocco): Geoenvironmental Disasters. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-020-00149-9.
Barakat, A., Ennaji, W., El Jazouli, A., Amediaz, R., & Touhami, F. (2017). A Multivariate analysis and GIS-based soil suitability diagnosis for sustainable intensive agriculture in Beni-Moussa irrigated subperimeter. Morocco: Modeling Earth Systems and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0272-5.
Barakat, A., Ennaji, W., Krimissa, S., & Bouzaid, M. (2019). Heavy metal contamination and ecological-health risk evaluation in peri-urban wastewater-irrigated soils of Beni-Mellal city (Morocco). International Journal of Environmental Health Research. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2019.1595540.
Behera, S. K., & Shukla, A. K. (2015). Spatial distribution of surface soil acidity, electrical conductivity, soil organic carbon content and exchangeable potassium, calcium and magnesium in some cropped acid soils of INDIA. Land Degradation and Development. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2306.
Behera, S. K., Singh, M. V., Singh, K. N., & Todwal, S. (2011). Distribution variability of total and extractable zinc in cultivated acid soils of India and their relationship with some selected soil properties. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.01.016.
Behera, S. K., Suresh, K., Rao, B. N., Mathur, R. K., Shukla, A. K., Manorama, K., et al. (2016). Spatial variability of some soil properties varies in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq) plantations of west coastal area of India. Solid Earth, 19, 10–24. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-7-979-2016.
Bhattacharyya, T., Pal, D. K., Mandal, C., Chandran, P., Ray, S. K., Sarkar, D., et al. (2013). Soils of India: historical perspective, classification and recent advances. Current Science, 104, 1308–1323.
Bouchaou, L., Michelot, J. L., Qurtobi, M., Zine, N., Gaye, C. B., Aggarwal, P. K., & Vengosh, A. (2009). Origin and residence time of groundwater in the Tadla basin (Morocco) using multiple isotopic and geochemical tools. Journal of Hydrology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.10.019.
Brevik, E. C., Calzolari, C., Miller, B. A., Pereira, P., Kabala, C., Baumgarten, A., & Jordán, A. (2016). Soil mapping, classification, and pedologic modeling: history and future directions. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.05.017.
Burgess, T. M., & Webster, R. (1980). Optimal interpolation and isarithmic mapping of soil properties: the variogram and punctual kriging. Journal of Soil Science. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1980.tb02100.x.
Cambardella, C. A., Moorman, T. B., Novak, J. M., Parkin, T. B., Karlen, D. L., Turco, R. F., & Konopka, A. E. (1994). Field scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800050033x.
Cemek, B., Gueler, M., Kilic, K., Demir, Y., & Arslan, H. (2007). Assessment of spatial variability in some soil properties as related to soil salinity and alkalinity in Bafra plain in northern Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9220-y.
Cerda, A., Morera, A. G., & Bodi, M. S. (2009). Soil and water losses from new citrus orchards growing on sloped soils in the western Mediterranean basin. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.1889.
Corwin, D. L., & Lesch, S. M. (2005). Apparent soil electrical conductivity measurements in agriculture. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2004.10.005.
Cressie, N. A. C. (1993). Statistics for spatial data (Revised). John Wiley: New York.
Dabin, B. (1970). Les facteurs chimiques de la fertilité des sols. Phosphore: Matière Organique.
De Lima, T. M., Weindorf, D. C., Curi, N., Guilherme, L. R., Lana, R. M., & Ribeiro, B. T. (2019). Elemental analysis of Cerrado agricultural soils via portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry: inferences for soil fertility assessment. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.06.045.
Deutsch, C. V., & Journel, A. G. (1998). GSLIB: geostatistical software library and user’s guide (1st ed.). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Doolittle, J. A., Sudduth, K. A., Kitchen, N. R., & Indorante, S. J. (1994). Estimating depth to claypans using electromagnetic induction methods. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 49, 572–575.
El Hamzaoui, E. H., El Baghdadi, M., Oumenskou, H., Aadraoui, M., & Hilali, A. (2020). Spatial repartition and contamination assessment of heavy metal in agricultural soils of Beni-Moussa. Tadla plain (Morocco): Modeling Earth Systems and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00756-3.
Ersahin, S. (2003). Comparing ordinary kriging and cokriging to estimate infiltration rate. Soil Science. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2003.184.
Foroughifar, A., Jafarzadeh, A., Torabi, H., Pakpour, A., & Miransari, M. (2013). Using geostatistics and geographic information system techniques to characterize spatial variability of soil properties, including micronutrients. Communcations in Soil Science and Plant Analysis. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2012.758279.
García-Orenes, F., Cerdà, A., Mataix-Solera, J., Guerrero, C., Bodí, M. B., Arcenegui, V., et al. (2009). Effects of agricultural management on surface soil properties and soil-water losses in eastern Spain. Soil and Tillage Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2009.06.002.
Goovaerts, P. (1997). Geostatistics for natural resources evaluation. New York: Oxford Univ Press.
Goovaerts, P. (1998). Geostatistical tools for characterizing the spatial variability of microbiological and physio-chemical soil properties. Biology and Fertility of Soils. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050439.
Goovaerts, P. (1999). Using elevation to aid the geostatistical mapping of rainfall erosivity. CATENA. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0341-8162(98)00116-7.
Hammond, C. (1992). Level I stability analysis (LISA) documentation for version 2.0. Newyork: US Department of Agriculture Forest Service, Intermountain Research Station.
Hamzeh, S., Naseri, A. A., AlaviPanah, S. K., Mojaradi, B., Bartholomeus, H. M., Clevers, J. G. P. W., & Behzad, M. (2013). Estimating salinity stress in sugarcane fields with space borne hyperspectral vegetation indices. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2012.07.002.
Hasany-Pak, A. A. (1998). Geostatistics. Tehran: Tehran University Press.
Heinze, S., & Raupp, J. (2010). Effects of fertilizer and spatial heterogeneity in soil pH on microbial biomass indices in a long-term field trial of organic agriculture. Plant and Soil. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0102-2.
Hilali, A., El Baghdadi, M., Barakat, A., & Ennaji, W. (2020). Contribution of GIS techniques and pollution indices in the assessment of metal pollution in agricultural soils irrigated with wastewater: case of the Day River. Beni Mellal (Morocco): Euro-Mediterranean Journal for Environmental Integration. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-020-00186-8.
Iqbal, J., Thomasson, J. A., Jenkins, J. N., Owens, P. R., & Whisler, F. D. (2005). Spatial variability analysis of soil physical properties of alluvial soils. Soil Science Society America Journal. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2004.0154.
Isaacks, E. H., & Srivastava, R. M. (1989). An introduction to applied geostatistics. New York: Oxford Univ Press.
Jenny, H. (1941). Factors of soil formation. New York: McGraw–Hill.
Johnson, C. K., Doran, J. W., Duke, H. R., Wienhold, B. J., Eskridge, K. M., & Shanahan, J. F. (2001). Field-scale electrical conductivity mapping for delineating soil condition. Soil Science Society of America Journal. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2001.1829.
Johnson, C. K., Eskridge, K. M., Wienhold, B. J., Doran, J. W., Peterson, G. A., & Buchleiter, G. W. (2003). Using electrical conductivity classification and within-field variability to design field-scale research. Agronomy Journal. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2003.6020.
Jung, W. K., Kitchen, N. R., Sudduth, K. A., Kremer, R. J., & Motavalli, P. P. (2005). Relationship of apparent soil electrical conductivity to claypan soil properties. Soil Science Society of America Journal. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2004.0202.
Lopez-Granados, F., Jurado-Exposito, M., Atenciano, S., Garcia-Ferrer, A., De la Orden, M. S., & Garcia-Torres, L. (2020). Spatial variability of agricultural soil parameters in southern Spain. Plant and Soil. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021568415380.
Mehrjardi, M. Z., Mehrjardi, R. T., & Akbarzadeh, A. (2010). Evaluation of geostatistical techniques for mapping spatial distribution of soil PH, salinity and plant cover affected by environmental factors in Southern Iran. Notulae Scientia Biologicae, 10, 10.
Mueller, T. G., Hartsock, N. J., Stombaugh, T. S., Shearer, S. A., Cornelius, P. L., & Barnhise, R. I. (2003). Soil electrical conductivity map variability in limestone soil overlain by loess. Agronomy Journal. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2003.4960.
Mukherjee, A., Zimmerman, A. R., Hamdan, R., & Cooper, W. T. (2014). Physicochemical changes in pyrogenic organic matter (biochar) after 15 months of field aging. Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-5-693-2014.
Novara, A., Rühl, J., La Mantia, T., Gristina, L., La Bella, S., & Tuttolomondo, T. (2015). Litter contribution to soil organic carbon in the processes of agriculture abandon. Solid Earth, 6(2), 425–432.
Ochoa-Cueva, P., Fries, A., Montesinos, P., Rodríguez-Díaz, J. A., & Boll, J. (2015). Spatial estimation of soil erosion risk by land-cover change in the Andes of southern Ecuador. Land Degradation and Development. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2219.
Oliver, M. A., & Webster, R. (2014). A tutorial guide to geostatistics: computing and modelling variograms and kriging. CATENA. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.09.006.
Ore, G., & Bruins, H. J. (2012). Design features of ancient agriculture terrace walls in the Negev Desert: human-made geodiversity. Land Degradation and Development. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2152.
Oumenskou, H., El Baghdadi, M., Barakat, A., Aquit, M., Ennaji, W., Karroum, L. A., & Aadraoui, M. (2018). Multivariate statistical analysis for spatial evaluation of physicochemical properties of agricultural soils from Beni-Amir irrigated perimeter. Tadla plain, Morocco: Geology Ecology and Landscapes. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2018.1504272.
Özgöz, E. (2009). Long term conventional tillage effect on spatial variability of some soil physical properties. Journal of Sustainable Agriculture. https://doi.org/10.1080/10440040802395056.
Pal, D. K., Wani, S. P., Sahrawat, K. L., & Srivastava, P. (2014). Red ferruginous soils of tropical Indian environments: a review of the pedogenic processes and its implications for edaphology. CATENA. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.05.023.
Pang, S., Li, T. X., Zhang, X. F., Wang, Y. D., & Yu, H. Y. (2011). Spatial variability of cropland lead and its influencing factors: a case study in Shuangliu county. Sichuan province, China: Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.01.002.
Pereira, P., Cerdà, A., Úbeda, X., Mataix-Solera, J., Martin, D., Jordán, A., & Burguet, M. (2013). Spatial models for monitoring the spatio-temporal evolution of ashes after fire – a case study of a burnt grassland in Lithuania. Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-4-153-2013.
Pereira, P., Cerdà, A., Úbeda, X., Mataix-Solera, J., Arcenegui, V., & Zavala, L. M. (2015). Modelling the impacts of wildfire on ash thickness in a short-term period. Land Degradation and Development. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2195.
Pohlmann, H. (1993). Geostatistical modelling of environmental data. CATENA, 20, 191–198.
Rhoades, J. D. (1982). Cation exchange capacity. In A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, & D. R. Keeney (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis. WI: American Society of Agronomy Madison.
Rhoades, J.D., Corwin, D. L., & Lesch, S.M. (1999). Geospatial measurements of soil electrical conductivity to assess soil salinity and diffuse salt loading from irrigation. Assessment of non-point source pollution in the vadose zone. American Geophysical Union. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Dennis_Corwin/publication/274063528_Geospatial_Measurements_of_Soil_Electrical_Conductivity_to_Determine_Soil_Salinity_and_Diffuse_Salt_Loading_from_Irrigation/links/5514988e0cf2eda0df3380cf.pdf. (Accessed 09 September 2020).
Saito, H., McKenna, A., Zimmerman, D. A., & Coburn, T. C. (2005). Geostatistical interpolation of object counts collected from multiple strip transects: ordinary kriging versus finite domain kriging. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-004-0207-3.
Saldana, A., Stein, A., & Zinck, J. A. (1998). Spatial variability of soil properties at different scales within three terraces of the Henare River (Spain). CATENA. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0341-8162(98)00090-3.
Samper-Calvete, F. J., & Carrera-Ramírez, J. (1996). Geostadística aplicaciones a la hidrología subterránea centro internacional de métodos numéricos en ingeniería (p. 484). España: Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya.
Saxton, K. E., & Rawls, W. J. (2006). Soil water characteristic estimates by texture and organic matter for hydrologic solutions. Soil Science Society of America Journal. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2005.0117.
Schimel, D., Melillo, J., Tian, H., McGuire, D., Kicklighter, D., Kittel, T., et al. (2000). Contribution of increasing CO2 and climate to carbon storage by ecosystems in the United States. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5460.2004.
Shapiro, S. S., & Wilk, M. B. (1965). An analysis of variance test for normality. Biometrika. https://doi.org/10.2307/2333709.
Shi, W., Liu, J., Du, Z., Song, Y., Chen, C., & Yue, T. (2009). Surface modelling of soil pH. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.01.020.
Six, J., Conant, R. T., Paul, E. A., & Paustian, K. (2002). Stabilization mechanism of soil organic matter: implications for C-saturation of soils. Plant and Soil. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016125726789.
Sokoti, S., Mahdian, M., Mahmoodi, S., & Ghahramani, A. (2006). Comparing the applicability of some geostatistics methods to predict soil salinity, a case study of Urmia plain. Pajuhesh and Sazandegi, 74, 90–98.
Stanchi, S., Falsone, G., & Bonifacio, E. (2015). Soil aggregation, erodibility, and erosion rates in mountain soils (NW Alps, Italy). Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-6-403-2015.
Subbiah, B. V., & Asija, G. L. (1956). A rapid procedure for the determination of the available nitrogen in the soil. Current Science, 25, 259–260.
Sudduth, K. A., Kitchen, N. R., Bollero, G. A., Bullock, D. G., & Wiebold, W. J. (2003). Comparison of electromagnetic induction and direct sensing of soil electrical conductivity. Agronomy Journal. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2003.4720.
Tesfahunegn, G. B., Tamene, L., & Vlek Paul, L. G. (2011). Catchment-scale spatial variability of soil properties and implications on site-specific soil management in northern Ethiopia. Soil and Tillage Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2011.09.005.
Thapa, G. B., & Yila, O. M. (2012). Farmers’ land management practices and status of agricultural land in the Jos Plateau. Nigeria: Land Degradation and Development. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.1079.
Tian, K., Huang, B., Xing, Z., & Hu, W. (2017). Geochemical baseline establishment and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in greenhouse soils from Dongtai, China. Ecological Indicators. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.08.037.
Tripathi, R., Nayak, A. K., Shahid, M., Raja, R., Panda, B. B., Mohanty, S., et al. (2015). Characterizing spatial variability of soil properties in salt affected coastal India using geostatistics and kriging. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2003-4.
Utset, A., Lopez, T., & Diaz, M. (2000). A comparison of soil maps, kriging and a combined method for spatially prediction bulk density and field capacity of Ferralsols in the Havana-Matanaz Plain. Geoderma, 96, 199–213.
Wakene, N. (2001). Assessment of important physio-chemical properties of dystric udalf (dystric Nitosols) under different management system in Bako area Western Ethiopia. School of Graduate Studies: Alemaya University, Ethiopia.
Walkley, A., & Black, I. A. (1934). An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 34, 29–38.
Wang, Z. M., Song, K. S., Zhang, B., Liu, D. W., Li, X. Y., Ren, C. Y., et al. (2009). Spatial variability and affecting factors of soil nutrients in croplands of Northeast China: a case study in Dehui county. Plant Soil and Environment, 55, 110–120.
Wang, C., Li, W., Yang, Z., Chen, Y., Shao, W., & Ji, J. (2015). An invisible soil acidification: critical role of soil carbonate and its impact on heavy metal bioavailability. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12735.
Wang, B., Wang, Y., & Wang, L. (2016). The effects of erosional topography on soil properties in a Pinus massoniana forest in southern China. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation. https://doi.org/10.2489/jswc.72.1.36.
Webster, R., & Oliver, M. A. (1990). Statistical methods in soil and land resource survey. London: Oxford University Press (OUP).
Zar, J. H. (1974). Circular distributions. Biostatistical Analysis, 22, 310–325.
Zhang, H., Zhuang, S., Qian, H., Wang, F., & Ji, H. (2015). Spatial variability of the topsoil organic carbon in the Moso bamboo forests of southern China in association with soil properties. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119175.
Zolekar, R. B., & Bhagat, V. S. (2015). Multi-criteria land suitability analysis for agriculture in hilly zone: remote sensing and GIS approach. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 9, 180–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2015.09.01.
Funding
The authors declare that they have no funding sources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by M. V. Alves Martins
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Hamzaoui, E., El Baghdadi, M. Characterizing spatial variability of some soil properties in Beni-Moussa irrigated perimeter from Tadla plain (Morocco) using geostatistics and kriging techniques. J. Sediment. Environ. 6, 381–394 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-021-00050-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-021-00050-x