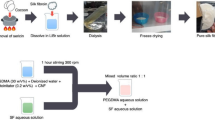
Abstract
Gelatin (G) is a commonly used natural biomaterial owing to its good biocompatibility and easy availability. However, using pure gelatin as a bioink can barely achieve an ideal shape fidelity in 3D printing. In this study, Antheraea pernyi silk fibroin nanofibers (ASFNFs) with arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) peptide and partial natural silk structure are extracted and combined with pure gelatin bioink to simultaneously improve the shape fidelity and cytocompatibility of corresponding 3D printed scaffold. Results show that the optimum printing temperature is 30 °C for these bioinks. The printed filaments using 16G/4ASFNFs bioink (16wt% gelatin and 4wt% ASFNFs) demonstrate better morphology and larger pore size than those printed by pure gelatin bioink (20G, 20wt% gelatin), thus successfully improve the shape fidelity and porosity of the 3D printed scaffold. The 16G/4ASFNFs scaffold also demonstrate higher swelling ratio and faster degradation rate than the pure gelatin scaffold. Moreover, the cell viability and proliferation ability of Schwann cells cultured on the 16G/4ASFNFs scaffold are significantly superior than those cultured on the pure 20G scaffold. The ASFNFs enhanced 16G/4ASFNFs scaffold reported here are expected to be a candidate with excellent potential for biomedical applications.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Labowska MB, Cierluk K, Jankowska AM, Kulbacka J, Detyna J, Michalak I. A review on the adaption of alginate-gelatin hydrogels for 3D cultures and bioprinting. Materials 2021;14:858.
der Elst Lv, de Lima CF, Gokce Kurtoglu M, Koraganji VN, Zheng M, Gumennik A. 3D printing in fiber-device technology. Adv Fiber Mater 2021;3:59–75.
Chawla S, Midha S, Sharma A, Ghosh S. Silk-based bioinks for 3D bioprinting. Adv Healthcare Mater 2018;7:1701204.
Suzuki S, Shadforth AMA, McLenachan S, Zhang D, Chen SC, Walshe J, Lidgerwood GE, Pebay A, Chirila TV, Chen FK, Harkin DG. Optimization of silk fibroin membranes for retinal implantation. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 2019;105:110131.
Liang XY, Chen GD, Lin ST, Zhang JJ, Wang L, Zhang P, Wang ZY, Wang ZB, Lan Y, Ge Q, Liu J. Anisotropically fatigue-resistant hydrogels. Adv Mater 2021;33:2102011.
Jing LZ, Fan SN, Yao X, Zhang YP. Effects of compound stimulation of fluid shear stress plus ultrasound on stem cell proliferation and osteogenesis. Regener Biomater 2021;8:rbab066.
Hang YC, Zhang YP, Jin Y, Shao HL, Hu XC. Preparation of regenerated silk fibroin/silk sericin fibers by coaxial electrospinning. Int J Biol Macromol 2012;51:980–6.
Dong YP, Zheng YQ, Zhang KY, Yao YM, Wang LH, Li XR, Yu JY, Ding B. Electrospun nanofibrous materials for wound healing. Adv Fiber Mater 2020;2:212–27.
Zhao JW, Cui WG. Functional electrospun fibers for local therapy of cancer. Adv Fiber Mater 2020;2:229–45.
Li Y, Shen Q, Shen J, Ding XB, Liu T, He JH, Zhu CY, Zhao D, Zhu JD. Multifunctional fibroblasts enhanced via thermal and freeze-drying post-treatments of aligned electrospun nanofiber membranes. Adv Fiber Mater 2021;3:26–37.
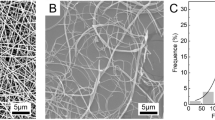
Zou SZ, Wang XR, Fan SN, Yao X, Zhang YP, Shao HL. Electrospun regenerated Antheraea pernyi silk fibroin scaffolds with improved pore size, mechanical properties and cytocompatibility using mesh collectors. J Mater Chem B 2021;9:5514–27.
Yang XP, Li LF, Yang DZ, Nie J, Ma GP. Electrospun core–shell fibrous 2D scaffold with biocompatible poly(glycerol sebacate) and poly-l-lactic acid for wound healing. Adv Fiber Mater 2020;2:105–17.
Eryildiz M, Altan M. Fabrication of polylactic acid/halloysite nanotube scaffolds by foam injection molding for tissue engineering. Polym Compos 2020;41:757–67.
Bhusari SA, Sharma V, Bose S, Basu B. HDPE/UHMWPE hybrid nanocomposites with surface functionalized graphene oxide towards improved strength and cytocompatibility. J R Soc Interface 2019;16:20180273.
McKenna E, Klein TJ, Doran MR, Futrega K. Integration of an ultra-strong poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) knitted mesh into a thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) PLGA porous structure to yield a thin biphasic scaffold suitable for dermal tissue engineering. Biofabrication 2020;12:015015.
Shi QW, Sun JQ, Hou CY, Li YG, Zhang QH, Wang HZ. Advanced functional fiber and smart textile. Adv Fiber Mater 2019;1:3–31.
Rosales-Ibanez R, Cubo-Mateo N, Rodriguez-Navarrete A, Gonzalez-Gonzalez AM, Villamar-Duque TE, Flores-Sanchez LO, Rodriguez-Lorenzo LM. Assessment of a PCL-3D printing-dental pulp stem cells triplet for bone engineering: an in vitro study. Polymers 2021;13:1154.
Meng YQ, Cao JL, Chen Y, Yu YR, Ye L. 3D printing of a poly(vinyl alcohol)-based nano-composite hydrogel as an artificial cartilage replacement and the improvement mechanism of printing accuracy. J Mater Chem B 2020;8:677–90.
Falcone G, Saviano M, Aquino RP, Gaudio PD, Russo P. Coaxial semi-solid extrusion and ionotropic alginate gelation: a successful duo for personalized floating formulations via 3D printing. Carbohydr Polym 2021;260:117791.
Zhang J, Allardyce BJ, Rajkhowa R, Zhao Y, Dilley RJ, Redmond SL, Wang X, Liu X. 3D printing of silk particle-reinforced chitosan hydrogel structures and their properties. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2018;4:3036–46.
Li QT, Xu S, Feng Q, Dai QY, Yao LT, Zhang YC, Gao HC, Dong H, Chen DF, Cao XD. 3D printed silk-gelatin hydrogel scaffold with different porous structure and cell seeding strategy for cartilage regeneration. Bioact Mater 2021;6:3396–410.
Helgeland E, Rashad A, Campodoni E, Goksoyr O, Pedersen TO, Sandri M, Rosen A, Mustafa K. Dual-crosslinked 3D printed gelatin scaffolds with potential for temporomandibular joint cartilage regeneration. Biomed Mater 2021;16:035026.
Etxabide A, Mate JI, Kilmartin PA. Effect of curcumin, betanin and anthocyanin containing colourants addition on gelatin films properties for intelligent films development. Food Hydrocolloid 2021;115:106593.
Osi AR, Zhang H, Chen J, Zhou Y, Wang R, Fu J, Muller-Buschbaum P, Zhong Q. Three-dimensional-printable thermo/photo-cross-linked methacrylated chitosan-gelatin hydrogel composites for tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Inter 2021;13:22902–13.
Curti F, Dragusin DM, Serafim A, Iovu H, Stancu IC. Development of thick paste-like inks based on superconcentrated gelatin/alginate for 3D printing of scaffolds with shape fidelity and stability. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 2021;122:111866.
Di Giuseppe M, Law N, Webb B, Macrae RA, Liew LJ, Sercombe TB, Dilley RJ, Doyle BJ. Mechanical behaviour of alginate-gelatin hydrogels for 3D bioprinting. J Mech Behav Biomed 2018;79:150–7.
Huang L, Du XY, Fan SN, Yang GS, Shao HL, Li DJ, Cao CB, Zhu YF, Zhu MF, Zhang YP. Bacterial cellulose nanofibers promote stress and fidelity of 3D-printed silk based hydrogel scaffold with hierarchical pores. Carbohydr Polym 2019;221:146–56.
Shin S, Park S, Park M, Jeong E, Na K, Youn HJ, Hyun J. Cellulose nanofibers for the enhancement of printability of low viscosity gelatin derivatives. BioResources 2017;12:2941–54.
Han CY, Wang XY, Ni ZJ, Ni YH, Huan WW, Lv Y, Bai SY. Effects of nanocellulose on alginate/gelatin bio-inks for extrusion-based 3D printing. BioResources 2020;15:7357–73.
Luo WB, Song ZY, Wang ZH, Wang ZG, Li ZH, Wang CY, Liu H, Liu QP, Wang JC. Printability optimization of gelatin-alginate bioinks by cellulose nanofiber modification for potential meniscus bioprinting. J Nanomater 2020;2020:3863428.
Silva SS, Kundu B, Lu S, Reis RL, Kundu SC. Chinese oak tasar silkworm Antheraea pernyi silk proteins: current strategies and future perspectives for biomedical applications. Macromol Biosci 2019;19:1800252.
Yao X, Ding JD. Effects of microstripe geometry on guided cell migration. ACS Appl Mater Inter 2020;12:27971–83.
Yao X, Wang XL, Ding JD. Exploration of possible cell chirality using material techniques of surface patterning. Acta Biomater 2021;126:92–108.
Yao X, Liu RL, Liang XY, Ding JD. Critical areas of proliferation of single cells on micropatterned surfaces and corresponding cell type dependence. ACS Appl Mater Inter 2019;11:15366–80.
Yao X, Peng R, Ding J. Effects of aspect ratios of stem cells on lineage commitments with and without induction media. Biomaterials 2013;34:930–9.
Zou SZ, Wang XR, Fan SN, Zhang JM, Shao HL, Zhang YP. Fabrication and characterization of regenerated Antheraea pernyi silk fibroin scaffolds for Schwann cell culturing. Eur Polym J 2019;117:123–33.
Zheng K, Hu YL, Zhang WW, Yu J, Ling SJ, Fan YM. Oxidizing and nano-dispersing the natural silk fibers. Nanoscale Res Lett 2019;14:250.
Zhang WW, Ye C, Zheng K, Zhong JJ, Tang YZ, Fan YM, Buehler MJ, Ling SJ, Kaplan DL. Tensan silk-inspired hierarchical fibers for smart textile applications. ACS Nano 2018;12:6968–77.
Das S, Pati F, Chameettachal S, Pahwa S, Ray AR, Dhara S, Ghosh S. Enhanced redifferentiation of chondrocytes on microperiodic silk/gelatin scaffolds: toward tailor-made tissue engineering. Biomacromol 2013;14:311–21.
Ou Yang LL, Yao R, Zhao Y, Sun W. Effect of bioink properties on printability and cell viability for 3D bioplotting of embryonic stem cells. Biofabrication 2016;8:035020.
Shao HP, He JZ, Lin T, Zhang ZN, Zhang YM, Liu SW. 3D gel-printing of hydroxyapatite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Ceram Int 2019;45:1163–70.
El Fawal GF, Abu-Serie MM, Hassan MA, Elnouby MS. Hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel for wound dressing: fabrication, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Int J Biol Macromol 2018;111:649–59.
Baniasadi H, Ramazani ASA, Mashayekhan S. Fabrication and characterization of conductive chitosan/gelatin-based scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol 2015;74:360–6.
Liu QQ, Huang JW, Shao HL, Song LJ, Zhang YP. Dual-factor loaded functional silk fibroin scaffolds for peripheral nerve regeneration with the aid of neovascularization. RSC Adv 2016;6:7683–91.
Leu Alexa R, Iovu H, Ghitman J, Serafim A, Stavarache C, Marin M-M, Ianchis R. 3D-printed gelatin methacryloyl-based scaffolds with potential application in tissue engineering. Polymers 2021;13:727.
Ruiz-Cantu L, Gleadall A, Faris C, Segal J, Shakesheff K, Yang J. Multi-material 3D bioprinting of porous constructs for cartilage regeneration. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 2020;109:110578.
Tisserand C, Fleury M, Brunel L, Bru P, Meunier G. Passive microrheology for measurement of the concentrated dispersions stability. Prog Coll Pol Sci S 2012;139:101–5.
Lopez Hernandez H, Souza JW, Appel EA. A quantitative description for designing the extrudability of shear-thinning physical hydrogels. Macromol Biosci 2021;21:2000295.
Rahimnejad M, Labonte-Dupuis T, Demarquette NR, Lerouge S. A rheological approach to assess the printability of thermosensitive chitosan-based biomaterial inks. Biomed Mater 2021;16:015003.
Khan H, Shukla RN, Bajpai AK. Genipin-modified gelatin nanocarriers as swelling controlled drug delivery system for in vitro release of cytarabine. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 2016;61:457–65.
Huang L, Yuan W, Hong Y, Fan SN, Yao X, Ren T, Song LJ, Yang GS, Zhang YP. 3D printed hydrogels with oxidized cellulose nanofibers and silk fibroin for the proliferation of lung epithelial stem cells. Cellulose 2021;28:241–57.
Lu L, Fan SN, Geng LH, Lin JY, Yao X, Zhang YP. Flow analysis of regenerated silk fibroin/cellulose nanofiber suspensions via a bioinspired microfluidic chip. Adv Mater Technol 2021;6:2100124.
Trang HMN, Abueva C, Van Hai H, Lee SY, Lee BT. In vitro and in vivo acute response towards injectable thermosensitive chitosan/TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofiber hydrogel. Carbohydr Polym 2018;180:246–55.
Salehi M, Bagher Z, Kamrava SK, Ehterami A, Alizadeh R, Farhadi M, Falah M, Komeili A. Alginate/chitosan hydrogel containing olfactory ectomesenchymal stem cells for sciatic nerve tissue engineering. J Cell Physiol 2019;234:15357–68.
Xu HX, Zhang LX, Bao Y, Yan XM, Yin YX, Li YP, Wang XY, Huang ZJ, Xu PH. Preparation and characterization of injectable chitosan-hyaluronic acid hydrogels for nerve growth factor sustained release. J Bioact Compat Pol 2017;32:146–62.
Huang Y, Li X, Lu Z, Zhang H, Huang J, Yan K, Wang D. Nanofiber-reinforced bulk hydrogel: preparation and structural, mechanical, and biological properties. J Mater Chem B 2020;8:9794–803.
Jiao Y, Lu KY, Lu Y, Yue YY, Xu XW, Xiao HN, Li J, Han JQ. Highly viscoelastic, stretchable, conductive, and self-healing strain sensors based on cellulose nanofiber-reinforced polyacrylic acid hydrogel. Cellulose 2021;28:4295–311.
Gao F, Xu ZY, Liang QF, Li HF, Peng LQ, Wu MM, Zhao XL, Cui X, Ruan CS, Liu WG. Osteochondral regeneration with 3D-printed biodegradable high-strength supramolecular polymer reinforced-gelatin hydrogel scaffolds. Adv Sci 2019;6:1900867.
Kim SM, Jeong DH, Lee HJ, Kim DJ, Jung SH. Succinoglycan dialdehyde-reinforced gelatin hydrogels with toughness and thermal stability. Int J Biol Macromol 2020;149:281–9.
Oustadi F, Imani R, Nazarpak MH, Sharifi AM. Genipin-crosslinked gelatin hydrogel incorporated with PLLA-nanocylinders as a bone scaffold: synthesis, characterization, and mechanical properties evaluation. Polym Adv Technol 2020;31:1783–92.
Zhang LL, Zheng TT, Wu LL, Han Q, Chen SY, Kong Y, Li GC, Ma L, Wu H, Zhao YH, Yu Y, Yang YM. Fabrication and characterization of 3D-printed gellan gum/starch composite scaffold for Schwann cells growth. Nonotechnol Rev 2021;10:50–61.
Yao X, Peng R, Ding JD. Cell-material interactions revealed via material techniques of surface patterning. Adv Mater 2013;25:5257–86.
Mi HY, Salick MR, Jing X, Crone WC, Peng XF, Turng LS. Electrospinning of unidirectionally and orthogonally aligned thermoplastic polyurethane nanofibers: fiber orientation and cell migration. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 2015;103:593–603.
Zhou W, Zhong X, Wu X, Yuan L, Zhao Z, Wang H, Xia Y, Feng Y, He J, Chen W. The effect of surface roughness and wettability of TiO2 film on TCA-8113 epithelial-like nanostructured cells. Surf Coat Technol 2006;200:6155–60.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (20ZR1402400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52173031, 51903045, 51703033), the Program of Shanghai Academic/Technology Research Leader (20XD1400100), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFC1910303, 2018YFC1105800), the Basic Research Project of the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (21JC1400100), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2232020D-04, 2232019A3-06, 2232019D3-02), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (20DZ2254900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: XY and HS; methodology: SZ, XY, and HS; experiment: SZ and XY; analysis of results: SZ, SF, ALO, XY, YZ, and HS; writing and revision: SZ, SF, ALO, XY, YZ, and HS; funding and resources: SF, XY, and YZ; supervision: XY, YZ, and HS.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, S., Fan, S., Oliveira, A.L. et al. 3D Printed Gelatin Scaffold with Improved Shape Fidelity and Cytocompatibility by Using Antheraea pernyi Silk Fibroin Nanofibers. Adv. Fiber Mater. 4, 758–773 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00135-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00135-w