Abstract
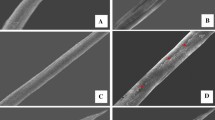
Two concentrations of Zinc Oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) were applied using three methods i.e., spray, seed treatment and soil inoculation for the management of disease complex of eggplant caused by Ralstonia solanacearum, Phomopsis vexans and Meloidogyne incognita. The highest increase in plant growth, chlorophyll and carotenoid contents was obtained by spray of NPs followed by seed treatment and soil inoculation. Plants sprayed with 200 ppm NPs resulted in higher increase in plant growth, and higher reduction in galling and nematode multiplication. 15 and 8 days early flowering and fruiting were observed in plants sprayed with 200 and 100 ppm NPs, respectively, over seed treatments. Scanning electron microscopy revealed that ZnO NPs had an adverse effect on cell wall/body wall of test pathogens. Wilt and blight indices was three and five when inoculated with single pathogen and inoculated together, respectively. Disease index was reduced to one when plants sprayed with 200 ppm NPs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alghuthaymi MA, Almoammar H, Rai M, Said-Galiev E, Abd-Elsalam KA (2015) Myconanoparticles: synthesis and their role in phytopathogens management. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 29(2):221–236
Cakmak I (2000) Possible roles of zinc in protecting plant cells from damage by reactive oxygen species. New Phytol 146:185–205
Da Silva LC, Oliva MA, Azevedo AA, De Araujo MJ (2006) Response of resting plant species to pollution from an iron pelletization factory. Water Air Soil Pollut 175:241–256
Dimapilis EAS, Hsu C-S, Mendoza RMO, Lu M-C (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles for water disinfection. Sustain Environ Res 28:47–56
Dimkpa CO, McLean JE, Latta DE, Manango´n E, Britt DW, Johnson WP, Boyanov MI, Anderson AJ (2012) CuO and ZnO nanoparticles: phytotoxicity, metal speciation and induction of oxidative stress in sand-grown wheat. J Nanopart Res 14:1125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1125-9
Faizan M, Faraz A, Yusuf M, Khan ST, Hayat S (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticle-mediated changes in photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant system of tomato plants. Photosynthetica 56:578–586
Fang M, Chen JH, Xu XL, Yang PH, Hildebrand HF (2006) Antibacterial activities of inorganic agents on six bacteria associated with oral infections by two susceptibility tests. Int J Antimicrob Agents 27:513–517
Gonzalez-Melendi P, Fernandez Pacheco R, Coronado MJ, Corredor E, Testillano PS, Risueno MC, Marquina C, Ibarra MR, Rubiales D, Perez-De-Luque A (2008) Nanoparticles as smart treatment-delivery systems in plants: assessment of different techniques of microscopy for their visualization in plant tissues. Ann Bot 101:187–195
Gupta S, Kushwah T, Vishwakarma A, Yadav S (2015) Optimization of ZnO-NPs to investigate their safe application by assessing their effect on soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Nanoscale Res Lett 10:303
Hayward AC (1991) Biology and epidemiology of Bacterial Wilt caused by Pseudomonas solanacearum. Annu Rev Phytopathol 29:65–87
He L, Liu Y, Mustapha A, Lin M (2011) Antifungal activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Botrytis cinerea and Penicillium expansum. Microbiol Res 166(3):207–215
Jameel A, Chaube HS (2006) Variabilty in phomopsis blight pathogen ((Phomopsis vexans(sacc. & Syd.) Harter). Indian Phytopath 59:439–444
Kelman A (1954) The relationship of pathogenicity in Pseudomonas solanacearum to colony appearance on a tetrazolium medium. Phytopathology 44:693–695
Khan M, Siddiqui ZA (2017) Interactions of Meloidogyne incognita, Ralstonia solanacearum and Phomopsis vexans on eggplant in sand mix and fly ash mix soils. Sci Hortic 225:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.06.016
Laware SL, Raskar S (2014) Influence of zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth, flowering and seed productivity in onion. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 3(7):874–881
Li S, Yu Y, Chen J, Guo B, Yang L, Din W (2016) Evaluation of the antibacterial effects and mechanism of action of protocatechualdehyde against Ralstonia solanacearum. Molecules 21(6):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060754
Lilley CJ, Kyndt T, Gheysen G (2011) Nematode resistant GM crops in industrialized and developing countries. In: Jones JT, Gheysen G, Fenoll C (eds) Genomics and molecular genetics of plant-nematode interactions. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 517–541
Lin D, Xing B (2008) Root uptake and phytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 42(15):5580–5585
Mackinney G (1941) Absorption of light by chlorophyll solutions. J Biol Chem 140:315–322
Muthuraman P, Ramkumar K, Kim DH (2014) Analysis of dose-dependent effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme activity in adipocytes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 174:2851–2863
Ocsoy I, Paret ML, Ocsoy MA, Kunwar S, Chen T, You MW, Tan W (2013) Nanotechnology in plant disease management: DNA-directed silver nanoparticles on graphene oxide as an antibacterial against Xanthomonas perforans. ACS Nano 7(10):8972–8980. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn4034794
Prasad TNVKV, Sudhakar P, Sreenivasulu Y et al (2012) Effect of nanoscale zinc oxide particles on the germination, growth and yield of peanut. J Plant Nutr 35:905–927
Riker AJ, Riker RS (1936) Introduction to research on plant diseases. John’s Swift Co., New York
Sabir S, Arshad M, Chaudhari SK (2014) Zinc oxide nanoparticles for revolutionizing agriculture: synthesis and applications. Sci World J 2014:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/925494 (Article ID 925494)
Sávoly Z, Hrács K, Pemmer B, Streli C, Záray G, Nagy PI (2016) Uptake and toxicity of nano-ZnO in the plant-feeding nematode, Xiphinema vuittenezi: the role of dissolved zinc and nanoparticle-specific effects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:9669–9678
Sawai J, Yoshikawa T (2004) Quantitative evaluation of antifungal activity of metallic oxide powders (MgO, CaO and ZnO) by an indirect conductimetric assay. J Appl Microbiol 96:803–809
Schaad NW (1992) Laboratory guide for the identification of plant pathogenic bacteria. 2nd edn. Published by Ibdchb. ISBN 10:8123925530/ISBN 13:9788123925530
Sharma, P.D. (2010). Microbiology 3rd ed. Rastogi publication, Meerut, India. 716 pp.ISBN 81-7133-935-2
Sood ML, Kalra S (1977) Histochemical studies on the body wall of nematodes: Haemonchus contortus (Rud., 1803) and Xiphinema insigne Loos, 1949. Zeitschrift für Parasitenkunde 51:265–273
Southey JF (1986) Laboratory methods for work with plant and soil nematodes. Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, Her Majesties Stationary Office, London
Taheri M, Qarache HA, Qarache AA, Yoosefi M (2015) The effects of Zinc-oxide nanoparticles on growth parameters of corn (SC704). STEM Fellowship J 1(2):17–19
Welch RM, Webb MJ, Loneragan JF (1982) Zinc in membrane function and its role in phosphorus toxicity. In: Scaife A (ed) Proceedings of the ninth plant nutrition colloquium. Warwick, UK. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 710–715
Yamamoto O, Komatsu M, Sawai J, Nakagawa Z (2008) Antibacterial activity of ZnO powder with crystallographic orientation. J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:1407–1412
Zhang H, Chen G (2009) Potent antibacterial activities of Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite powders synthesized by a one-pot sol–gel method. Environ Sci Technol 43:2905–2910
Acknowledgements
Junior Research Fellowship award to first author by University Grants Commission New Delhi, India is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest has been declared by authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M., Siddiqui, Z.A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for the management of Ralstonia solanacearum, Phomopsis vexans and Meloidogyne incognita incited disease complex of eggplant. Indian Phytopathology 71, 355–364 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-018-0064-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-018-0064-5