Abstract
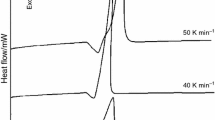
In this work, the effect of heating rate and mechanical activation on the reaction of kaolin and aluminium powder was investigated. A batch comprised of 89.5 wt% kaolin and 10.5 wt% aluminium powders was mixed and milled in a planetary ball-mill for 1, 5, 10, 20 and 40 h. The mixture powders were heat treated with a heating rate of 5, 10, 15, 20, 30 and 40 °C/min, respectively. After milling for 20 and 40 h, the results showed the formation of free silicon, quartz and nacrite (Al2Si2(OH)4) at room temperature. The kaolinite dehydroxylation, aluminium oxidation and the θ- to α-Al2O3 transformations are highly affected by heating rate and mechanical activation. As compared with the smallest heating rate, the mixtures heated with faster heating rate show the disappearance of the peak corresponding to the oxidation of aluminium and the appearance of a second peak corresponding to the formation of α-Al2O3. The intensity of the last peak increases with increasing of the heating rate and milled at lower milling time. The effects of heating rate in the reaction of kaolin and aluminium powder are attributed to the amorphization of kaolinite, the diffusion of Al3+ to form an amorphous alumina layer on the particle surface and the generation of microcracks at the particle surface of aluminium powder.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, J.: Fabrication and properties of porous mullite ceramics from calcined carbonaceous kaolin and α-Al2O3. Ceram. Int. 36(2), 673–678 (2010)
Schneider, H., Schreuer, J., Hildmann, B.: Structure and properties of mullite—a review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28(2), 329–344 (2008)
Singh, A.K., Sarkar, R.: Nano mullite bonded refractory castable composition for high temperature applications. Ceram. Int. 42(11), 12937–11294 (2016)
Romero, M., Pérez, J.M.: Relation between the microstructure and technological properties of porcelain stoneware. A review. Mater. Constr. 65(320), e065 (2015)
Wang, Z., Feng, P., Wang, X., Geng, P., Akhtar, F., Zhang, H.: Fabrication and properties of freeze-cast mullite foams derived from coal-series kaolin. Ceram. Int. 42(10), 12414–12421 (2016)
Guo, H., Ye, F., Li, W., Song, X., Xie, G.: Preparation and characterization of foamed microporous mullite ceramics based on kyanite. Ceram. Int. 41(10), 14645–14651 (2015)
Sousa, L.L., Souza, A.D.V., Fernandes, L., Arantes, V.L., Salomao, R.: Development of densification-resistant castable porous structures from in situ mullite. Ceram. Int. 41(8), 9443–9454 (2015)
Ganesh, I., Ferreira, J.M.F.: Influence of raw material type and of the overall chemical composition on phase formation and sintered microstructure of mullite aggregates. Ceram. Int. 35(5), 2007–2015 (2009)
Viswabaskaran, V., Gnanam, F.D., Balasubramanian, M.: Mullitization behaviour of calcined clay–alumina mixtures. Ceram. Int. 29(5), 561–571 (2003)
Liu, Y.F., Liu, X.Q., Tao, S.W., Meng, G.Y., Sorensen, O.T.: Kinetics of the reactive sintering of kaolinite-aluminum hydroxide extrudate. Ceram. Int. 28(5), 479–486 (2002)
Esharghawi, A., Penot, C., Nardou, F.: Contribution to porous mullite synthesis from clays by adding Al and Mg powders. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29(1), 31–38 (2009)
Chen, Y.F., Wang, M.C., Hon, M.H.: Transformation kinetics for mullite in kaolin-Al2O3 ceramics. J. Mater. Res. 18(6), 1355–1362 (2003)
Sahnoune, F., Chegaar, M., Saheb, N., Goeuriot, P., Valdivieso, F.: Algerian kaolinite used for mullite formation. Appl. Clay Sci. 38(3–4), 304–310 (2008)
Chen, Y.F., Chang, Y.H., Wang, M.C., Hon, M.H.: Effects of Al2O3 addition on the phases, flow characteristics and morphology of the porous kaolin ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 373, 221–228 (2004)
Tezuka, N., Low, I.M., Davies, I.J., Prior, M., Studer, A.: In situ neutron diffraction investigation on the phase transformation sequence of kaolinite and halloysite to mullite. Physica B. 385-386(1), 555–557 (2006)
Vijayan, C., Soundararajan, N., Chandramohan, R., Ramaswamy, S., Gnanadurai, P.: The effect of heating rate on the phase transition and crystallization kinetics of Ag2Se0.2Te0.8 alloy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 119(1), 91–97 (2015)
Soifer, L., Korin, E.: Effect of heating rate on crystallization kinetics of amorphous Al91La5Ni4 alloys by DSC. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 56(1), 437–446 (1999)
Katoh, K., Ito, S., Kawaguchi, S., Higashi, E., Nakano, K., Ogata, Y., Wada, Y.: Effect of heating rate on the thermal behavior of nitrocellulose. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 100(1), 303–308 (2010)
Sahraoui, T., Belhouchet, H., Heraiz, M., Brihi, N., Guermat, A.: The effects of mechanical activation on the sintering of mullite produced from kaolin and aluminum powder. Ceram. Int. 42(10), 12185–12193 (2016)
Welham, N.J., Berbenni, V., Chapman, P.G.: Increased chemisorption onto activated carbon after ball-milling. Carbon. 40(13), 2307–2315 (2002)
Zyryanov, V.V.: Ultrafast mechanochemical synthesis of mixed oxides. Inorg. Mater. 41(4), 378–392 (2005)
Tamborenea, S., Mazzoni, A.D., Aglietti, E.F.: Mechanochemical activation of minerals on the cordierite synthesis. Thermochim. Acta. 411(2), 219–224 (2004)
Neto, J.B.R., Moreno, R.: Effect of mechanical activation on the rheology and casting performance of kaolin/talc/alumina suspensions for manufacturing dense cordierite bodies. Appl. Clay Sci. 38(3–4), 209–218 (2008)
Boldyrev, V.V.: Mechanochemistry and mechanical activation of solids. Solid State Ionics. 63-65, 537–543 (1993)
Chen, L., Ye, G., Xu, D., Zhu, L., Lu, Z., Dong, L., Liu, Y.: Chemical bond change of gibbsite and fumed silica mixture during mechanical activation. Mater. Lett. 85(15), 91–94 (2012)
Behmanesh, N., Heshmati-Manesh, S., Ataie, A.: Role of mechanical activation of precursors in solid state processing of nano-structured mullite phase. J. Alloys Compd. 450(1–2), 421–425 (2008)
Kong, L.B., Zhang, T.S., Ma, J., Boey, F.: Anisotropic grain growth of mullite in high-energy ball milled powders doped with transition metal oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23(13), 2247–2256 (2003)
Aguilar-Santillan, J., Balmori-Ramirez, H., Bradt, R.C.: Dense mullite from attrition milled kyanite and α-alumina. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 8(1), 1–11 (2007)
Ebadzadeh, T.: Effect of mechanical activation and microwave heating on synthesis and sintering of nano-structured mullite. J. Alloys Compd. 489(1), 125–129 (2010)
Razavi-Tousi, S.S., Nematollahi, G.A., Ebadzadeh, T., Szpunar, J.A.: Modifying aluminum-water reaction to generate nano-sized aluminium hydroxide particles beside hydrogen. Powder Technol. 241, 166–173 (2013)
Belhouchet, H., Hamidouche, M., Bouaouadja, N., Garnier, V., Fantozzi, G.: Kinetics of mullite formation in zircon and boehmite mixture. Ann. Chimie Sci. Materiaux. 35(1), 17–25 (2010)
Elmas, E., Yildiz, K., Toplan, N., Toplan, H.O.: The non-isothermal kinetics of mullite formation in mechanically activated kaolinite-alumina ceramic system. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 108(3), 1201–1206 (2012)
Shahverdi-Shahraki, K., Ghosh, T., Mahajan, K., Ajji, A., Carreau, P.J.: Effect of dry grinding on chemically modified kaolin. Appl. Clay Sci. 105-106, 100–106 (2015)
Dellisanti, F., Valdrè, G.: The role of microstrain on the thermostructural behaviour of industrial kaolin deformed by ball milling at low mechanical load. Int. J. Miner. Process. 102-103, 69–77 (2012)
Chen, C.Y., Lan, G.S., Tuan, W.H.: Preparation of mullite by the reaction sintering of kaolinite and alumina. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 20(14–15), 2519–2525 (2000)
Hasani, S., Panjepour, M., Shamania, M.: The oxidation mechanism of pure aluminum powder particles. Oxid. Met. 78(3–4), 179–195 (2012)
Issaoui, M., Limousy, L., Lebeau, B., Bouaziz, J., Fourati, M.: Design and characterization of flat membrane supports elaborated from kaolin and aluminum powders. C. R. Chimie. 19(4), 496–504 (2016)
Suvaci, E., Simkovich, G., Messing, G.: The reaction-bonded aluminium oxide process: I, the effect of attrition milling on the solid-state oxidation of aluminium powder. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83(2), 299–305 (2000)
Bafrooei, H.B., Ebadzadeh, T., Majidian, H.: Microwave synthesis and sintering of forsterite nanopowder produced by high energy ball milling. Ceram. Int. 40(2), 2869–2876 (2014)
Castelein, O., Soulestin, B., Bonnet, J.P., Blanchart, P.: The influence of heating rate on the thermal behaviour and mullite formation from a kaolin raw material. Ceram. Int. 27(5), 517–522 (2001)
Chen, L., Song, W.L., Lv, J., Wang, L., Xie, C.S.: Effect of heating rates on TG-DTA results of aluminum nanopowders prepared by laser heating evaporation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 96(1), 141–145 (2009)
Levin, I., Brandon, D.: Metastable alumina polymorphs: crystal structures and transition sequences. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81(8), 1995–2012 (1998)
Dynys, F.W., Halloran, J.W.: Alpha alumina formation in alum-derived gamma alumina. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 65(9), 442–448 (1982)
Bossert, J., Fidancevska, E.: Effect of mechanical activation on the sintering of transition nanoscaled alumina. Sci. Sinter. 39(2), 117–125 (2007)
Chen, G., Qi, H., Xing, W., Xu, N.: Direct preparation of macroporous mullite supports for membranes by in situ reaction sintering. J. Membr. Sci. 318(1–2), 38–44 (2008)
Sainz, M.A., Serrano, F.J., Amigo, J.M., Bastida, J., Caballero, A.: XRD microstructural analysis of mullites obtained from kaolinite-alumina mixtures. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 20(4), 403–412 (2000)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Mrs. P. Díaz and Mrs. E. Sánchez for their technical assistance. K. Belhouchet wants to thank University Ferhat Abbas of Sétif 1 for providing financial support to carry out a scientific stay at the IETcc-CSIC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belhouchet, H., Sahraoui, T., Belhouchet, K. et al. Influence of heating rate and mechanical activation on the reaction between kaolin and aluminium powder. J Aust Ceram Soc 55, 135–144 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-018-0219-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-018-0219-y