Abstract
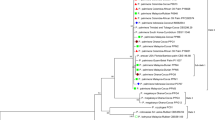
Grey mildew/false mildew of cotton caused by R. areola regarded as destructive on desi-cotton genotypes. Generally, causes premature defoliation of leaves and immature bolls in many susceptible cultivars/genotypes. The prolonged low temperature coupled with high humidity micro-climate conditions were predisposing factors for disease spread in resistance genotypes. Highest diseases incidence of grey mildew was observed in the transitional zone of Karnataka (Dharwad, Gadag, Haveri and Belgaum districts) and zero disease incidence was recorded in northern dry-zones of Karnataka. Direct transfer of conidia or transfer of germinated conidia on modified Kirchoffs + cotton leaves decoction medium was best for the sporulation and isolation of fungus. The molecular variability of isolates was confirmed through RAPD primers, 18–67% coefficient variation was observed in the isolates. Conidia of the fungus were short-lived in a natural condition, perpetuate for long times in leaf debris by producing dormant ascospores. However, low temperature and high soil moisture increase the viability of conidia under field condition. Out of 25 G. arboreum lines, EIPSD-4 entry showed resistant reaction followed by moderately resistant in A-1 and A-4 entries and none of the entries were immune to grey mildew.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson GF (1890) A new Ramularia on cotton. Bot Gazette 15:166–168
Brunk CF, Jone KC, James TW (1979) Assay for nanogram quantities of DNA in cellular homogenates. Anal Biochem 92:497–500
Butler EJ (1918) Fungi and diseases in plants. Thacker Spink and Company, Calcutta, p 200
Chakrabarty PK, Mukewar PM, Raj S (2003) Development of sensitive molecular diagnostic tools for detection of economically important fungal pathogens of cotton Annual Report Central institute for cotton research Nagpur India
Chattannavar SN, Ammajamma R, Hiremath SV, Patil SB, Khadi BM (2009) Catalase isozyme pattern of different groups of Ramularia areola. J Cotton Res Dev 22(2):246–427
Chattannavar SN, Hiremath SV, Sharmila AS, Khadi BM (2005) Evaluation of desi cotton genotypes for Grey mildew. J Cotton Res Dev 19(2):268–269
Chattannavar SN, Prakash Hegde, Khadi BM, Gaddanakeri MA and Hiremath SV (2001) Field reaction of cotton genotypes against foliar disease. Paper presented at Nation. Symp Cotton Res Strat New Mill held at CCSHAU, Hissar on April 16th.
Chauhan MS (1985) Grey mildew disease of arboreum cotton in Haryana. Ind J Myco Pl Pathol 13:214–215
Ehrlich J, Wolf FA (1932) Areolate mildew of cotton. Phytopathology. 22:229–239
FAO (2016) Cotton. OECD-FAO agricultural outlook 2016–2025. OECD Publishing, Paris, pp 113–133
Gadd CH (1926) Report of the division of mycology. Administration representative. Director of Agriculture, Ceylon 19:13–15
Gokhale VP, Moghe PG (1965) Preliminary investigation of Dahiya disease of cotton caused by Ramularia areola in Vidharbha. Nagpur Agril Coll Magaz 38:27–31
Gokhale VP, Moghe PG (1967) first record of the perithecial stage of Ramularia areola Atk on cotton in India. Indian Phytopath. 20(2):174–175
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research. Wiley, Singapore, pp 139–153
Govindarao P, Subbaiah J (1954) Grey mildew on cotton and its control. Andhra Agric J 1:362–363
Harlapur SI, Chattannavar SN, Wali MC, Kulkarni MS (2004) Cotton disease problems in Ghataprabha left bank canal command region of Karnataka. Inter Symp Strat Sust Cotton Prod A Global Vision 3, Crop Production, 23–25, (November 2004) Uni. Agric. Sci, Dharwad (India), pp 362–363
Hosagoudar GN, Chattannavar SN (2009) Biochemical studies in cotton genotypes having a differential reaction of grey mildew (Ramularia areola Atk). Karnataka J Agric Sci 22(2):331–335
Moghe PG and Dahule KK (1970) Studies on Ramularia areola Atk. causing Dahiya disease of cotton with special reference to pathogenicity crop losses, varietal reaction and nutritional aspects of mass culture. Unpublished M.Sc. (Agri.) Thesis Dept. of Plant Pathology Agril. College Nagpur (India).
Mukewar PM, Sheo Raj, Chakrabarty PK (1994) The Epidemic occurrence of Grey mildew disease of cotton in Central India. J Ind Soc Cotton Imp 19: 170-172.
Ponnanna KN (1998) Studies on Grey mildew (R. areola Atk) of cotton in Karnataka. M. Sc. (Agri.) Thesis, Univ. Agric. Sci. Dharwad (India).
Raj S (1988) Grading for cotton disease, CICR, Nagpur. Bull. pp 1-7.
Rathaiah Y (1973) Study on false mildew of cotton, growth, and sporulation of the fungus in culture. Cotton et Fibres Tropicales 28:287–296
Rohlf FI (1998) NTSYS-PC Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis version 2.0. Applied Biostatistics Inc, New York.
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgesen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF and Maniatis T (1989) Gel electrophoresis of DNA. In: Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. and Maniatis, T. (Eds.) Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor.
Shivankar SK, Wangikar PD (1992) Estimation of crop losses due to grey mildew disease of cotton caused by Ramularia areola. Indian Phytopath. 45:74–76.
Siddiqui MR, Rao SBP (1965) A short note on testing Gossypium arboreum under artificial epiphytotics for resistance to Grey mildew. Indian Cotton J. 19:256–257
Volponi J, Matos JN, Girotto L, Marangoni MS, Galbieri R, Mehta YR (2014) Spore types and spore production of Ramularia areola for screening cotton germplasm for resistance. Am J Plant Sci Temuco 5(1):2413–2417
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramanagouda, G., Ashtaputre, S.A. Collection and characterization of grey mildew (Ramularia areola Atk.) pathogen of cotton. Indian Phytopathology 72, 301–307 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-019-00123-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-019-00123-y