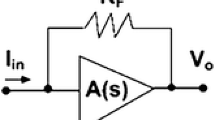
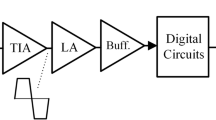
Abstract
Transimpedance amplifier (TIA) is an essential component of optical receivers, and this type of amplifier converts the photocurrent to a voltage signal. The overall performance of the optical receiver greatly depends on the performance of this component. Low-power, low-noise, and compact TIA has been realized in current development in CMOS technology. The high demands of an optical receiver has led to the optimization and development of the TIA designed specifications. However, the conventional CMOS TIA design is limited mainly because of its dependency on input node capacitance. In this article, the advancement of TIAs in data communication and instrumentation based on different design architectures and performances is discussed. This review will serve as a comparative study and reference for designing fully integrated CMOS TIA for future optical receivers.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Marufuzzaman, M.B.I. Reaz, L.S. Yeng, L.F. Rahman, T.I. Badal, Design of low-cost transimpedance amplifer for optical receiver. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 19(1), 7–13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-018-0008-x
M.A.S. Bhuiyan, M.B.I. Reaz, T.I. Badal, M.A. Mukit, N. Kamal, Design of an active inductor-based T/R switch in 0.13 μm CMOS technology for 2.4 GHz RF transceivers. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 17, 261–269 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4313/teem.2016.17.5.261
L.F. Rahman, M.B.I. Reaz, M. Marufuzzaman, M.B. Mashur, M.T.I. Badal, Evaluation of low power and high speed CMOS current comparators. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 17(6), 317–328 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4313/TEEM.2016.17.6.317
M.A.S. Bhuiyan, Y. Zijie, J.S. Yu, M.B.I. Reaz, N. Kamal, T.G. Chang, Active inductor based fully integrated CMOS transmit/receive switch for 2.4 GHz RF transceiver. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 88, 1089–1098 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201620150123
J.M. García del Pozo, W.A. Serdijn, A. Otín, S. Celma, 2.5 Gb/s CMOS preamplifier for low-cost fiber-optic receivers. Analog. Integr. Circuits Process. 66, 363–370 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/2Fs10470-010-9526-0
S. Kudszus, A. Shahani, S. Pavan, D.K. Shaeffer, and M. Tarsia, A 46-GHz distributed transimpedance amplifier using SiGe bipolar technology, in IEEE international MTT-S in Microwave Symposium Digest (2003), pp. 1387–1390. https://doi.org/10.1109/mwsym.2003.1212630
H. Zheng, R. Ma, M. Liu, A 77-dB dynamic range low-power variable-gain transimpedance amplifier for linear LADAR. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 65(2), 171–175 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2017.2684822
M.A.S. Bhuiyan, M.B.I. Reaz, Shunt-feedback transimpedance amplifier in 0.18 μm CMOS technology, in 2013 2nd International Symposium on Instrumentation and Measurement, Sensor Network and Automation (IMSNA) (2013), pp. 687–690. https://doi.org/10.1109/IMSNA.2013.6743369
T. Takemoto, H. Yamashita, T. Yazaki, N. Chujo, Y. Lee, Y. Matsuoka, A 25-to-28 Gb/s high-sensitivity (9.7 dBm) 65 nm CMOS optical receiver for board-to-board interconnects. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 49, 2259–2276 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/2Fjssc.2014.2349976
S.M. Rezaul Hasan, Design of a low-power 3.5 GHz broad-band CMOS transimpedance amplifier for optical transceivers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 52, 1061–1072 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2005.849101
U. Alvarado, G. Bistué, I. Adin, Low Power RF Circuit Design in Standard CMOS Technology (Springer, Berlin, 2011), p. 104. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-22987-9
Z. Lu, K.S. Yeo, W.M. Lim, M.A. Do, C.C. Boon, Design of a CMOS broadband transimpedance amplifier with active feedback. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 18, 461–472 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/tvlsi.2008.2012262
Q. Gao, S. Xie, L. Mao, S. Wu, Y. Gu, H. Li, Q. Song, A single-to-differential broadband transimpedance amplifier for 12.5 Gb/s optical links. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 14, 2 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1587/elex.13.20161153
H.-L. Chen, C.-H. Chen, W.-B. Yang, J.-S. Chiang, Inductorless CMOS receiver front-end circuits for 10-Gb/s optical communications. Tamkang J. Sci. Eng. 12, 449–458 (2009)
J. Charlamov, R. Navickas, Design of CMOS differential transimpedance amplifier. Elektron. Elektrotech. 21, 37–41 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.eee.21.1.4548
Y. Fei, Low-voltage CMOS current-mode preamplifier: analysis and design. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 53, 26–39 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2005.854414
O. Momeni, H. Hashemi, E. Afshari, A 10 Gb/s inductorless transimpedance amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 57, 926–930 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2010.2087971
A. Trabelsi, M. Boukadoum, Comparison of two CMOS front-end transimpedance amplifiers for optical biosensors. IEEE Sens. J. 13, 657–663 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2012.2225141
W. Xu, D.L. Mathine, J.K. Barton, High-gain differential CMOS transimpedance amplifier with on-chip buried double junction photodiode. Electron. Lett. 42, 803–805 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:20061560
P. Wright, K.B. Ozanyan, S.J. Carey, H. McCann, Design of high-performance photodiode receivers for optical tomography. IEEE Sens. J. 5, 281–288 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2004.841869
M. Li, B. Hayes-Gill, I. Harrison, 6 GHz transimpedance amplifier for optical sensing system in low-cost 0.35 µm CMOS. Electron. Lett. 42, 1278–1279 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:20062961
R. Yun, V.J. Koomson, A novel CMOS frequency-mixing transimpedance amplifier for frequency domain near infrared spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 60, 84–94 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/biocas.2010.5709615
F. Aznar, W. Gaberl, H. Zimmermann, A 0.18 μm CMOS transimpedance amplifier with 26 dB dynamic range at 2.5 Gb/s. Microelectron. J. 42, 1136–1142 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2011.06.005
Y.H. Chang, Y.C. Chiang, C.Y. Yang, A 42.15–68.35 dBΩ tunable gain transimpedance amplifier using 0.18-μm CMOS process. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 57, 830–832 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/mop.28969
E. Säckinger, Broadband Circuits for Optical Fiber Communication (Wiley, New York, 2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/0471726400
H. Zquez, F. Dualibe, G. Popov, A 0.5 V fully differential transimpedance amplifier in 65-nm CMOS technology, in IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/mwscas.2017.8053035.s
C.-H. Lu, W.-Z. Chen, Bandwidth enhancement techniques for transimpedance amplifier in CMOS technologies, in Proceedings of the 27th European Solid-State Circuits Conference (2001), pp. 174–177. https://doi.org/10.1109/icm.2013.6734945
J. Jun-De, S.S.H. Hsu, A 40-Gb/s transimpedance amplifier in 0.18-μm CMOS technology. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 43, 1449–1457 (2008)
Y. Zhang, Design of CMOS Front-End Receivers for Optical Wireless Communication (Tufts University, Medford, 2008)
C.A. Holt, Electronic Circuits: Digital and Analog (Wiley, New York, 1978)
P. Muller, Y. Leblebici, Transimpedance Amplifier Design: CMOS Multichannel Single-Chip Receivers for Multi-gigabit Optical Data Communications (Springer, Dordrecht, 2007), pp. 73–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-5912-4
Z. Yan, P.-I. Mak, R.P. Martins, Two stage operational amplifiers: power and area efficient frequency compensation for driving a wide range of capacitive load. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 11, 26–42 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/mcas.2010.939783
B. Razavi, A 622 Mb/s 4.5 pA/spl radic/Hz CMOS transimpedance amplifier for optical receiver front-end, in IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), Digest of Technical Papers (2000), pp. 162–163. https://doi.org/10.1109/isscc.2000.839732
E. Sackinger, W. Guggenbuhl, A high-swing, high-impedance MOS cascode circuit. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 25, 289–298 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1109/4.50316
B. Chen, RFIC Applications with CMOS Technology (City University of New York, Ann Arbor, 2006)
J.H. Chuah, D. Holburn, Design of low-noise CMOS transimpedance amplifier. Microelectron. Int. 30, 115–124 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1108/mi-11-2012-0080
M. Atef, H. Zimmermann, Low-power 10 Gb/s inductorless inverter based common-drain active feedback transimpedance amplifier in 40 nm CMOS. Analog Integr. Circuits Process 76, 367–376 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0117-8
P. Muller, Y. Leblebici, CMOS Multichannel Single-Chip Receivers for Multi-gigabit Optical Data Communications (Springer, Berlin, 2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-5912-4
A. Tanabe et al., A single-chip 2.4-Gb/s CMOS optical receiver IC with low substrate cross-talk preamplifier. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 33, 12 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1109/4.735558
M. Azadeh, Optical receiver design, in Fiber Optics Engineering, ed. by B. Mukherjee (Springer, Berlin, 2009), pp. 235–264
C. Kromer et al., A low-power 20-GHz 52-dBΩ transimpedance amplifier in 80-nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 39, 885–894 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/jssc.2004.827807
D. Li, G. Minoia, M. Repossi, D. Baldi, E. Temporiti, A. Mazzanti et al., A low-noise design technique for high-speed CMOS optical receivers. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 49, 1437–1447 (2014)
S. Shahdoost, A. Medi, N. Saniei, Design of low-noise transimpedance amplifiers with capacitive feedback. Analog Integr. Circuits Process. 86, 233–240 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-015-0669-x
D. Chen, K.S. Yeo, X. Shi, M.A. Do, C.C. Boon, W.M. Lim, “Cross-coupled current conveyor based CMOS transimpedance amplifier for broadband data transmission. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 21, 1516–1525 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/tvlsi.2012.2211086
H. Escid, M. Attari, M. Aitaidir, W. Mechti, CMOS optical sensor for an integrated transimpedance circuit. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 4, 467–481 (2011). https://doi.org/10.21307/ijssis-2017-451
T.-H. Ngo, T.-W. Lee, H.-H. Park, 4.1 mW 50 dBΩ 10 Gbps transimpedance amplifier for optical receivers in 0.13 μm CMOS. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 53, 448–451 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/mop.25741
J. Sangirov, I.A. Ukaegbu, T.-W. Lee, M.H. Cho, H.-H. Park, 10 Gbps transimpedance amplifier-receiver for optical interconnects. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 17, 44–49 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3807/josk.2013.17.1.044
D. Abd-elrahman, M. Atef, M. Abbas, M. Abdelgawad, Low power transimpedance amplifier using current reuse with dual feedback, in IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits, and Systems (ICECS) (2015), pp. 244–247
S.M.R. Hasan, A 0.8 V 40 Gb/s novel CMOS regulated cascode trans-impedance amplifier for optical sensing a lications. J. Signal Process. Syst. 72, 63–68 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-012-0707-1
L. Chih-Fan, L. Shen-Iuan, 40 Gb/s transimpedance-AGC amplifier and CDR circuit for broadband data receivers in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 43, 642–655 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/jssc.2007.916626
S. Salhi, A. Slimane, H. Escid, S.A. Tedjini, Design and analysis of CMOS RCG transimpedance amplifier based on elliptic filter approach. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 12, 497–504 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cds.2017.0449
K. Joohwa, J.F. Buckwalter, Bandwidth enhancement with low group-delay variation for a 40-Gb/s transimpedance amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 57, 1964–1972 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2010.2041502
V. Kushwah, A. Quazi, N. Muchhal, Design of CMOS based transimpedance amplifier for bandwidth enhancement with large gain. Int. J. Comput. A 1, 138 (2016). https://doi.org/10.5120/ijca2016909067
E. Kamrani, F. Lesage, M. Sawan, Low-noise, high-gain transimpedanee amplifier integrated with SiAPD for low-intensity Ncar-infrared light detection. IEEE Sens. J. 14, 258–269 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2013.2282624
A. Chaddad, C. Tanougast, Low-noise transimpedance amplifier dedicated to biomedical devices: near infrared spectroscopy system, in International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT) (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/codit.2014.6996963
M.A.S. Bhuiyan, K.A. Tarumaraja, M.B.I. Reaz, F.H. Hashim, S.H.M. Ali, Low noise low power transimpedance amplifier in 0.18 µM CMOS technology. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 62, 16–20 (2014)
H. Jiaping, K. Yong-Bin, J. Ayers, A low power 100 M ohm CMOS front-end transimpedance amplifier for biosensing applications, in 53rd IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS) (2010), pp. 541–544. https://doi.org/10.1109/mwscas.2010.5548884
H.M. Lavasani, P. Wanling, B. Harrington, R. Abdolvand, F. Ayazi, A 76 dBohm 1.7 GHz 0.18 μm CMOS tunable TIA using broadband current pre-amplifier for high frequency lateral MEMS oscillators. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 46, 224–235 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/jssc.2010.2085890
E. Kamrani, F. Lesage, M. Sawan, Low-noise, high-gain TIA integrated with CMOS APD for low-intensity light detection in near-infrared spectroscopy. IEEE Sens. J. 15, 1 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2013.2282624
R. Yun, V.M. Joyner, A monolithically integrated phase-sensitive optical sensor for frequency-domain NIR spectroscopy. IEEE Sens. J. 10, 1234–1242 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2010.2044502
J. Salvia, P. Lajevardi, M. Hekmat, B. Murmann, A 56 MΩ CMOS TIA for MEMS applications, in IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (2009), pp. 199–202. https://doi.org/10.1109/cicc.2009.5280878
P. Sung Min, L. Jaeseo, Y. Hoi-Jun, 1-Gb/s 80-dBohm fully differential CMOS transimpedance amplifier in multichip on oxide technology for optical interconnects. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 39, 971–974 (2004)
J.H. Chuah, D. Holburn, Design of low-noise high-gain CMOS transimpedance amplifier for intelligent sensing of secondary electrons. IEEE Sens. J. 15, 5997–6004 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2015.2452934
A. Atef, M. Atef, M. Abbas, E. E. M. Khaled, High-sensitivity regulated inverter cascode transimpedance amplifier for near infrared spectroscopy, in Fourth International Japan–Egypt Conference on Electronics, Communications and Computers (JEC-ECC) (2016), pp. 99–102. https://doi.org/10.1109/jec-ecc.2016.7518977
J. Han, B. Choi, M. Seo, J. Yun, D. Lee, T. Kim et al., A 20-Gb/s transformer-based current-mode optical receiver in 0.13-CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 57, 348–352 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2010.2047309
W.-Z. Chen, Y.-L. Cheng, D.-S. Lin, A 1.8-V 10-Gb/s fully integrated CMOS optical receiver analog front-end. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 40, 1388–1396 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/esscir.2004.1356668
C.-H. Wu, C.-H. Lee, W.-S. Chen, S.-I. Liu, CMOS wideband amplifiers using multiple inductive-series peaking technique. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 40, 548–552 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/jssc.2004.840979
B. Razavi, Prospects of CMOS technology for high-speed optical communication circuits. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 37, 1135–1145 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/jssc.2002.801195
Y.-H. Oh, S.-G. Lee, An inductance enhancement technique and its application to a shunt-peaked 2.5 Gb/s transimpedance amplifier design. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 51, 624–628 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2004.836883
C. Talarico, G. Agrawal, J. W. Roveda, A 60 dBO 2.9 GHz 0.18 µm CMOS transimpedance amplifier for a fiber optic receiver application, in 57th IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS) (2014), pp. 181–184. https://doi.org/10.1109/prime.2016.7519513
Z. Lu, K.S. Yeo, J. Ma, M.A. Do, W.M. Lim, X. Chen, Broad-band design techniques for transimpedance amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 54, 590–600 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2006.887610
Acknowledgements
This research is financially supported by University Kebangsaan Malaysia and MOSTI. Project Code: AP-2017-008/1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badal, M.T.I., Reaz, M.B.I., Yeng, L.S. et al. Advancement of CMOS Transimpedance Amplifier for Optical Receiver. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 20, 73–84 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-018-00092-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-018-00092-5