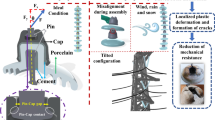
Abstract
In this study, we investigated 154-kV porcelain insulators with various failure types and discussed the causes of the failures. In South Korea, 1,223,538 154 kV porcelain insulators (produced by a foreign company) are in active service in 2017, installed in overhead power transmission lines. Among them, 797,659 (65.19%) have been used over 30 years in active service. Porcelain insulators employed in transmission lines need to exhibit a high electrical resistance, mechanical strength, stability, and ability to maintain satisfactory performance under various environments. In this study, a life-time assessment strategy is proposed for the 154 kV porcelain insulators according to the operational circumstances. The life-time extrapolation of porcelain insulators in 154-kV transmission lines is very challenging, owing to the complex aging process. As the first step of the life-time extrapolation, we characterized the failure types. Various factors such as temperature, rain, dust, acids, corrosion, vibrations, and mechanical and electrical stresses, over a long period of time can lead to various types of failures in porcelain insulators.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.F. Hampton, Flashover mechanism of polluted insulation. Proc. IEE 111, 985 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1049/piee.1964.0155
P.J. Lambeth, Effect of pollution on high-voltage outdoor insulator. Proc. IEE IEE Rev. 118, 1107 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1049/piee.1971.0245
G. Karady, Surface contamination: genesis, detection, and control, 945 (1979)
E. Nasser, IEEE Conference Paper, Paper. No. 70
T.C. Cheng, C.T. Wu, Performance of HVDC insulators under contaminated conditions. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 3, 270 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1109/tei.1980.298320
M. Kawai, Research at project UHV on the performance of contaminated insulators Part I Basic problems. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. PAS-92, 1102 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpas.1973.293677
G. Karady, The effect of fog parameters on the testing of artificially contaminated insulators in a fog chamber. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 94, 378 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1109/t-pas.1975.31864
M.M. Hussain, S. Farokhi, S. McMeekin, M. Farzaneh, IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 24, 1068 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2017.006386
P. Haberecht, Pollution deposition rates on insulator (HV) surfaces for use in atmospheric corrosivity estimation. Doctor Thesis
A. Rawat, R. Gorur, Microstructure based evaluation of field aged and new porcelain suspension insulators. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 16, 107 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2009.4784557
E. Cherney, A.C. Baker, J. Kuffel, Z. Lodi, A. Philips, D.G. Powell, G.A. Stewart, Evaluation of and replacement strategies for aged high voltage porcelain suspension-type insulators. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 29, 275 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRD.2013.2288776
E. Cherney, Electromechanical integrity of suspension insulator. Ontario Hydro Res. Rev. 5, 19 (1982)
E. Cherney, Cement growth failure of porcelain suspension insulators. IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst. PAS-102, 2765 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpas.1983.317959
T. Tsuru, in 16th International Corrosion Congress, 56, paper 18-C (2005)
A.A. Mikhailov, The classification system of ISO 9223 Standard and the dose-response functions assessing the corrosivity of outdoor atmospheres. Prot. Met. 40, 541 (2004)
I. Suzuki, Corrosion–Resistant Coatings Technology (Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 1989)
C. Leygraf, I.O. Wallinder, J. Tidblad, T. Graedel, Atmospheric Corrosion (Wiley, New York, 2016)
ISO 9223, Corrosion of Metals and Alloys: Corrosivity of Atmospheres—Classification (ISO 9223: 1992. Switzerland, ISO, 1992), p. 1–13
D.E. Alexander, Portland cement curing and volume characteristics. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 96, 14 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1109/T-PAS.1977.32300
S.-W. Han, Accelerating aging of transmission line porcelain suspension insulators by autoclaving, in IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference and Electrical Manufacturing Expo, vol. 114 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/eeic.2007.4562600
K. Chrzan, Hygroscopic properties of pollutants on HV insulators. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 24, 107 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1109/14.19874
F. Obenaus, Contamination State and Creepage Path. Deutsche Elektrotechnik 12, 135 (1958)
M.H. Samimi, Effect of humidity on the flashover voltage of insulators at varying humidity and temperature conditions. J. Basic Appl. Sci. Res. 2, 4299 (2012)
M. Ishii, Effect of ambient temperature on the performance of contaminated DC insulators. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 2, 129 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1109/tei.1984.298784
M.A. E1-Koshairy, F.A. Rizk, Performance of EHV transmission line insulators under desert pollution conditions. CIGRE Paper (1970)
M. Farzaneh, AC flashover performance of insulators covered with artificial ice. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 10, 1038 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1109/61.400824
T. Fujimura, Performance of insulators covered with snow or ice. IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst. 98, 1621 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpas.1979.319479
K. Morita, Steep impulse voltage characteristics of suspension insulators. Electr. Eng. Japan 115, 21 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/eej.4391150203
E. S. Zobel, Insulators lose strength with age. Elect. World 40–42 (1962)
A. A. Klein, Constitution and microstructure of porcelain. No. 79-81. US Government Printing Office (1916)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, IH., Kim, TK., Yoon, YB. et al. A Study on the Life-Time Assessment Ways and Various Failure Types of 154 kV Porcelain Insulators Installed in South Korea. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 19, 188–194 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-018-0027-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-018-0027-7