Abstract
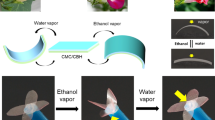
Being inspired by the “seismonastic reaction” of Mimosa pudica, an asymmetric swelling system was constructed to induce the controllable directional deformation of filter paper. In this work, multifunctional biomimetic Janus paper was facilely fabricated via depositing poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) on one side of Qualitative Filter Paper (QFP), the permeation of polymer solutions within filter paper was well controlled during fabrication. The wetting and swelling behavior of the prepared Janus paper were detected. The Janus paper showed controllable swelling-induced deformations in water. Both the degree and orientation of the deformation were fully investigated. On the one hand, the degree of deformation depends on the gradient wettability and hygroscopicity of the Janus paper, on the other hand, the orientation of deformation is related to the storage and release of stress. Additionally, the steady deformation during swelling endows the Janus paper with novel shape memory property both under idling and loading conditions. The Janus paper was also applied to achieve reversible energy conversion from the swelling potential energy to mechanical potential energy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang H C, Hou J, Chen V, Xu Z K. Janus membranes: Exploring duality for advanced separation. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55, 13398–13407.
Neinhuis C, Barthlott W. Characterization and distribution of water-repellent, self-cleaning plant surfaces. Annals of Botany, 1997, 79, 667–677.
Cheng Q F, Li M Z, Zheng Y M, Su B, Wang S T, Jiang L. Janus interface materials: Superhydrophobic air/solid interface and superoleophobic water/solid interface inspired by a lotus leaf. Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 5948–5951.
Zhao Y Y, Yu C M, Lan H, Cao M Y, Jiang L. Improved interfacial floatability of superhydrophobic/superhydrophilic Janus sheet inspired by lotus leaf. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27, 1701466.
Yamaoka K, Saharinen P, Pesu M, Holt V, Silvennoinen O, O’Shea J. The Janus kinases (Jaks). Genome Biology, 2004, 5, 253.
Royer Y, Staerk J, Costuleanu M, Courtoy P J, Constantinescu S N. Janus kinases affect thrombopoietin receptor cell surface localization and stability. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2015, 280, 27251–27261.
Walther A, Müller A. Janus particles: Synthesis, self-assembly, physical properties, and applications. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113, 5194.5261.
Fujii S, Yokoyama Y, Nakayama S, Ito M, Yusa S, Nakamura Y. Gas bubbles stabilized by Janus particles with varying hydrophilic-hydrophobic surface characteristics. Langmuir, 2018, 34, 933–942.
Wong W, Li M, Nisbet D R, Craig V, Wang Z, Tricoli A. Mimosa origami: A nanostructure-enabled directional self-organization regime of materials. Science Advances, 2016, 2, e1600417.
Sasaki K, Tenjimbayashi M, Manabe K, Shiratori S. Asymmetric superhydrophobic/superhydrophilic cotton fabrics designed by spraying polymer and nanoparticles. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8, 651.659.
Yan X, Li J, Yi L. Fabrication of pH-responsive hydrophilic/hydrophobic Janus cotton fabric via plasma-induced graft polymerization. Materials Letters, 2017, 208, 46.49.
Si Y F, Chen L W, Yang F C, Guo F, Guo Z G. Stable Janus superhydrophilic/hydrophobic nickel foam for directional water transport. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 509, 346–352.
Wang Z, Liu G, Huang S. In situ generated Janus fabrics for the rapid and efficient separation of oil from oil-in-water emulsions. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 128, 14830–14833.
Wang Z, Wang Y, Liu G. Rapid and efficient separation of oil from oil-in-water emulsions using a Janus cotton fabric. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55, 1291–1294.
Zhao Y, Wang H, Zhou H, Lin T. Directional fluid transport in thin porous materials and its functional applications. Small, 2017, 13, 160107.
Tian X L, Jin H, Sainio J, Ras R, Ikkala O. Droplet and fluid gating by biomimetic Janus membranes. Advanced Func tional Materials, 2014, 24, 6023–6028.
Ibañez D, Valles E, Gomez E, Colina A, Heras A. Janus electrochemistry: Asymmetric functionalization in one step. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9, 35404.35410.
Wu M, Yang H, Wang J, Wu G, Xu Z. Janus membranes with opposing surface wettability enabling oil-to-water and water-to-oil emulsification. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9, 5062.5066.
Ahmed E M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. Journal of Advanced Research, 2015, 6, 105.121.
Ullah F, Othman M B H, Javed F, Ahmad Z, Akil H M. Classification, processing and application of hydrogels: A review. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2015, 57, 414.433.
Singamaneni S, McConney M, Tsukruk V. Swelling-induced folding in confined nanoscale responsive polymer gels. ACS Nano, 2010, 4, 2327.2337.
Lim H, Lee J, Walish J, Thomas E. Dynamic swelling of tunable full-color block copolymer photonic gels via counterion exchange. ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 8933.8939.
Currie J A. Gas diffusion through soil crumbs: The effects of wetting and swelling. Journal of Soil Science, 1983, 34, 217.232.
Grant C D, Dexter A R. Air entrapment and differential swelling as factors in the mellowing of moulded soil during rapid wetting. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 1990, 28, 361.369.
Wang Y, Tong L, Steinhart M. Swelling-induced morphology reconstruction in block copolymer nanorods: Kinetics and impact of surface tension during solvent evaporation. ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 1928.1938.
Wei C, Plucinski A, Nuasaen S, Tripathi A, Tangboriboonrat P, Tauer K. Swelling-induced deformation of spherical latex particles. Macromolecules, 2017, 50, 349.363.
Volkov A G, Foster J C, Markin V S. Signal transduction in Mimosa pudica: Biologically closed electrical circuits. Plant Cell & Environment, 2010, 33, 816–827.
Allen R. Mechanism of the seismonastic reaction in Mimosa pudica. Plant Physiology, 1969, 44, 1101–1107.
Wang Z J, Zhu C N, Hong W, Wu Z L, Zheng Q. Cooperative deformations of periodically patterned hydrogels. Science Advances, 2017, 3, e1700348.
Xue B, Kozlovskaya V, Kharlampieva E. Shaped stimuli-responsive hydrogel particles: Syntheses, properties and biological responses. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2017, 5, 9–35.
Wang J, Wang J, Chen Z, Fang S, Zhu Y, Baughman R H, Jiang L. Tunable, fast, robust hydrogel actuators based on evaporation-programmed heterogeneous structures. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29, 9793.9801.
Bligh E, Dyer W. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian Journal Biochemistry Physiology, 1959, 37, 911.917.
Du C, Wang J, Chen Z, Chen D. Durable superhydrophobic and superoleophilic filter paper for oil–water separation prepared by a colloidal deposition method. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 313, 304–310.
Chen L W, Si Y F, Zhu H, Jiang T, Guo Z G. A study on the fabrication of porous PVDF membranes by in-situ elimination and their applications in separating oil/water mixtures and nano-emulsions. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016, 520, 760–768.
Ju J, Wang T, Wang Q. A facile approach in fabricating superhydrophobic and superoleophilic poly (vinylidene fluoride) membranes for efficient water–oil separation. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2015, 132, 42077.
Wenzel R N. Resistance of solid surface to wetting by water. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 1936, 28, 988–994.
Budtova T, Navard P. Swelling kinetics of a polyelectrolyte gel in water and salt solutions. Coexistence of swollen and collapsed phases. Macromolecules, 1998, 31, 8845–8850.
Velankar S S, Lai V. Swelling-induced delamination causes folding of surface-tethered polymer gels. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2012, 4, 24.29.
Tanaka T, Fillmore D J. Kinetics of swelling of gels. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1979, 70, 1214.
Zaleski R, Krasucka P, Skrzypiec K, Goworek J. Macro-and nanoscopic studies of porous polymer swelling. Macromolecules, 2017, 50, 5080.5089.
Tekes A T, Sınag A, Mısırlıoglu Z, Canel M. Determination of swelling properties of Soma-Isıklar Lignite (Turkey). Energy and Fuels, 2002, 16, 1309–1313.
Park B, Lee D. Equilibrium orientation of nonsphericalbJanus particles at fluid-fluid interfaces. ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 782–790.
Liu X, Zheng H, Zhong L, Huang S, Karki K, Zhang L, Liu Y, Kushima A, Liang W, Wang J, Cho J, Epstein E, Dayeh S, Picraux S, Zhu T, Li J, Sullivan J, Cumings J, Wang C, Mao S, Ye Z, Zhang S, Huang J. Anisotropic swelling and fracture of silicon nanowires during lithiation. Nano Letter, 2012, 11, 3312–3318.
Guney Y, Sari D, Cetin M, Tuncan M. Impact of cyclic wetting-drying on swelling behavior of lime-stabilized soil. Building and Environment, 2007, 42, 681–688.
Oppermann W. Swelling behavior and elastic properties of ionic hydrogels. ACS Symposium Series, 1992, 480, 159–170.
Mott P H, Roland C M. Elasticity of natural rubber networks. Macromolecules, 1996, 29, 6941–6945.
Fang Z Q, Kuang Y D, Zhou P P, Ming S Y, Zhu P H, Liu Y, Ning H L, Chen G. Programmable shape recovery process of water-responsive shape-memory poly(vinyl alcohol) by wettability contrast strategy. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9, 5495.5502.
Brostowitz N, Weiss R, Cavicchi K A. Facile fabrication of a shape memory polymer by swelling cross-linked natural rubber with stearic acid. ACS Macro Letters, 2014, 3, 374.377.
Espinha A, Guidetti G, Serrano M, Frka-Petesic B, Dumanli A, Hamad W, Blanco Á, López C, Vignolini S. Shape memory cellulose-based photonic reflectors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8, 31935.31940.
Flory P J. Statistical mechanics of swelling of network structures. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1950, 18, 108.
Haldrup S, Catalano J, Hinge M, Jensen G, Pedersen J, Bentien A. Tailoring membrane nanostructure and charge density for high electrokinetic energy conversion efficiency. ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 2415.2423.
Erbas A, Cruz M. Energy conversion in polyelectrolyte hydrogels. ACS Macro Letters, 2015, 4, 857.861.
Pashkin E Y, Pankov A M, Kulnitskiy B A, Perezhogin I A, Karaeva A R, Mordkovich V Z, Popov M Y, Sorokin P B, Blank V O. The unexpected stability of multiwall nanotubes under high pressure and shear deformation. Applied Physical Letters, 2016, 109, 081904.
Ha H O, Kim D S, Color change of an iodinated poly(vinyl alcohol) film by physical deformation. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2016, 133, 43036.
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51522510, 51675513 and 51735013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, P., Guo, Z. Biomimetic Janus Paper with Controllable Swelling for Shape Memory and Energy Conversion. J Bionic Eng 16, 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42235-019-0001-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42235-019-0001-z