Abstract
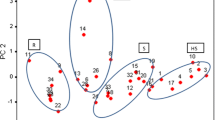
Association between rice grain characteristics and Sitophilus oryzae development were deciphered through laboratory experiments. Among the different physical characteristics evaluated, significant and negative correlation of 100 seed weight was observed with weevil emergence (r = − 0.53) and susceptibility index (r = − 0.51). Hence, 100 seed weight was found out to be important characteristics of grain. Similarly, hardness of the grain delayed weevil emergence (r = − 0.41) and reduced the grain weight loss (r = − 0.245). Biochemical characteristic of grain, like protein was found positively associated with weevil emergence (r = 0.741) and negatively associated with median developmental period (r = − 0.537). Amylose being an important component of grain had negative relation with weevil emergence (r = − 0.007); median development period (r = − 0.093). Among different varieties tested, Cross-12 was found to be moderately resistant compared to others. It was the only variety having long broad grain and recorded highest 100 seed weight indicating size of the substrate could hinder the development of weevils. The aim of the current study is to decipher the association of development of S. oryzae and physico-chemical characteristics of grain governing it.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abebe F, Tefera T, Mugo S, Beyene Y, Vidal S (2009) Resistance of maize varieties to the maize weevil Sitophilus zeamais (Motsch.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Afr J Biotechnol 8:5937–5943
Abraham T (1991) The biology, significance and control of the maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais Motsch. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) on stored maize. An M.Sc. Thesis presented to the School of Graduate Studies of Haramaya University of Agriculture, Ethiopia, p 250
Ahmad E, Jaiswal JP (2018) Inheritance of resistance to rice weevil (Sitophilus oryzae L.) in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Electron J Plant Breed 9:1083–1093
Antunes C, Mendes R, Lim A, Barros G, Fields P, Costa LBD, Rodrigues JC, Silva MJ, Correia AM, Carvalho MO (2016) Resistance of rice varieties to the stored-product insect, Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Econ Entomol 109(1):445–453
Ashamo MO (2001) Varietal resistance of maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais Motsch. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Plant Dis Protect 108:314–319
Bamaiyi LJ, Dike MC, Onu I (2007) Relative susceptibility of some sorghum varieties to the rice weevil Sitophilus oryzae L. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Entomol 4:387–392
Bottega DB, Rodrigues CA, Jesus FG, Silva AGS, Peixoto N (2012) Resistência de genótipos de feijão-vagem ao ataque de bruquíneos em condições de laboratório. Caatinga 25:92–97
Campbell J (2002) Influence of seed size on exploitation by the rice weevil, Sitophilus oryzae. J Insect Behav 15:429–445
Chijindu EN, Boateng BA (2008) Effect of nutritional content of processed cassava chips on development of Prostephanus truncatus (Horn). World J Agric Sci 4:404–408
Derera J, Pixley KV, Giga DP, Makanda I (2014) Resistance of maize to the maize weevil: III. Grain weight loss assessment and implications for breeding. J Stored Prod Res 59:24–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspr.2014.04.004
Dhingra D (2016) Evolution and trends in food grain storage in India. Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Controlled Atmosphere and Fumigation in Stored Products (CAF2016) In: Navarro S, Jayas DS, Alagusundaram K (eds) CAF Permanent Committee Secretariat, Winnipeg, Canada, pp 47–52
Dobie P (1974) The laboratory assessment of the inherent susceptibility of maize varieties to post-harvest infestation by Sitophilus zeamais. J Stored Prod Res 10:183–197
Dobie P (1984) Biological methods for integrated control of insects and mites in tropical stored products. I: the use of resistant varieties. Trop Stored Prod Inf 48:4–8
Ewer RF (1945) The effect of grain size on the oviposition of Calandra granaria Linn. (Coleoptera, Curculionidae). Entomol Soc Lond (A) 20:57–63
Fontes LS, Almeida Filho AJ, Arthur V (2003) Danos causados por Sitophilus oryzae (Linné, 1763) Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky, 1855 (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) em cultivares de arroz (Oryza sativa L.). Arquivos do Instituto Biológico 70:303–307
Garcia-Lara Bergvinson DJ, Burt AJ, Ramputh AI, Diaz-Pontones DM, Arnason JT (2004) The role of pericarp cell wall components in maize weevil resistance. Crop Sci 44:1560–1567
Gudrups I, Floyd S, Jennifer G, Nilsa KA, Bosque P, Orchard JE (2001) A comparison of two methods of assessment of maize varietal resistance to the maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais Motsch. and the influence of kernel hardness and size on susceptibility. J Stored Prod Res 37:287–302
Gwinner JR, Harnish Muck O (1996) Manual on the prevention of post harvest grain loss. GTZ, Eschborn
Haine C (1991) Insects and arachnids of tropical stored products: their biology and identification, 2nd edn. NRI, Gillingham
HLPE (2014) Food losses and waste in the context of sustainable food systems. A Report by the high level panel of experts on Food Security and Nutrition of the Committee on World Food Security. www.fao.org/cfs/cfs-hlpe. Accessed 25 June 2018
Hong KJ, Lee W, Park YJ, Yang JO (2018) First confirmation of the distribution of rice weevil, Sitophilus oryzae, in South Korea. J Asia-Pac Biodiv 11:69–75
Horber E (1988) Methods to detect and evaluate resistance in maize to seed insects in the field and in storage. In Towards insect resistance maize for the third world: Proceedings of international symposium on methodologies for developing host plant resistance to maize insects. CYMMYT, El Batan, Mexico, pp 140–150
Hossain F, Lacroix M, Salmieri S, Vu K, Follett PA (2014) Basil oil fumigation increases radiation sensitivity in adult Sitophilus oryzae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Stored Prod Res 59:108–112
Howe RW (1971) A parameter for expressing the suitability of an environment for insect development. J Stored Prod Res 7:63–65
Juliano BO (1971) Simplified assay for milled-rice amylose. Cereal Sci Today 16:334–338
Kalsa KK, Subramanyam B, Demissie G, Worku AF, Habtu NG (2019) Major insect pests and their associated losses in quantity and quality of farm-stored wheat seed. Ethiop J Agric Sci 29(2):71–82
Kaur M (2017) Development of stored grain insect pests on important cultivars of wheat (Triticum aestivum L., T. durum Desf.) and Triticale (Triticale hexaploide Lart.). M.Sc Thesis, Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana
Keba T, Sori W (2013) Differential resistance of maize varieties to maize weevil (Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) under Laboratory Conditions. J Entomol 10:1–12
Kossou D, Mareck J, Bosque-Perez N (1993) Comparison of improved and local maize varieties in the Republic of Benin with emphasis on susceptibility to Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky. J Stored Prod Res 29:333–343
Krishna DR, Lakshmi KV (2008) Varietal preference of maize genotypes to Sitophilus oryzae (Linn) attack in storage and its relation to physico-chemical characters of the grain. J Plant Prot Environ 5:45–51
Lale NES, Kartay MO (2006) Role of physical characteristics of the seeds in the resistance of local cultivars of maize to Sitophilus zeamais infestation in storage. Trop Sci 45:112–114
Lale NES, Yusuf BA (2001) Potential of varietal resistance and Piper guineense seed oil to control infestation of stored millet seeds and processed products by Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). J Stored Prod Res 37:63–75
Lara FM (1991) Princípios de resistência de plantas aos insetos. Ícone, São Paulo
Lee SE, Lee BH, Choi WS, Park BS, Kim JG, Campbell BC (2001) Fumigant toxicity of volatile natural products from Korean spices and medicinal plants towards the rice weevil Sitophilus oryzae (L). Pest Manag Sci 57:548–553
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Marsaro Júnior AL, Lazzari SMN, Figueira ELZ, Hirooka EY (2005) Inibidores de amilase em híbridos de milho como fator de resistência a Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Neotrop Entomol 34:443–450
McGaughey WH, Speirs RD, Martin CR (1990) Susceptibility of classes of wheat grown in the United States to stored-grain insects. J Econ Entomol 37:292–302
Mohammad I, Waseem AG, Azam K (1988) Maize grain resistance to Sitotroga cerealella and Sitophilus oryzae. Pak J Agric Res 9(4):15–21
Morallo-Rejesus B, Javier PA, Juliano BO (1982) Properties of brown rice and varietal resistance to storage insects. Philipp Entomol 5:227–238
Murad MS, Batool Z (2017) Relative Biochemical basis of susceptibility in commercial wheat varieties against Angoumois grain moth, Sitotroga cerealella (Olivier) and construction of its life table. J Biom Biostat 8:333. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6180.1000333
Nagpal M, Kumar A (2012) Grain losses in India and government policies. Qual Assur Saf Crops Foods 4:143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1757-837X.2012.00150.x
Naveena NL, Jagadeesh Babu CS, Sudhirkumar S, Prakash K (2011) Performance of Callosobruchus theobromae on different genotypes of fieldbean. Lablab purpureus L. J Entamol Res 35:75–79
Nwana IE, Akibo-Betts DT (1982) The resistance of some rice varieties to damage by Sitophilus zeamais Motsch., during storage. Trop Stored Prod Inf 43:10–15
Nwaubani SI, Opit GP, Otitodun GO, Adesida MA (2014) Efficacy of two Nigeria derived diatomaceous earths against Sitophilus oryzae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and Rhyzopertha dominica (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae) on wheat. J Stored Prod Res 59:9–16
Osipitan AA, Odebiyi A (2007) Laboratory evaluation of twenty maize (Zea mays L.) varieties for resistance to the larger grain borer, Prostephanus truncatus (Horn) (Coleoptera; Bostrichidae) in Ibadan. Oyo State. Nigeria Niger J Entomol 24:54–67
Pederson JR (1979) Selection of oviposition sites on wheat kernels by Sitophilus spp.: effect of moisture, temperature and kernel size, Ph.D. dissertation, Kansas State University, Manhattan
Peters LL, Fairchild ML, Zuber MS (1972) Effect of corn endosperm containing different levels of amylose on Angoumois grain moth biology. J Econ Entomol 65:576–578
Piesik D, Wenda-Piesik A (2015) Sitophilus granarius responses to blends of five groups of cereal kernels and one group of plant volatiles. J Stored Prod Res 63:63–66
Prasad GS, Babu KS, Sreedhar M, Padmaja PG, Subbarayudu B, Kalaisekar A, Patil JV (2015) Resistance in sorghum to Sitophilus oryzae (L.) and its association with grain parameters. Phytoparasitica 43:391–399
Ramputha A, Teshome A, Bergvinson DJ, Nozzolilloa C, Arnason JT (1999) Soluble phenolic content as an indicator of sorghum grain resistance to Sitophilus oryzae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Stored Prod Res 35:57–64
Reddy DB (1951) Determinaton of sex in adult rice and granary weevils (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Pan-Pac Entomol 25:13–16
Ribeiro BM, Guedes RNC, Oliveira EE, Santos JP (2003) Insecticide resistance and synergism in Brazilian populations of Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Stored Prod Res 39:21–31
Ribeiro LP, Vendramim JD, Bicalho KU, Andrade MS, Fernandes JB, Moral RA, Demetrio CGB (2013) Annona mucosa Jacq. (Annonaceae): a promising source of bioactive compounds against Sitophilus zeamais Mots. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Stored Prod Res 55:6–14
Saad ASA, Tayeb EHM, El-Shazli MM, Baheeg SA (2018) Susceptibility of certain Egyptian and imported wheat cultivars to infestation by Sitophilus oryzae and Rhyzopertha dominica. Arch Phytopathol Plant Prot 51:14–29
Sahoo G, Sahoo BK (2016) Grain hardness and protein content of milled rice grains and their relationship with infestation of rice weevil Sitophilus oryzae L., (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Oryza 53(3):332–336
Segrove F (1951) Oviposition behaviour in the two strains of the rice weevil, Calandra oryzae Linn. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Exp Biol 28:281–297
Seshagiri Rao D (1953) The breeding of Sitophilus oryzae (L.) in rice. Indian J Entomol 15:157–159
Singh BB, Singh SR, Adjadi O (1984) Bruchid resistance in cowpea. Crop Sci 25:736–739
Siwale J, Mbata K, Mcrobert J, Lungu D (2009) Comparative resistance of improved maize genotype and landraces to maize weevil. Afr Crop Sci J 17:1–16
Smith CM (2005) Plant resistance to arthropods: molecular and conventional approaches. Springer, Berlin
Soujanya LP, Sekhar JC, Karjagi CG, Paul D, Kumar P (2017) Evaluation of biophysical, anatomical and biochemical traits of resistance to Sitophilus oryzae L (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in stored maize. Phytoparasitica 45:485
Soumia PS, Srivastava C, Dikshit HK, Guru Pirasanna Pandi G (2015) Screening for resistance against pulse beetle, Callosobruchus analis (F.) in Greengram (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek) accessions. Proc Natl Acad Sci 87:551–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0635-5
Sousa JR, Barrigossi JAF, Boiça Junior AL, Gonçalves KKM, Torres ERS, Mondego JM (2010) Avaliação de resistência em variedades de arroz (Oryza sativa L.) ao ataque do Sitophilus oryzae Linnaeus, 1763 (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Núcleos 7:259–266
Souza AR, Silva TM, Santos JFL (2012) Seleção e desenvolvimento de Sitophilus oryzae (Linné, 1763) em três substratos. Magistra 24:160–163
Stejskal V, Kucerova Z (1996) The effect of grain size on the biology of Sitophilus granarius L. (Coleoptera Curculionidae). I. Oviposition, distribution of eggs and adult emergence. J Appl Entomol 120:143–146
Stevens PA, Mills RB (1973) Comparison of techniques for screening sorghum grain varieties for resistance to rice weevil. J Econ Entomol 66:1222
Throne JE, Baker JE, Messina FJ, Kramer KJ, Howard JA (2000) Varietal resistance. In: Subramanyam B, Hagstrum DW (eds) Alternatives to pesticides in stored product IPM. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp 165–192
Tripathi K, Bhalla S, Prasad TV, Srinivasan K (2012) Differential reaction of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) genotypes to pulse beetle (Callosobruchus maculatus). Vegetos 25:367–374
Tripathi K, Chauhan SK, Gore PG, Mehta PS (2017) Evaluation of wheat landraces of north-western Himalaya against rice weevil, Sitophilus oryzae L. vis-à-vis physical seed parameters. Plant Genetic Res 15(4):321–326
Wenda-Piesik A, Piesik D, Nowak A, Wawrzyniak M (2016) Tribolium confusum responses to blends of cereal kernels and plant volatiles. J Appl Entomol 140:558–563
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge Director, ICAR-National Rice Research Institute, Cuttack, India for constant support in formulating the project, funding as well as providing all the facilities (Grant no. Institute project 3.1). Authors duly acknowledge Dr. H. N. Subudhi, Principal Scientist, ICAR-NRRI for supplying seeds of rice varieties used in the study. We thank Dr. N. N. Jambhulkar, Scientist, ICAR-NRRI for his guidance in statistical analysis and Dr. Sutapa Sarkar for sharing pedigree information. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gowda, G.B., Patil, N.B., Adak, T. et al. Physico-chemical characteristics of rice (Oryza Sativa L.) grain imparting resistance and their association with development of rice weevil, Sitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleoptera:Curculionidae). Environmental Sustainability 2, 369–379 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-019-00087-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-019-00087-9