Abstract
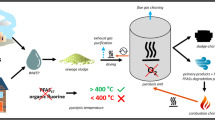
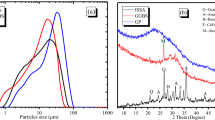
A technical idea of returning stainless steel pickling sludge to smelting process so as to recycle valuable metals of Fe, Cr, and Ni was proposed, expecting to realize sludge detoxification and resource utilization. Thermodynamics calculation showed that not only most valuable elements including Fe, Cr and Ni, but also the harmful element of sulfur in pickling sludge can be enriched into molten metal. As a result, a theoretical study on desulfurization thermodynamics of sludge pre-treatment was conducted, and results indicated that complete desulfurization temperature of pure pickling sludge was above 1400 °C. When 0.5–0.8% carbon was added as reducing agent, the complete desulfurization temperature was reduced to 1000 °C or below. Desulfurization roasting experiment indicated that desulfurization rate at 1400 °C under inert environment was 78.74% and maximum desulfurization rate at 1000 °C under reducing environment was 91.62%.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.M. Li, G. Xie, M. Hojamberdiev, Y.R. Cui, J.X. Zhao, J. Cent. South Univ. 21 (2014) 3241–3246.
X.M. Li, E. Mousa, J.X. Zhao, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 16 (2009) 480–484.
P. Ma, B. Lindblom, B. Björkman, Scand. J. Metall. 34 (2005) 31–40.
F.Y. Hui, Y. Sun, J. Zhang, in: Energy Technology 2015: Carbon Dioxide Management and Other Technologies, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2016, 219–226.
W. Han, Baosteel Tech. Res. (2009) No. 3, 27–30.
P. Hou, An Integrated Technology for Recovery of Heavy Metals from Stainless Steel Pickling Sludge, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 2012.
Y. Sun, J. Zhang, T. Li, Shanghai Metals 38 (2016) No. 2, 64–68.
N. Yoshikawa, K. Mashiko, E. Ishizuka, in: The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, The 4th International Congress on the Science and Technology of Steelmaking, ISIJ, Gifu, 2008, pp. 646–649.
L.K. Singhal, N. Rai, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 69 (2016) 1319–1325.
L. Shi, R.H. Chen, R.Y. Wang, Recycling Research 4 (2011) No. 6, 33–36.
L. Shi, R.H. Chen, R.Y. Wang, in CSM: 2011 CSM Annual Meeting Proceedings, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2011, pp. 1297–1302.
L. Gao, China Water Wastewater 25 (2009) No. 10, 83–86.
B. Lindblom, M. Ping, in: Metals and Materials Society, Global Symposium on Recycling Waste Treatment & Clean Technology, Minerals, TMS, Sansebastian, Spain, 1999, pp. 1493–1501.
J. Zhang, Y. Sun, X.L. Liu, Q.J. Li, Chin J. Process Eng. 05 (2014), 782–786.
J. Yang, S.G. Zhang, D.A. Pan, Rare Met. 35 (2016) 269–274.
S.G. Zhang, J. Yang, B. Liu, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 23 (2016) 220–224.
Y. Yang, Removal of Pb2+ from Wastewater Using Ferrite Prepared from Pickling Sludge, Nanjing University of Science & Technology, Nanjing, 2015.
Z.Q. Xue, Research on Cold Rolled Stainless Steel Dewatering Sludge Used as the Cement Raw Materials, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, 2009.
C.P. Wang, Technology Research on Potimal Utilization of Cold Rolled Starinless Steel By-product Sludge.Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 2011.
B.B. Fang, Environ. Sci. Tech. 29 (2016) No. 4, 35–37.
K. Liu, Research on High-performance Ceramsite Prepared by Cold Rolled Stainless Steel Dewatering Sludge, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, 2012.
H.H. Zhang, L.M. Pan, Y.Z. Pan, J. Zhejiang Univ. Tech. 41 (2013) 295–299.
Y.K. Chen, C.P. Wang, X. Li, Cement Engineering 2 (2011) 26–26.
H.Y. Fan, Mutual Transformation Mechanism of Calcium Sulfate and Calcium Sulfide at High Temperature in Different Reacting Atmosphere, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 2004.
S. Chen, S.W. Liu, J. Chem. Ind. Eng. 33 (2012) No. 5, 7–11.
R.W. Xu, Study on the Influence of Coke and Its Impurities on Pyrolysis Process of Calcium Sulfate, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, 2011.
C.P. Yan, Q.C. Yu, D.C. Liu, Chin. J. Vac. Sci. Tech. 34 (2014) 517–521.
X.M. Zhang, R.W. Xu, S.Y. Sun, Environ. Sci. Tech. 33 (2010) No. 12F, 144–148.
Z.Q. Yan, Z.A. Wang, X.F. Wang, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25 (2015) 3490–3497.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51574189, 51774224, 51604210) and Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2016JQ5042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Xm., Lv, M., Yin, Wd. et al. Desulfurization thermodynamics experiment of stainless steel pickling sludge. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 26, 519–528 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0113-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0113-4