Abstract
The aim
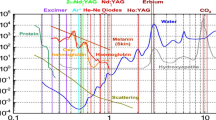
The present study aims to conduct a descriptive analysis by reviewing in vivo and in vitro studies concerned with the antibacterial effect of diode lasers (810 nm, 940 nm, and 980 nm) and their effects on implant surfaces at different parameters for peri-implantitis treatment.
Materials and methods
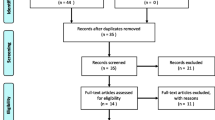
The PubMed and Google Scholar had been used to search for articles focused on the antibacterial effect of diode lasers (810 nm, 940 nm, and 980 nm) in the treatment of peri-implantitis and their effects on implant surfaces. This literature search was limited to 10 years (January 2007–March 2017).
Results
Diode laser is an effective adjunctive tool in treatment of peri-implantitis in combination with a conventional therapy without any negative effect on the surrounding soft and hard tissues, and on the implant surfaces where the favorable settings regarding to vivo and vitro studies are 810 nm in non-contact continuous wave mode at 1 W for 20 s, five times with 30-s pause after each 20-s application time, and 600-μm fiber tip or 810 nm in non-contact pulse wave mode at 1 W, 50 Hz and a pulse duration of 100 ms/pulse, 30-s application time (2 times for each side).
Conclusion
Eight hundred ten-nanometer diode laser wavelength with a low average power and appropriate irradiation time treat the peri-implantitis significantly without affecting the surrounding tissues or alteration of the implant surfaces.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carl E. Misch (2007) Contemporary implant dentistry. 3rd edn. pp 3–25
Greenstein G, Cavallaro J, Romanos G, Tarnow D (2008) Clinical recommendation for avoiding and managing surgical complications associated with implant dentistry. A review. J Periodontol 79(8):1317–1329. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2008.070067
Judith A. Porter, J. Anthony von Fraunhofer (2005) Success or failure of dental implants? A literature review with treatment considerations. Peer-Reviewed journal of the academy of general dentistry
Jacques Malet, Francis Mora, Philippe Bouchard (2012) Implant dentistry at a glance. 1st edn. Pp 24–25, 102–103, 106–108
Rosen P, Cochran D, Froum S, McAllister B, Renvert S, Wang H-L (2013) Peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: a current understanding of their diagnosis and clinical implications. J Periodontol 84(4):436–443. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2013.134001
Figuero E, Graziani F, Sanz I, Herrera D, Sanz M (2014) Management of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. Periodontology 2000 66:255–273
Romanos GE, Gupta B, Yunker M, Romanos EB, Malmstrom H (2013) Laser use in dental implantology. Implant Dent 22(3):282–288. https://doi.org/10.1097/ID.0b013e3182885fcc
Scott Froum, DDS (2011) Review of the treatment protocols for peri-implantitis. http://www.dentistryiq.com/articles/2011/10/review of the treatment protocols for peri-implantitis.html
Javed F, Romanos GE (2009) Impact of diabetes mellitus and glycemic control on the osseointgration of dental implants: a systematic literature review. J Periodontol 80:1719–1730. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.090283
Renvert S, Quirynen M (2015) Risk indicators for peri-implantitis. A narrative review. Clin Oral Implants Res 26(11):15–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12636
Maruyama N, Maruyama F, Takeuchi Y, Aika- wa C, Izumi Y, Nakagawa I (2014) Intraindividual variation in core microbiota in peri-implantitis and periodontitis. Scientific Reports 4:6602. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06602
Heitz-Mayfield LJA, Lang NP (2010) Comparative biology of chronic and aggressive periodontitis vs. peri-implantitis. Periodontology 2000(53):167–181. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2010.00348.x
Renvert S, Polyzois I (2015) Risk indicators for peri-implant mucositis: a systematic literature review. Journal of Clinincal Periodontology 42:172–186. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12346
Lang NP, Berglundh T (2011) Periimplant diseases: where are we now? -consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology. J Clin Periodontol 38(s11):178–181. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01674.x
Linkevicius T, Puisys A, Vindasiute E, Linke- viciene L, Apse P (2013) Does residual cement around implant-supported restorations cause peri-implant disease? A retrospective case analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 24:1179–1184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02570.x
Dalago HR, Schuldt Filho G, Rodrigues MA, Renvert S, Bianchini MA (2016) Risk indicators for peri-implantitis. A cross sectional study with 916 patients. Clin Oral Implants Res 00:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12772
Strietzel FP, Reichart PA, Kale A, Kulkarni M, Wegner B, Kuchler I (2007) Smoking interferes with the prognosis of dental implant treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Periodontol 34(6):523–544. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2007.01083.x
Klokkevold PR, Han TJ (2007) How do smoking, diabetes, and periodontitis affect outcomes of implant treatment? Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 22:173–202
Rinke S, Ohl S, Ziebolz D, Lange K, Eickholz P (2011) Prevalence of peri-implant disease in partially edentulous patients: a practice based cross sectional study. Clin Oral Implants Res 22(8):826–833. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.02061.x
Laine ML et al (2006) IL-1RN gene polymorphism is associated with peri-implantitis. Clin Oral Implants Res 17(4):380–385. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2006.01249.x
Fu J-H, Hsu Y-T, Wang H-L (2012) Identifying occlusal overload and how to deal with it to avoid marginal bone loss around implants. Eur J Oral Implantol 5:91–103
Oates TW, Dowell S, Robinson M, McMahan CA (2009) Glycemic control and implant stabilization in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Dent Res 88:367–371. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034509334203
Krennmair G, Seemann R, Piehslinger E (2010) Dental implants in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: clinical outcome and peri-implant findings. J Clin Periodontol 37(10):928–936. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01606.x
Galindo-Moreno P (2005) Influence of alcohol and tobacco habits on peri-implant marginal bone loss: a prospective study. Clin Oral Implants Res 16(5):579–586. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2005.01148.x
Froum SJ, Rosen PS (2012) A proposed classification for peri-implantitis. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 32(5):533–540
Bobia F, Pop RV (2010) Periimplantitis. Aetiology, diagnosis, treatment. A review from the literature. Curr Health Sci J 36(3):171–175
Algraffee H, Borumandi F, Cascarini L (2011) Peri-implantitis (review). Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 50:689–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2011.11.020
Prathapachandran J, Suresh N (2012) Management of peri-implantitis. Dent res J (Isfahan) 9(5):516–521
Roncati M, Lucchese A, Carinci F (2013) Non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis with the adjunctive use of an 810 nm diode laser. J Indian Soc Periodontol 17(6):812–815. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-124X.124531
Smeets R et al (2014) Definition, etiology, prevention and treatment of peri-implantitis, a review. Head Face Med 10(34):4–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-160X-10-34
Stübinger S et al (2010) Surface alteration of polished and sandblasted and acid-etched titanium implants after Er:YAG, carbon dioxide, and diode laser irradiation. Int J Oral Maxillofacial Implants 25(1):104–111
Schwarz F, Aoki A, Sculean A, Becker J (2009) The impact of laser application on periodontal and peri-implant wound healing. Periodontology 2000 51:79–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2009.00301.x
Dr. rer. Medic. René Franzen lectures. Module 1. 21-25.09.2015. Master of science in laser in dentistry. Aachen university. “EN2015”
Robert A. Convissar (2015) Principles and practice of laser dentistry, 2nd edn. Elsevier, pp 107–109
Romanos GE, Gutknecht N, Dieter S, Schwarz F, Crespi R, Sculean A (2009) Laser wavelengths and oral implantology: Review Article. Laser Med Sci 24(6):961–970
Azma E, Safavi N (2013) Diode laser application in soft tissue oral surgery. Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences 4(4):206–211
Natto ZS, Aladmawy M, Jr L, Paul A, Wang H-L (2015) Comparison of the efficacy of different types of lasers in the treatment of peri-implantitis: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 30(2):338–345
Hauser-Gerspach I, Stübinger S, Meyer J (2010) Bactericidal effect of different laser systems on Bacteria adherent to dental implant surface: an in vitro study comparing zirconia with titanium. Clin Oral Impl Res 21(3):277–283
Sennhenn-Kirchner S et al (2007) Decontamination of rough titanium surfaces with diode lasers microbiological findings on in vivo grown biofilms. Clin Oral Impl Res 18:126–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2006.01298.x
Efeoglu E, Eyyupoglu GT (2008) Treatment of peri-implantitis lesions with laser-assisted therapy and a minimally invasive approach: a case report. Journal of Oral laser application 8:109–116
Roncati M, Lauritano D, Tettamanti L, Tagliabue A, Carinci F (2015) Nonsurgical periodontal management of iatrogenic peri-implantitis: a clinical report. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 29:177–183
Arisan V et al (2015) A randomized clinical trial of an adjunct diode laser application for the nonsurgical treatment of peri-implantitis. Photomed Laser Surg 33(11):547–554. 10.1089/pho.2015.3956
Mettraux GR, Sculean A, Bürgin WB, Salvi GE (2016) Two-year clinical outcomes following non-surgical mechanical therapy of peri-implantitis with adjunctive diode laser application. Clin. Oral Impl. Res 27:845–849. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12689
Lerario F et al (2016) Non-surgical periodontal treatment of peri-implant diseases with the adjunctive use of diode laser: preliminary clinical study. Lasers Med Sci 31:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-015-1785-7
Hauser-Gerspach I, Stübinger S, Meyer J (2016) Bactericidal effects of different laser systems on bacteria adhered to dental implant surfaces: an in vitro study comparing zirconia to titanium. Clin Oral Impl Res 21:277–283. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01835.x
Castro GL et al (2007) Scanning electron microscopic analysis of diode laser-treated titanium implant surfaces. Photomed Laser Surg 25(2):124–128. https://doi.org/10.1089/pho.2006.1086
Stübinger S et al (2008) Effect of Er:YAG, CO2 and diode laser irradiation on surface properties of zirconia endosseous dental implants. Lasers Surg Med 40:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.20614
Geminiani A, Caton JG, Romanos GE (2012) Temperature change during non-contact diode laser irradiation of implant surfaces. Lasers Med Sci 27:339–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-010-0876-8
Giannelli M, Lasagnia M, Bani D (2015) Thermal effects of λ=808 nm GaAlAs diode laser irradiation on different titanium surfaces. Lasers Med Sci 30:2341–2352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-015-1801-y
Kushima SS et al (2015) Evaluation of temperature and roughness alteration of diode laser irradiation of zirconia and titanium for peri-implantitis treatment. Photomed Laser Surg 34(5):194–199. https://doi.org/10.1089/pho.2015.4026
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smeo, K., Nasher, R. & Gutknecht, N. Antibacterial effect of diode lasers in the treatment of peri-implantitis and their effects on implant surfaces: a literature review. Laser Dent Sci 2, 193–200 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41547-018-0039-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41547-018-0039-y