Abstract
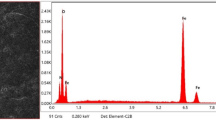
The lower head of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) will endure a great temperature gradient above the phase transition temperature, and the creep and fracture will be the primary failure mode for the RPV material in such a situation. The interrupted creep tests were performed on a typical RPV material, SA508 Gr3 steel, at 800 °C. The microstructure of different creep stages was examined by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The results showed that the microscopic damage is mainly induced by creep cavities and coarse second-phase particles. Furthermore, the volume fractions of creep cavities and coarse second-phase particles show a linear relationship with the extended creep time. The second-phase particles are determined to be MoC in the second creep stage and Mo2C in the third creep stage, according to the results of selected-area electron diffraction pattern. Combined with energy-dispersive spectrum analysis, the segregation of precipitates caused by the migration of atoms is finally unveiled, which leads to the coarsening of the particles.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Hashimoto, S. Ugawa, K. Nanko, K. Shichi, Sci. Rep. 2 (2012) 416.
S. M. Friedman, Bulletin Atom. Sci. 67 (2011) 55–65.
G. Steinhauser, A. Brandl, T. E. Johnson, Sci. Total Environ. 470 (2014) 800–817.
T. G. Theofanous, C. Liu, S. Additon, S. Angelin, O. Kymäläinen, T. Salmassi, Nucl. Eng. Des. 169 (1997) 1–48.
J. Zhu, J. Mao, L. Li, S. Bao, Z. Gao, J. Mech. Eng. 53 (2016) 45–52.
J. Zhu, J. Mao, Y. Li, S. Bao, Z. Gao, J. Chin. Soc. Power Eng. 37 (2017) 335–340.
J. Zhu, S. Bao, Y. Li, Z. Gao, in: ASME 2014 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Anaheim, 2014, pp. 1–7.
J. Mao, J. Zhu, S. Bao, L. Luo, Z. Gao, J. Press. Vess. Tech. 139 (2016) 107–116.
J. Mao, X. Li, S. Bao, L. Luo, Z. Gao, Nucl. Eng. Des. 316 (2017) 63–74.
C.C. Sainte, Report DMT/95-236, CEA Saclay, 1995.
D. S. Sui, F. Chen, P. P. Zhang, Z. S. Cui, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21 (2014) 1022–1029.
J. H. Kim, E. P. Yoon, J. Kor. Inst. Met. Mater. 36 (1998) 1329–1337.
S. Kim, S. Y. Kang, S. Lee, S. Oh, S. Kwon, O. Kim, J. Hong, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 31 (2000) 1107–1119.
Z. G. Xie, Y. M. He, J. G. Yang, Z. Gao, Trans. Tech. Publications 853 (2016) 153–157.
Y. Q. Deng, L. H. Zhu, Q. J. Wang, F. M. Zou, J. Iron Steel Res. 19 (2007) 46–50.
Q. Zhao, X. K. Peng, R. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. 22 (2010) 56–58.
Z. Xie, J. Yang, Y. He, Z. Gao, Nucl. Power Eng. 5 (2016) 33–39.
J. Wu, The heat treatment effect on microstructure and mechanical properties of A508-3 steel, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 2009.
Z. Sheng, H. Xiao, F. Peng, Nucl. Power Eng. 9 (1988) 49–53.
A. Argon, Strengthening mechanisms in crystal plasticity, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2007.
A. Mallick, Comp. Mater. Sci. 67 (2013) 27–34.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51575489) and National 13th Five-Year Key Technologies R&D Program (No. 2016YFC0801902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Zg., He, Ym., Yang, Jg. et al. Microscopic damage mechanism of SA508 Gr3 steel in ultra-high temperature creep. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 25, 453–459 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0055-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0055-x