Abstract
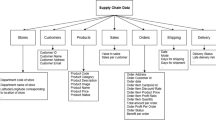
This article applies the improved stochastic forest algorithm to online supply chain financial risk assessment and establishes the index system and corresponding model of the online supply chain financial risk assessment based on improved random forest. Data analysis proves the feasibility and accuracy of improved random forest applied to an online financial risk assessment of a supply chain, which provides a new risk assessment method.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu P, Nair SK (2012) Supply chain finance enabled early pay: unlocking trapped value in B2B logistics. Int J Logis Syst Manag 12(3):334–353
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32
Gornall W, Strebulaev IA (2018) Financing as a supply chain: the capital structure of banks and borrowers. J Financ Econ 129:510–530
Guo J, Shi J, Wang Z (2014) Research on the mode evolution and risk management of the online supply chain finance based on the third-party B2B E-commerce platform. J Bus Econ 267(1):13–22
Heng M (2001) Implications of e-commerce for banking and finance. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology 74(6):317–327
Kaplan S, Sawhney M (2000) E-hubs: the new B2B (business-to-business) marketplaces. Harv Bus Rev 78(3):97–103
Kouvelis P, Zhao W (2012) Financing the newsvendor: supplier vs. Bank, and the structure of optimal trade credit contracts. Oper Res 60(3):566–580
Nejad MG (2016) Challenges and opportunities for innovation in financial services. Int J Bank Mark 34(1):2–8
Shimizu T, Park Y, Hong P (2013) Supply chain risk management and organisational decision making: a case study of a major Japanese automotive firm. Int J Serv Oper Manag 15(3):293–312
Sun WB, Jiang Y, He WZ (2012) Core competitiveness cultivation in small-medium construction enterprises. Appl Mech Mater 174-177:3309–3312
Wu, Y., Li, Y., and Li, P. SMEs' financing decision: Based on the supply chain finance. ICSSSM12. IEEE, 2012
Zhang G, Zhang QJ (2019) Multiportfolio optimization with CVaR risk measure. Journal of Data, Information and Management, pp 1–16
Zhao L, Huo B, Sun L, Zhao X (2013) The impact of supply chain risk on supply chain integration and company performance: a global investigation. Supply Chain Manag 18(2):115–131
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by 2018 Beijing Talents foundation of organization department of Beijing Municipal Committee of the CPC (No.2018000026833ZS09), Science and technology innovation service capacity provincial-ministerial scientific research platform construction social science provincial-ministerial scientific research platform construction project (No.19008020111, No.19002020217).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Shi, Y. & Tong, J. Online supply chain financial risk assessment based on improved random forest. J. of Data, Inf. and Manag. 3, 41–48 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42488-021-00042-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42488-021-00042-6