Abstract
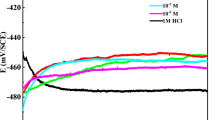
Electrochemical behavior of brass electrode (Cu–40Zn) in oxalic acid solution was studied in the absence and presence of organic inhibitor 2-Mercaptobenzimidazole (2-MBI) with different concentrations at ambient temperature using voltammetry, general corrosion (Rp) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The results showed that the electrochemical behavior of brass surface is similar to the copper one in the same conditions and revealed also the absence of the complexity phenomenon between the brass and the oxalate. Evolution of abandonment potential presents two different behaviors of electrode surface according to the concentration of organic inhibitor (2-MBI). Polarization curves showed that the addition of organic inhibitor (2-MBI) decreases the current density and shifts the anodic and cathodic branches towards more positive and more negative potentials. The plot of C/θ against the inhibitor concentration (C) shows that (2-MBI) strongly physisorbed on the brass electrode according to Langmuir isotherm. Measurements of polarization resistance and impedances show that the optimal concentration of the inhibitor is (0.5 mM) which gives a protection rate exceeds 89%.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- E:
-
Potential
- i:
-
Current density
- R:
-
Perfect gas constant
- T:
-
Temperature
- C:
-
Concentration
- v:
-
Scan rate
- 2 MBI:
-
2-Mercaptobenzimidazol
- Ecorr :
-
Corrosion potential
- icorr :
-
Corrosion current density
- Rp :
-
Polarization resistance
- Rtc :
-
Charge transfer resistance
- Rel :
-
Electrolyte resistance
- Cd :
-
Double layer capacitance
- Zreal :
-
Real part of impedance
- Zim :
-
Imaginary part of impedance
- f:
-
Frequency
- P %:
-
Protection rate
- K:
-
Equilibrium constant
- \(\Delta G_{ads}^{0}\) :
-
Adsorption standard enthalpy
- E%:
-
Inhibition efficiency
- \(\beta a\) :
-
Anodic coefficient transfer
- \(\beta c\) :
-
Cathodic coefficient transfer
References
Arnaud D, Barbery J, Biais R, Fragette B, Naudot P (2018) Propriétés du cuivre et de ses alliages, Technique de l’Ingénieur:M430
Barbery J (2018) Données numériques sur le cuivre et ses alliages corroyés, Technique de l’Ingénieur:M433
Diagrams (1992) ASM Handbook, vol 3: alloy phase. ASM International, Materials Park, OH
Heidersbach RH, Verink ED (1972) Corrosion 28:397–418
Hideo S, Hideaki E (1967) Corros Sci 7:513–523
Davis JR (2001) Copper and copper alloys. ASM International, Materials Park
Habib K, Riad W, Muhanna K, Al-Sumait H (2002) Desalination 142:5–9
Sohn S, Kang T (2002) J Alloy Compd 335:281–289
Karpagavalli R, Balasubramaniam R (2007) Corros Sci 49:963–979
Newman RC, Shahrabi T, Sieradzki K (1988) Corros Sci 28:873–879
El-Sherif RM, Ismail KM, Badawy WA (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:5139–5150
Ismail KM, Elsherif RM, Badawy WA (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:5151–5160
Bond JW (2008) J Forensic Sci 53:812–822
Wilhelm SM, Tanizawa Y, Liu C, Hackerman N (1982) Corros Sci 22:791–805
Kermani M, Scully JC (1979) Corros Sci 19:111–122
Cole AT, Newman RC, Sieradzki K (1988) Corros Sci 28:109–118
Zhang X, Liu X, Wallinder IO, Leygraf C (2016) Corros Sci 103:20–29
Hosseinpour S, Forslund M, Johnson CM, Pan J, Leygraf C (2016) Surf Sci 648:170–176
Fan H, Li S, Zhao Z, Wang H, Shi Z, Zhang L (2011) Corros Sci 53:4273–4281
Li Y, He J-B, Zhang M, He X-L (2013) Corros Sci 74:116–122
Gao G, Liang CH (2007) Corros Sci 49:3479–3493
Gerengi H, Darowicki K, Bereket G, Slepski P (2009) Corros Sci 51:2573–2579
Antonijevic MM, Milic SM, Serbula SM, Bogdanovic GD (2005) Electrochim Acta 50:3693–3701
Gao G, Liang C (2007) Electrochim Acta 52:4554–4555
Mihit M, El Issami S, Bouklah M, Bazzi L, Hammouti B, Ait Addi E, Salghi R, Kertit S (2006) Appl Surf Sci 252:2389–2395
Ramde T, Rossi S, Zanella C (2014) Appl Surf Sci 307:209–216
Abed Y, Kissi M, Hammouti B, Taleb M, Kertit S (2004) Prog Org Coat 50:144–147
Davoodi A, Honarbakhsh S, Farzi GA (2015) Prog Org Coat 88:106–115
Müller B, Schubert M (1999) Prog Org Coat 37:193–197
Ravichandran R, Nanjundan S, Rajendran N (2004) Appl Surf Sci 236:241–250
Kosec T, Milošev I, Pihlar B (2007) Appl Surf Sci 253:8863–8873
Mamaş S, Kıyak T, Kabasakaloğlu M, Koç A (2005) Mater Chem Phys 93:41–47
Kılınççeker G (2008) Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 329:112–118
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2001) Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications. Wiley, New York
Mihit M, El Issami S, Bouklah M, Bazzi L, Hammouti B, Ait Addi E, Salghi R, Kertit S (2006) Appl Surf Sci 252:2389–2395
Langmuir I (1947) J Am Chem Soc 39:1848
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (1980) Electrochemical methods. Wiley, New York, p 517
Abo El-khair BA, Khalifa OR, Abdelhamid IA (1987) Corros Prevent Control 34:1952
Otieno-Alego V, Hope GA, Notoya T, Schweinsberg DP (1996) Corros Sci 38:213
Dafali A, Hammouti B, Aouniti A, Mokhlisse R, Kertit S, El Kacemi K (2000) Ann Chim Sci Mater 25:437
Abdallah M, El-Naggar MM (2001) Mater Chem Phys 71:291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dilmi, O. Effect of 2-Mercaptobenzimidazole Concentration on Electrochemical Behavior of Brass (Cu–40Zn) Surface in Acid Medium. Chemistry Africa 1, 145–154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-018-0019-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-018-0019-3