Abstract
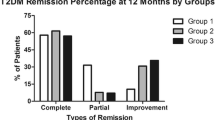
The objective of this study is to observe whether the patients’ loss weight is long term after bariatric surgery, as well as evaluating the blood pressure and certain chemical parameters. This retrospective study was carried out based on the files of 70 patients, who underwent laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) operation between January 2013 and December 2017. Paired sample t test and Wilcoxon tests were used for comparison of patients’ weight, blood pressure, and other parameters related to obesity within at least 6 months after LSG. While the body mass index (BMI) average of patients before bariatric surgery was 45.82 ± 4.73 kg/m2, it was reduced to 27.33 ± 2.98 kg/m2 within approximately 3 years after the operation (p < 0.01). It was confirmed that there was a significant remission in hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, serum insulin, HbA1C, and HOMA-IR parameters of patients after bariatric surgery (p < 0.05). Additionally, it was also detected that the antihypertensive and antidiabetic drug usage dosage of patients was either minimized or discontinued after bariatric surgery. In our study, it was detected that the weight loss of patients after LSG was satisfactory and that blood pressure, including certain biochemical parameters related to obesity, was on remission. Therefore, it is thought that LSG in the early period is a reliable operation, which ensures the weight loss, provided that the patients accommodate themselves to the changes in their lifestyles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight [Internet]. 2018 Feb 16; [cited 2018 July 31]. Available from: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
Republic of Turkey Ministry of Health. The Ministry of Health of Turkey, health statistics yearbook 2016. Ankara: SB-SAGEM-2017; [cited 2018 August 03]. Available from: http://ohsad.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/13160.pdf.
Vgontzas AN, Tan TL, Bixler EO, Martin LF, Shubert D, Kales A. Sleep apnea and sleep disruption in obese patients. Arch Intern Med. 1994;154(15):1705–11.
Costa AL, Varela JS, Cruz MR, Costa AF, Picon PD, Moriguch E, et al. Body mass index, cognitive deficit and depressive symptoms in high cardiovascular risk patients. Dement Neuropsychol. 2010;4(4):313–9.
Wu T, Wu S, Ouyang G. Periostin: a new extracellular regulator of obesity-induced hepatosteatosis. Cell Metab. 2014;20(4):562–4.
American Diabetes Association. Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:S47–53.
Prospective Studies Collaboration, Whitlock G, Lewington S, Sherliker P, Clarke R, Emberson J, et al. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults: collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet. 2009;373(9669):1083–96.
Institute of Health Economics. Bariatric treatments for adult obesity [Internet]. Edmonton, Alberta, Canada: Institute of Health Economics (IHE); 2012 Mar [cited 2018 Aug 03]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0099199/pdf/PubMedHealth_PMH0099199.pdf.
Talebpour M, Sadid D, Talebpour A, Sharifi A, Davari FV. Comparison of short-term effectiveness and postoperative complications: laparoscopic gastric plication vs laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg. 2018;28(4):996–1001.
Al Zabadi H, Daqour A, Hawari A, Hasouni J. Short-term outcomes of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy among obesity patients in the Northern West Bank: a retrospective records review. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7:85.
Young MT, Gebhart A, Phelan MJ, Nguyen NT. Use and outcomes of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy vs laparoscopic gastric bypass: analysis of the American College of Surgeons NSQIP. J Am Coll Surg. 2015;220(5):880–5.
Våge V, Sande VA, Mellgren G, Laukeland C, Behme J, Andersen JR. Changes in obesity-related diseases and biochemical variables after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: a two-year follow-up study. BMC Surg. 2014;14:8.
Yakar B, Ertekin YH. Screening cardiovascular risk in patients with high depression scores. Pak J Med Sci. 2018;34(3):610–5.
Rodríguez A, Becerril S, Valentí V, Ramírez B, Martín M, Méndez-Giménez L, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy reduces blood pressure in obese (fa/fa) Zucker rats. Obes Surg. 2012;22(2):309–15.
Lavie CJ, De Schutter A, Parto P, Jahangir E, Kokkinos P, Ortega FB, et al. Obesity and prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and prognosis-the obesity paradox updated. ProgCardiovasc Dis. 2016;58(5):537–47.
Iancu M, Copăescu C, Şerban M, Ginghină C. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy reduces the predicted coronary heart disease risk and the vascular age in obese subjects. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2013 Sep-Oct;108(5):659–65.
Boscolo M, Féry F, Cnop M. Beneficial outcomes of sleeve gastrectomy in a morbidly obese patient with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. J Endocr Soc. 2017;1(4):317–22.
Khalifa K, Ansari A, Alsayed AR, Violato C. The impact of sleeve gastrectomy on hyperlipidemia: a systematic review. J Obes. 2013;643530.
Lupattelli G, De Vuono S, Mannarino E. Patterns of cholesterol metabolism: pathophysiological and therapeutic implications for dyslipidemias and the metabolic syndrome. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2011;21(9):620–7.
Benetti A, Del Puppo M, Crosignani A, Veronelli A, Masci E, Frigè F, et al. Cholesterol metabolism after bariatric surgery in grade 3 obesity: differences between malabsorptive and restrictive procedures. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(6):1443–7.
De Vuono S, Ricci MA, Siepi D, Boni M, Gentili A, Scavizzi M, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy modifies cholesterol synthesis but not cholesterol absorption. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2017;11(1):118–22.
Benaiges D, Flores Le-Roux JA, Pedro-Botet J, Chillarón JJ, Renard M, Parri A, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass are equally effective in correcting insulin resistance. Int J Surg. 2013;11(4):309–13.
Gill RS, Birch DW, Shi X, Sharma AM, Karmali S. Sleeve gastrectomy and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2010 Nov-Dec;6(6):707–13.
Switzer NJ, Prasad S, Debru E, Church N, Mitchell P, Gill RS. Sleeve gastrectomy and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review of long-term outcomes. Obes Surg. 2016 Jul;26(7):1616–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Surgery
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kocaöz, S., Parlak, Ö. The Body Weight, Blood Pressure, and Biochemical Parameters of the Patients After Obesity Surgery. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 1, 646–649 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-019-00098-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-019-00098-x