Abstract
Introduction
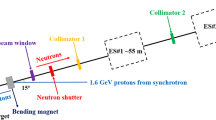
The neutron capture cross sections are very important in the field of nuclear device design and basic physics research. Hydrogen-free liquid scintillator such as C6D6 detectors are widely used in the neutron capture cross-sectional measurements for the low neutron sensitivity and fast time response. The Back-n white neutron source at China Spallation Neutron Source is the first spallation white neutron source in China, and it is suitable for neutron capture cross-sectional measurement.
Materials and methods
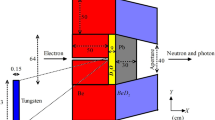
A C6D6 detector system was built in the Back-n experimental station. The pulse height weighting technique was used to determine the system’s detection efficiency. The response to gamma rays of the C6D6 detector was measured, and the energy resolution function was determined. Monte Carlo simulation with Geant4 code was carried out to get the weighting function of this C6D6 detector system. Additionally, the systematic uncertainty of the weighting function was also determined.
Conclusion
According to the experimental and simulation results, this C6D6 detector system can be used to measure neutron capture cross section.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.D. Bowman, Accelerator-driven systems for nuclear waste transmutation. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 48, 505 (1998)
F. Kappeler, H. Beer, K. Wisshak, S-process nucleosynthesis: nuclear physics and the classical model. Rep. Prog. Phys. 52, 945 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/52/8/002
L.C. Mihailescu, L. Oláh, C. Borcea et al., A new HPGe setup at Gelina for measurement of gamma-ray production cross-sections from inelastic neutron scattering. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 531(3), 375–391 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2004.05.119
C. Guerrero, U. Abbondanno, G. Aerts et al., The n_TOF total absorption calorimeter for neutron capture measurements at CERN. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 608, 424–433 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2009.07.025
B. Baramsai, G.E. Mitchell et al., Neutron resonance parameters in 155Gd measured with the DANCE γ-ray calorimeter array. Phys. Rev. C 85, 024622-13 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.85.024622
M.C. Moxon, E.R. Rae, A gamma-ray detector for neutron capture cross section measurements. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 24, 445 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554x(63)90364-1
F. Corvi, C. Bastian, K. Wisshak, Neutron capture in the 1.15 keV resonance of 56Fe using Moxon-Rae detectors. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 93(4), 348–358 (1986)
J.N. Wilson, B. Haas, S. Boyer et al., Measurements of (n, γ) neutron capture cross-section with liquid scintillator detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 511(2003), 388–399 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-9002(03)01944-2
J.Y. Tang, S.N. Fu, H.T. Jing et al., Proposal for muon and white neutron sources at CSNS. Chin. Phys. C 34, 121–125 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1137/34/1/022
H. Chen, X.L. Wang, China’s first pulsed neutron source. Nat. Mater. 15, 689 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4655
H.T. Jing, J.Y. Tang, H.Q. Tang, H.H. Xia et al., Studies of back-streaming white neutrons at CSNS. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 621, 91–96 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2010.06.097
Q. An, H.Y. Bai, J. Bao et al., Back-n white neutron facility for nuclear data measurement at CSNS. J. Instrum. 12, 7–22 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-0221/12/07/P07022
J. Ren, R. Xichao, H. Tang et al., Simulation of the background of experimental end-stations and the collimator system of the CSNS back-streaming white neutron source. Nucl. Tech. 37(10), 210–215 (2014). https://doi.org/10.11889/j.0253-3219.2014.hjs.37.100521
EJ-315 deuterated liquid scintillator data sheet, www.eljentechnology.com. Accessed 5 Nov 2017
B series data sheet, www.electrontubes.com. Accessed 5 Nov 2017
Q. Wang, P. Cao, X. Qi et al., General-purpose readout electronics for white neutron source at China Spallation Neutron Source. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89, 013511 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5006346
G. Dietze, H. Klein, Gamma-calibration of NE 213 scintillation counters. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 193(3), 549–556 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(82)90249-X
Geant4 Collaboration, GEANT4 User’s Guide for Application Developers (version:10.2), http://geant4.cern.ch. Accessed 4 Dec 2015
C.D. Pardo, New radiative neutron capture measurement of 207Pb and 209Bi. Ph.D. thesis, CSIC-University of Valencia, 2005
R. Plag, M. Heil, F. Kappeler et al., An optimized C6D6 detector for studies of resonance-dominated (n, γ) cross-sections. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 496, 425–436 (2003)
P. Schillebeeckx, B. Becker, Y. Danon et al., Determination of resonance parameters and their covariances from neutron induced reaction cross section data. Nucl. Data Sheets 113(12), 3054–3100 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nds.2012.11.005
U. Abbondanno, G. Aerts, H. Alvarez et al., New experimental validation of the pulse height weighting technique for capture cross-section measurements. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 521, 454–467 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2003.09.066
R.L. Macklin, J.H. Gibbons, Capture-cross-section studies for 30–220-keV neutrons using a new technique. Phys. Rev. 159, 1007 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrev.159.1007
J.L. Tain, F. Gunsing, D. Cano et al., Accuracy of the pulse height weighting technique for capture cross section measurements. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 39, 689–692 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1080/00223131.2002.10875193
F. James, MINUIT turorial, (1972), http://seal.web.cern.ch. Accessed 14 Mar 2017
F. Corvi, A. Prevignano, H. Liskien et al., An experimental method for determining the total efficiency and the response function of a gamma-ray detector in the range 0.5–10 MeV. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 265(3), 475–484 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-9002(98)90016-x
Geant4 Collaboration, GEANT4 Physics Reference Manual (version: 10.2), http://geant4.cern.ch. Accessed 4 Dec 2015
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11790321 and 11805282) and the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFA0401601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, J., Ruan, X., Bao, J. et al. The C6D6 detector system on the Back-n beam line of CSNS. Radiat Detect Technol Methods 3, 52 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-019-0129-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-019-0129-8