Abstract
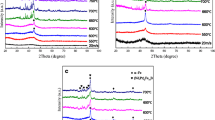
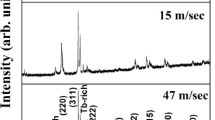
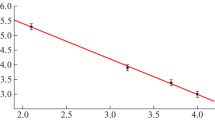
The Fe78Si8B14 and Fe78P8B14 ribbons with different wheel speeds were prepared by melt-spinning, and their responses to He+ ion irradiation were investigated. Previous studies had shown that the ion beam resistance capability of amorphous ribbons was better than their corresponding crystalline counterparts. However, no significant changes on the surface at low fluence are observed. At a relatively higher fluence, both the ribbons prepared at low and high wheel speeds behave the similar irradiation responses: peeling, flaking and multi-layer damages occur. The fully amorphous ribbons prepared at a high wheel speed can accommodate partial incident ions owing to the inherent disordered structure. As the irradiation fluence increases, they fail to accommodate the excess incident ions, which easily aggregate to result in the surface damage. While the partial amorphous ribbons prepared at a low wheel speed possess lots of unstable crystalline grain boundaries owing to the precipitation of Si- or P-rich phase, which may act as the source for the irradiation-induced defects annihilation. Results show that the size and the fraction of precipitate phases in amorphous matrix may play a dominated role in resisting the ion irradiation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.L. Greer, E. Ma, MRS Bull. 32 (2011) 611–619.
M.D. Demetriou, W.L. Johnson, K. Samwer, J. Alloy. Compd. 483 (2009) 644–650.
W.H. Wang, R.J. Wang, F.Y. Li, D.Q. Zhao, M.X. Pan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 74 (1999) 1803–1805.
S.V. Ketov, Y.H. Sun, S. Nachum, Z. Lu, A. Checchi, A.R. Beraldin, H.Y. Bai, W.H. Wang, D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin, M.A. Carpenter, A.L. Greer, Nature 524 (2015) 200–203.
J. Schroers, Adv. Mater. 22 (2010) 1566–1597.
K. Zhang, Z. Hu, F. Li, B. Wei, Appl. Surf. Sci. 390 (2016) 941–945.
N. Nita, R. Schaeublin, M. Victoria, J. Nucl. Mater. 329-333 (2004) 953–957.
Y. Chimi, A. Iwase, N. Ishikawa, J. Nucl. Mater. 297 (2001) 355–357.
M. Rose, A.G. Balogh, H. Hahn, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Section B 127 (1997) 119–122.
X.M. Bai, A.F. Voter, R.G. Hoagland, Science 327 (2010) 1631–1634.
G. Ackland, Science 327 (2010) 1587–1588.
G.A. Kachurin, M.O. Ruault, A.K. Gutakovsky, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Section B 147 (1998) 356–360.
M.C. Ridgway, G.D.M. Azevedo, R.G. Elliman, C.J. Glover, D.J. Llewellyn, R. Miller, W. Wesch, G.J. Foran, J. Hansen, A. Nylandsted-Larsen, Phys. Rev. B 71 (2004) 094107.
A. Meldrum, L.A. Boatner, R.C. Ewing, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 (2002) 025503.
Á. Révész, A. Concustell, L.K. Varga, S. Suriñach, M.D. Baró, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375-377 (2004) 776–780.
L. Yang, X.T. Zu, Z.G. Wang, F. Gao, X.Y. Wang, H.L. Heinisch, R.J. Kurtz, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Section B 265 (2007) 541–546.
K. Arakawa, R. Imamura, K. Ohota, K. Ono, J. Appl. Phys. 89 (2001) 4752–4757.
K. Morishita, R. Sugano, B.D. Wirth, T. Diaz de la Rubia, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Section B 202 (2003) 76–81.
K.Y. Yu, Y. Liu, C. Sun, H. Wang, L. Shao, E.G. Fu, X. Zhang, J. Nucl. Mater. 425 (2012) 140–146.
K. Nagashio, K. Kuribayashi, Acta Mater. 54 (2006) 2353–2360.
W. Hou, X. Mei, Z. Wang, Y. Wang, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Section B 342 (2015) 221–227.
T.H. Woo, H.S. Cho, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Section A 652 (2011) 69–72.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51401028, 51271193, 11402277) and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDB22040303). The authors also thank to the support of Opening Fund of State Key Lab of Nuclear Physics and Technology at Peking University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Yh., Zhang, K., Zhao, Zq. et al. Helium ions irradiation-induced surface damage in Fe-based melt-spun ribbons. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 25, 268–274 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0029-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0029-z