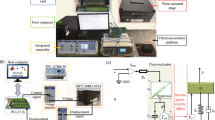
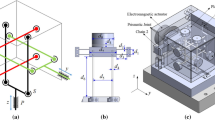
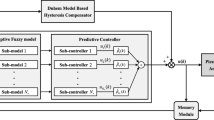
Abstract
Micropositioning systems are widely employed in industrial applications. Nonminimum-phase (NMP) is a normal phenomenon in micropositioning system, which leads to a great challenge for control system design. Model predictive control (MPC) is effective in handling the NMP problem. However, the parameter tuning of MPC is quite complicated and time-consuming using traditional methods for motion tracking control implementation. In this paper, an efficient neural networks (NN) model is established to optimize the MPC controller parameters including the prediction horizon, control horizon, and weighting factor. With the developed NN model, the motion tracking process of the micropositioning system is more intelligent and adaptive. The effectiveness of the presented novel NN-MPC control strategy has been verified by conducting extensive simulation studies. Furthermore, the results demonstrate that the NN-MPC scheme has good robustness under model parameter variation and noise condition.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali A., Ahmed, S.F., Joyo, M.K., Kushsairy K.: Mpc-pid comparison for controlling therapeutic upper limb rehabilitation robot under perturbed conditions. In: Proc. of 2017 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Social Sciences (ICETSS), 2017, pp. 1–5
Chen, Z., Zheng, J., Zhang, H., Ding, H.: Tracking of piezoelectric actuators with hysteresis: a nonlinear robust output regulation approach. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 27(15), 2610–2626 (2017)
Cheng, L., Liu, W., Hou, Z., Yu, J., Tan, M.: Neural-network-based nonlinear model predictive control for piezoelectric actuators. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(12), 7717–7727 (2015)
Dong, R., Tan, Y., Xie, Y., Janschek, K.: Recursive identification of micropositioning stage based on sandwich model with hysteresis. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 25(1), 317–325 (2017)
Elmali, H., Olgac, N.: Sliding mode control with perturbation estimation (SMCPE): a new approach. Int J Control 56(4), 923–941 (1992)
Hauser, J., Sastry, S., Meyer, G.: Nonlinear control design for slightly non-minimum phase systems: application to v/stol aircraft. Automatica 28(4), 665–679 (1992)
Hoagg, J.B., Bernstein, D.S.: Nonminimum-phase zeros—much to do about nothing—classical control—revisited part ii. IEEE Control Syst Mag 27(3), 45–57 (2007)
Kapur J.N., Kesavan H.K.: Entropy optimization principles and their applications. In: Entropy and Energy Sissipation in Water Resources. Springer, 1992, pp. 3–20
Liu, W., Cheng, L., Hou, Z., Yu, J., Tan, M.: An inversion-free predictive controller for piezoelectric actuators based on a dynamic linearized neural network model. IEEE/ASME Trans Mech 21(1), 214–226 (2016)
Mohammadzaman I., Sedigh, A.K., Nasirian, M.: Predictive control of non-minimum phase motor with backlash in an earth station antenna. In: Proc. of 2006 Chinese Control Conference (CCC 2006), 2006, pp. 900–905
Park, K., Desai, J.P.: Micropositioning and control of an underactuated platform for microscopic applications. IEEE/ASME Trans Mech 21(6), 2635–2646 (2016)
Qin, S.J., Badgwell, T.A.: A survey of industrial model predictive control technology. Control Eng Pract 11(7), 733–764 (2003)
Rana, M.S., Pota, H.R., Petersen, I.R.: Performance of sinusoidal scanning with mpc in afm imaging. IEEE/ASME Trans Mech 20(1), 73–83 (2015)
Rawlings, J.B.: Tutorial overview of model predictive control. IEEE Control Syst Mag 20(3), 38–52 (2000)
Richalet, J.: Industrial applications of model based predictive control. Automatica 29(5), 1251–1274 (1993)
Rossiter, J.A.: Model-based predictive control: a practical approach. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2017)
Sin, G., De Pauw, D.J., Weijers, S., Vanrolleghem, P.A.: An efficient approach to automate the manual trial and error calibration of activated sludge models. Biotechnol Bioeng 100(3), 516–528 (2008)
Wan, S., Xu, Q.: Design and analysis of a new compliant xy micropositioning stage based on roberts mechanism. Mech Mach Theory 95, 125–139 (2016)
Wang P., Xu Q.: Model predictive control design of a flexure-based micropositioning system. In: Proc. of 2016 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), 2016, pp. 5232–5236
Wang L.: Model predictive control system design and implementation using MATLAB®. Springer, 2009
Wills, A.G., Bates, D., Fleming, A.J., Ninness, B., Moheimani, S.O.R.: Model predictive control applied to constraint handling in active noise and vibration control. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 16(1), 3–12 (2008)
Wojsznis, W., Gudaz, J., Blevins, T., Mehta, A.: Practical approach to tuning mpc. ISA Trans 42(1), 149–162 (2003)
Xiao, H., Li, Z., Yang, C., Zhang, L., Yuan, P., Ding, L., Wang, T.: Robust stabilization of a wheeled mobile robot using model predictive control based on neurodynamics optimization. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64(1), 505–516 (2017)
Xu, Q.: New flexure parallel-kinematic micropositioning system with large workspace. IEEE Trans Robot 28(2), 478–491 (2012)
Xu, Q.: Digital integral terminal sliding mode predictive control of piezoelectric–driven motion system. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(6), 3976–3984 (2016)
Yan Y., Xu Q.: Neural networks-based pid precision motion control of a piezo-actuated microinjector. In: Intelligent Robotics and Applications. ICIRA 2019, H. Yu, J. Liu, L. Liu, Z. Ju, Y. Liu, D. Zhou, Eds., Springer, 2019, Lecture Notes in Computer Science 11745, ISBN: 978-3-030-27528-0, pp. 407-418
Zhang, R., Gao, F.: Multivariable decoupling predictive functional control with non-zero-pole cancellation and state weighting: application on chamber pressure in a coke furnace. Chem Eng Sci 94, 30–43 (2013)
Zhang, X., Xu, Q.: Design and testing of a new 3-DOF spatial flexure parallel micropositioning stage. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 19(1), 109–118 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Yu, L.-C.: Single-cell microinjection technology in cell biology. Bioessays 30(6), 606–610 (2008)
Zhang, H., Hu, B., Li, L., Chen, Z., Wu, D., Xu, B., Huang, X., Gu, G., Yuan, Y.: Distributed hammerstein modeling for cross-coupling effect of multiaxis piezoelectric micropositioning stages. IEEE/ASME Trans Mech 23(6), 2794–2804 (2018)
Zou, Q., Leang, K., Sadoun, E., Reed, M., Devasia, S.: Control issues in high-speed afm for biological applications: collagen imaging example. Asian J Control 6(2), 164–178 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was funded in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (File No. 51575545), The Science and Technology Development Fund, Macau SAR (File Nos. 0008/2020/A, 0153/2019/A3 and 0022/2019/AKP) and University of Macau (File Nos. MYRG2018-00034-FST and MYRG2019-00133-FST).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Xu, Q. Neural networks-based model predictive control for precision motion tracking of a micropositioning system. Int J Intell Robot Appl 4, 164–176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-020-00134-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-020-00134-3