Abstract
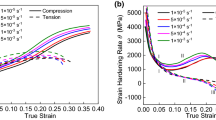
Strongly textured commercially pure titanium alloy TA2 plates with different initial textures have been rolled at cryogenic and ambient temperatures to 4% reduction and then post-annealed at 50 °C for 12 h. Microstructures of the samples were investigated using electron backscatter diffraction. The mechanical property of the sheets was tested via quasi-static uniaxial tensile tests along the rolling direction at room temperature. The effects of initial texture and rolling temperature on twin activity and mechanical property have been investigated. Twinning is very active in TA2 titanium during rolling at either room or cryogenic temperature. \(\{ 11\overline{2} 2\}\) contraction twins can be observed in all the sheets and are the dominant twin mode for the sheets with an initial texture having c-axes parallel to the normal direction (ND). Extension twins have rarely been seen in sheets having an initial texture with c-axes parallel to ND, but play quite an important role in the sheets having an initial texture with c-axes perpendicular to ND. The initial texture of the sheet is considered to determine the twin mode while the cryogenic rolling temperature is found to increase the numbers of twins. Post-annealing does not change obviously the rolled microstructure. After annealing, the strength decreases and elongation to fracture slightly increases. The cryorolled sample has the better strength with little loss in elongation, and this mechanical enhancement is attributed to massive twinning.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.B. Chun, S.H. Yu, S.L. Semiatin, S.K. Hwang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 398 (2005) 209–219.
D.K. Yang, P. Cizek, P.D. Hodgson, C.E. Wen, Acta Mater. 58 (2010) 4536–4548.
S.G. Song, G.T. III Gray, Acta Metall. Mater. 43 (1995) 2339–2350.
S.V. Zherebtsov, G.S. Dyakonov, A.A. Salem, V.I. Sokolenko, G.A. Salishchev, S.L. Semiatin, Acta Mater. 61 (2013) 1167–1178.
F. Xu, X. Zhang, H. Ni, Y. Cheng, Y. Zhu, Q. Liu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 564 (2013) 22–33.
M.H. Yoo, J.K. Lee, Phil. Mag. A 63 (1991) 987–1000.
Q. Liu, Acta Metall. Sin. 46 (2010) 1458–1472.
D. Guo, Z. Zhang, G. Zhang, M. Li, Y. Shi, T. Ma, X. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 591 (2014) 167–172.
D.K. Yang, P.D. Hodgson, C.E. Wen, Acta Mater. 63 (2010) 941–944.
D.K. Yang, P. Cizek, D. Fabijanic, B.S. Li, P.D. Hodgson, Acta Mater. 61 (2013) 2840–2852.
A. Salem, S.R. Kalidindi, R.D. Doherty, Acta Mater. 514 (2003) 4225–4237.
Q.Y. Sun, H.C. Gu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 316 (2001) 80–86.
H. Conrad, Cryogenic 24 (1984) 293–304.
S. Sandlobes, S. Zaefferer, I. Schestakow, S. Yi, R. Gonzalez-Martinez, Acta Mater. 59 (2011) 429–439.
J.W. Qiao, A.C. Sun, E.W. Huang, Y. Zhang, P.K. Liaw, C.P. Chuang, Acta Mater. 59 (2011) 4126–4137.
H.P. Ng, P. Nandwana, A. Devaraj, M. Semblanet, S. Nag, P.N.H. Nakashima, S. Maher, C.J. Bettles, M.A. Gibson, H.L. Fraser, B.C. Muddle, R. Banerjee, Acta Mater. 84 (2015) 457–471.
F. Xu, X. Zhang, H. Ni, Q. Liu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 541 (2012) 190–195.
X.G. Deng, S.X. Hui, W.J. Ye, X.Y. Song, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 575 (2013) 15–20.
S.G. Song, G.T. III Gray, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 26 (1995) 2665–2675.
H. Qin, J.J. Jonas, H. Yu, N. Brodusch, R. Gauvin, X. Zhang, Acta Mater. 71 (2014) 293–305.
H. Qin, J.J. Jonas, Acta Mater. 75 (2014) 198–211.
J.R. Luo, X. Song, J.S. Zhang, L.Z. Zhuang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 23 (2016) 74–77.
J.W. Qiao, T. Zhang, F.Q. Yang, P.K. Liaw, S. Pauly, B.S. Xu, Sci. Rep. 3 (2013) 1–6.
S. Mu, J.J. Jonas, G. Gottstein, Acta Mater. 60 (2012) 2043–2053.
G. Lutjering, J.C. Williams, Titanium, 2nd Edition, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2011.
A. Akhtar, Metall. Trans. A 6 (1975) 1105–1113.
M.R. Barnett, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 464 (2007) 1–7.
M.R. Barnett, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 464 (2007) 8–12.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51401019, 51401190, 11405150). The authors are grateful to Dr. Adrien Chapuis in Chongqing University for editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Jr., Song, X. & Wang, My. Effects of different types of twinning on microstructure and mechanical properties of a strongly textured TA2 commercially pure titanium alloy subjected to rolling at ambient and cryogenic temperatures. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 25, 275–281 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0026-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0026-2