Abstract
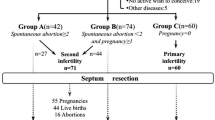
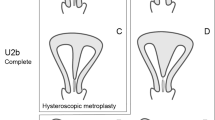
The purpose of study is to assess reproductive outcome in patients with septate uterus who have undergone hysteroscopic metroplasty by monopolar resectoscope. Nine hundred forty-eight women with septate uterus who were evaluated for infertility were included in this cohort study. All of them had hysteroscopic septum resection by monopolar resectoscope. They used hormone for 2 months after procedure, and hysterosalpingography was done for evaluating uterine cavity after surgery. The age, cause of infertility, pregnancy rate per cycle, and reproductive performance after surgery were evaluated in intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), frozen embryo transfer (FET), and intrauterine insemination (IUI) cycles. The mean age of patients in ICSI, FET, and IUI group was 34.78±2.25, 34.25±2.37, and 31.03±1.52, respectively. One hundred forty (23.9%) women in ICSI group and 60 (36.8%) women in frozen embryo transfer group and 42 (20.8%) patients in IUI group got pregnant after procedure. The main factor of infertility in ICSI and FET group was male factor 46.2% and 52%, respectively, while in IUI group, ovulatory factor was 39.9%. There was no uterine perforation in patients. Hysteroscopic metroplasty is a safe, simple, and effective procedure that improve reproductive outcome in infertility patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nouri K, Ott J, Huber JC, Fischer E-M, Stogbauer L, Tempfer CH. Reproductive outcome after hysteroscopic septoplasty in patients with septate uterus- a retrospective cohort study and systematic review of the literature. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2010;8:52.
Grimbizis GF, Camus M, Tarlatzis BC, Bontis JN, Devroey P. Clinical implications of uterine malformations and hysteroscopic treatment result. Hum Reprod Update. 2001;7:161–74.
Brau P, Grau FV, Pons RM. Is hysterosalpangography able to diagnose all uterine malformations correctly? Eur J Radiol. 2005;53:274–9.
Pabuccu R, Gomel V. Reproductive outcome after hysteroscopic metroplasty in women with septate uterus and otherwise unexplained infertility. Fertil Steril. 2004;81:1675–8.
Sanders B. Uterine factors and infertility. J Reprod Med. 2006;51:169–76.
-Sparac V, Kupesic S, Ilijas M, Zodan T, Kurjak A, Histologic architecture and vascularization of hysteroscopically excised intrauterine septa.
Mollo A, De Franciscis P, Colacurci N, Cobellis L, Perino A, Venezia R, Hysteroscopic resection of the septum improves the pregnancy rate of women with unexplained infertility: a prospective controlled trial.
Fedele L, Arcaini L, Parazzini F, Vercellini P, di Nola G. Reproductive prognosis after hysteroscopic metroplasty in 102 women: life table analysis. Fertil Steril. 1993;59:768–72.
Wang JH, Xu KH, Lin J, Chen XZ. Hysteroscopic septum resection of complete septate uterus with cervical duplication, sparing the double cervix in patients with recurrent spontaneous abortions or infertility. Fertil Steril. 2009;91(6):2643–9.
Jakiel G, Robak-Chołubek D, Przytuła-Piłat M. Two-year study of women with fertility problems following uterine septum hysteroscopic treatment. Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska. 2004;59(2):65–9.
Saygili-Yilmaz ES, Erman-Akar M, Yilmaz Z. A retrospective study on the reproductive outcome of the septate uterus corrected by hysteroscopic metroplasty. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2002;78:59–60.
Kormanyos Z, Molnar BG, Pal A. Removal of a residual portion of a uterine septum in women of advanced reproductive age: obstetric outcome. Hum Reprod. 2006;21:1047–51.
Taylor E, Gomel V. The uterus and fertility. Fertil Steril. 2008;89:1–16.
Bradley LD. Complications in hysteroscopy: prevention, treatment and legal risk. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2002;14:409–15.
Grynberg M, Gervaise A, Faivre E, Deffieux X, Frydman R, Fernandez H. Treatment of twenty-two patients with complete uterine and vaginal septum. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19(1):34–9.
Tehrani Nejad ES, Naderi T, Irani S, Azimi NE. Frequency distribution of pregnancy occurrence in infertile women after diagnostic-surgical hysteroscopy. Iranian J Reprod Med. 2007;5:99–102.
Raga F, Bauset C, Remohi J, Bonilla-Musoles F, Simon C, Pellicer A. Reproductive impact of congenital uterine anomalies. Hum Reprod. 1997;12:2277–81.
Sentilhes L, Sergent F, Roman H, Verspyck E, Marpeau L. Late complications of operative hysteroscopy: predicting patients at risk of uterine rupture during subsequent pregnancy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2005;120(2):134–8.
Cararach M, Penella J, Ubeda A, Labatisda R. Hysteroscopic incision of septate uterus: scissors versus resectoscope. Hum Reprod. 1994;9:87–9.
Guarino S, Incandela S, Maneschi S. Hysteroscopic treatment of uterine septum. Acta Eur Fertil. 1989;20(5):321–5.
Mulayim B, Celik NY, Onalan G, Bagis T, Zeyneloglu HB. Sublingual misoprostol for cervical ripening before diagnostic hysteroscopy in premenopausal women: A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial. Fertil Steril. 2010;93(7):2400–4.
Availability of Data and Materials
The data that support the findings of the study are available from the corresponding author in SPSS form upon reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was funded by the Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EAN, FDT, and VH developed the original idea and the protocol, abstracted, and prepared the manuscript. EAN and VH participated in the study design and analyzed the data. FDT and EST contributed to the study design and data gathering. All authors read and approved the final manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Institutional review board approval was obtained from the ethics committees of Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Consent for Publication
Written and informed consent was obtained from the patients.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Surgery
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanha, F.D., Nekoo, E.A., Tehraninejad, E.S. et al. Hysteroscopic Septum Resection by Monopolar Electrode and Reproductive Outcome in 948 Women with Septate Uterus. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 3, 1399–1403 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-021-00894-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-021-00894-4