Abstract
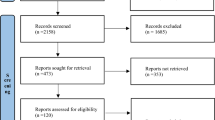
Sepsis is a serious disease that affects many people worldwide, and many therapies are used, including corticosteroids such as dexamethasone. However, there is no conclusion as yet, concerning the use of dexamethasone in patients with sepsis or septic shock. The aim of this study was to perform a literature review to assess the mortality of patients with sepsis or septic shock using dexamethasone, answering the following question: What is the effect of dexamethasone on mortality in adult and elderly patients with sepsis compared with mortality in patients who do not use anti-inflammatory therapy? The protocol of this study was registered in the PROSPERO database. The systematic literature search was performed in four electronic databases. Bias risk assessments were performed using the Cochrane Collaboration tool, and notification quality was assessed using the CONSORT-based checklist. The literature search initially identified 13,999 records. The three selected studies included eighty adult patients with sepsis or septic shock who had received dexamethasone as an intervention. Of the three articles, two concluded that the use of dexamethasone significantly reduces the mortality in patients with sepsis or septic shock. The Cochrane Collaboration tool bias risk results showed that none of the studies was completely bias-free and through the CONSORT checklist, it was found that none of the studies met 50% or more of the applicable requirements. Thus, it is clear from this review that further randomized clinical trials comparing the use of dexamethasone to placebo in adjunctive therapy for sepsis patients are needed. The registration number in the PROSPERO database is CRD42018088150.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Poll T, van de Veerdonk FL, Scicluna BP, Netea MG. The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17:407–20.
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315:801–10.
Napolitano LM. Sepsis 2018: definitions and guideline changes. Surg Infect. 2018;19:117–25.
Brent AJ. Sepsis. Medicine. 2017;45:649–53.
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet. 2020;395:200–11.
Hotchkiss RS, Moldawer LL, Opal SM, Reinhart K, Turnbull IR, Vincent J-L. Sepsis and septic shock. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:1–21.
Shaikh S, Verma H, Yadav N, Jauhari M, Bullangowda J. Applications of steroid in clinical practice: a review. Int Sch Res Notices 2012;2012:1–10.
Fink MP, Warren HS. Strategies to improve drug development for sepsis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13:741–58.
Matik PE. Steroids for sepsis: yes, no or maybe. J Thorac Dis. 2018;10:1070–3.
Gupta P, Bhatia V. Corticosteroid physiology and principles of therapy. Indian J Pediatr. 2008;75:1039–44.
Gibbison B, López-López JA, Higgins JPT, Miller T, Angelini GD, Lightman SL, et al. Corticosteroids in septic shock: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2017;21:1–8.
Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5928.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Version 2. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700.
Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D, CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomized trials. Ann Intern Med Logo. 2010;152:726–32.
Cicarelli DD, Benseñor FEM, Vieira JE. Effects of single dose of dexamethasone on patients with systemic inflammatory response. Sao Paulo Med J. 2006;124:90–5.
Funk D, Doucette S, Pisipati A, Dodek P, Marshall J, Kumar A. Low-dose corticosteroid treatment in septic shock: a propensity-matching study. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:2333–41.
Sprung CL, Caralis PV, Marcial EH, Pierce M, Gelbard MA, Long WM, et al. The effects of high-dose corticosteroids in patients with septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1984;311:1137–43.
Cicarelli DD, Vieira JE, Benseñor FEM. Early dexamethasone treatment for septic shock patients: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Sao Paulo Med J. 2007;125:237–41.
Schumer W. Steroids in the treatment of clinical septic shock. Ann Surg. 1976;184:333–41.
Lucas CE, Ledgerwood AM. The cardiopulmonary response to massive doses of steroids in patients with septic shock. Arch Surg. 1984;119:537–41.
Scheinman RI, Cogswell PC, Lofquist AK, Baldwin AS Jr. Role of transcriptional activation of I kappa B alpha in mediation of immunosuppression by glucocorticoids. Science. 1995;270:283–6.
Schimmer BP, Parker KL. Adrenocorticotropic hormone; adrenocortical steroids and their synthetic analogs; inhibitors of the synthesis and actions of adrenocortical hormones. In: Hardman JG, Limbird LE, Molinoff PB, Ruddon RW, Gilman AG, editors. Goodman and Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 9th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1996. p. 1459–85.
Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinge P, Fein AM, Knaus WA, et al. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992;101:1644–55.
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS international sepsis definitions conference. Intensive Care Med. 2003;29:530–8.
Funding
This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, Brazil) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES, Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This systematic review did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Medicine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fratoni, E., dos Santos Nascimento, M.V.P., Bramorski Mohr, E.T. et al. Effect of Dexamethasone on Mortality in Adult and Elderly Patients with Sepsis: a Systematic Review. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2, 886–892 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-020-00334-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-020-00334-9