Abstract
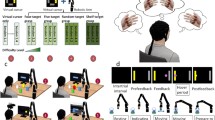
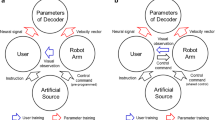
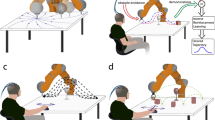
In brain machine interfaces (BMI), the brain activities are recorded by invasive or noninvasive approaches and translated into command signals to control external prosthetic devices such as a computer cursor, a wheelchair, or a robotic arm. Although many studies confirmed the capability of BMI systems in controlling multi degrees-of-freedom (DOF) prosthetic devices using invasive approaches, BMI research using noninvasive paradigms is still in its infancy. In this paper, a new robotic BMI platform has been developed using electroencephalography (EEG) technology to control a 6-DOF robotic arm. EEG signals were collected from the scalp using a wireless headset exploiting a new fast-training paradigm named as “imagined body kinematics”. A regression model was employed to decode the kinematic parameters from the EEG signals. The subjects were instructed to voluntarily control a virtual cursor in multiple trials to hit different pre-programmed targets on a screen in an optimized sequence. The command signals generated from hitting the targets during trials were applied to control sequential movements of the robotic arm in a discrete manner to manipulate an object in a two-dimensional workspace. This approach is derived from a basic shared control strategy where the robotic arm is responsible for carrying out complex maneuvers based on the user’s intention. Our proposed BMI platform yielded a high success rate of 70% in a sequence-based manipulation task after only a short time of training (10 min). The developed platform serves as a proof-of-concept for EEG-based neuro-prosthetic devices.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abiri, R., et al.: EEG-based control of a unidimensional computer cursor using imagined body kinematics. In: Biomedical Engineering Society Annual Meeting (BMES 2015). 2015a
Abiri, R., et al.: A real-time brainwave based neuro-feedback system for cognitive enhancement. In: ASME 2015 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference (Columbus, OH). 2015b
Abiri, R., et al.: Planar control of a quadcopter using a zero-training brain machine interface platform. In: Biomedical Engineering Society Annual Meeting (BMES 2016). 2016
Abiri, R., et al.: Brain computer interface for gesture control of a social robot: an offline study. In: 2017 Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE). IEEE, New York, 2017
Agashe, H., Contreras-Vidal, J.L.: Observation-based training for neuroprosthetic control of grasping by amputees. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE. IEEE, New York, 2014
Agashe, H.A., et al.: Global cortical activity predicts shape of hand during grasping. Front. Neurosci. 9, 121 (2015)
Aiqin, S., Binghui, F., Chaochuan, J.: Motor imagery EEG-based online control system for upper artificial limb. In: International Conference on Transportation, Mechanical, and Electrical Engineering (TMEE), 2011. 2011
Antelis, J.M., et al.: On the usage of linear regression models to reconstruct limb kinematics from low frequency EEG signals. PLoS ONE 8(4), e61976 (2013)
Bacher, D., et al.: Neural point-and-click communication by a person with incomplete locked-in syndrome. Neurorehabilit Neural Repair 29(5), 462–471 (2015)
Baxter, B.S., Decker, A., He, B.: Noninvasive control of a robotic arm in multiple dimensions using scalp electroencephalogram. In: 2013 6th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, (NER) 2013. IEEE, New York (2013)
Bhattacharyya, S., Konar, A., Tibarewala, D.: Motor imagery, P300 and error-related EEG-based robot arm movement control for rehabilitation purpose. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 52(12), 1007–1017 (2014)
Bhattacharyya, S., Shimoda, S., Hayashibe, M.: A synergetic brain-machine interfacing paradigm for multi-DOF robot control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 46(7), 957–968 (2016)
Bhuiyan, M., Choudhury, I., Dahari, M.: Development of a control system for artificially rehabilitated limbs: a review. Biol. Cybern. 109(2), 141–162 (2015)
Bradberry, T.J., Gentili, R.J., Contreras-Vidal, J.L.: Decoding three-dimensional hand kinematics from electroencephalographic signals. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2009, 5010–5013 (2009)
Bradberry, T.J., Gentili, R.J., Contreras-Vidal, J.L.: Reconstructing three-dimensional hand movements from noninvasive electroencephalographic signals. J. Neurosci. 30(9), 3432–3437 (2010)
Bradberry, T.J., Gentili, R.J., Contreras-Vidal, J.L.: Fast attainment of computer cursor control with noninvasively acquired brain signals. J. Neural Eng. 8(3), 036010 (2011)
Carmena, J.M., et al.: Learning to control a brain–machine interface for reaching and grasping by primates. PLoS Biol. 1(2), e42 (2003)
Chen, C.W., Lin, C.C.K., Ju, M.S.: Hand orthosis controlled using brain–computer interface. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 29(5), 234–241 (2009)
Collinger, J.L., et al.: High-performance neuroprosthetic control by an individual with tetraplegia. Lancet 381(9866), 557–564 (2013)
DFRobot
Doud, A.J., et al.: Continuous three-dimensional control of a virtual helicopter using a motor imagery based brain-computer interface. PLoS ONE 6(10), e26322 (2011)
Emotiv. http://emotiv.com/
Fifer, M.S., et al.: Simultaneous neural control of simple reaching and grasping with the modular prosthetic limb using intracranial EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 22(3), 695–705 (2014)
Gilja, V., et al.: A high-performance neural prosthesis enabled by control algorithm design. Nat. Neurosci. 15(12), 1752–1757 (2012)
Guger, C., et al.: Prosthetic control by an EEG-based brain-computer interface (BCI). In: Proceedings of AAATE 5th European conference for the advancement of assistive technology, 1999
Hazrati, M.K., Hofmann, U.G.: Avatar navigation in Second Life using brain signals. In: IEEE 8th International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing (WISP), 2013. IEEE, New York, 2013
Hazrati, M.K., et al.: Controlling a simple hand prosthesis using brain signals. Biomed. Eng./Biomed. Tech. 59, 1152–1155 (2014)
He, B., et al.: Noninvasive brain-computer interfaces based on sensorimotor rhythms. Proc. IEEE 103(6), 907–925 (2015)
Hochberg, L.R., et al.: Reach and grasp by people with tetraplegia using a neurally controlled robotic arm. Nature 485(7398), 372–375 (2012)
Horki, P., et al.: Combined motor imagery and SSVEP based BCI control of a 2 DoF artificial upper limb. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 49(5), 567–577 (2011)
Hortal, E., et al.: SVM-based brain–machine interface for controlling a robot arm through four mental tasks. Neurocomputing 151, 116–121 (2015)
Iturrate, I., et al.: Teaching brain-machine interfaces as an alternative paradigm to neuroprosthetics control. Sci. Rep. 5, 13893 (2015)
Kim, S.P., et al.: Neural control of computer cursor velocity by decoding motor cortical spiking activity in humans with tetraplegia. J. Neural Eng. 5(4), 455 (2008)
Kim, Y.J., et al.: A study on a robot arm driven by three-dimensional trajectories predicted from non-invasive neural signals. Biomed. Eng. Online 14(1), 1 (2015)
Kreilinger, A., Neuper, C., Müller-Putz, G.R.: Error potential detection during continuous movement of an artificial arm controlled by brain–computer interface. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 50(3), 223–230 (2012)
LaFleur, K., et al.: Quadcopter control in three-dimensional space using a noninvasive motor imagery-based brain–computer interface. J. Neural Eng. 10(4), 046003 (2013)
Li, T., et al.: Brain–machine interface control of a manipulator using small-world neural network and shared control strategy. J. Neurosci. Methods 224, 26–38 (2014)
Luth, T., et al.: Low level control in a semi-autonomous rehabilitation robotic system via a brain-computer interface. In: IEEE 10th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, 2007. ICORR 2007. IEEE, New York, 2007
MathWorks. http://www.mathworks.com/
McFarland, D.J., Sarnacki, W.A., Wolpaw, J.R.: Electroencephalographic (EEG) control of three-dimensional movement. J. Neural Eng. 7(3), 036007 (2010)
Meng, J., et al.: Noninvasive electroencephalogram based control of a robotic arm for reach and grasp tasks. Sci. Rep. 6, 38565 (2016)
Millán, J.D.R.: Brain-machine interfaces: the perception-action closed loop: a two-learner system. IEEE Syst. Man Cybern. Mag. 1(1), 6–8 (2015)
Miranda, R.A., et al.: DARPA-funded efforts in the development of novel brain–computer interface technologies. J. Neurosci. Methods 244, 52–67 (2015)
Muller-Putz, G.R., Pfurtscheller, G.: Control of an electrical prosthesis with an SSVEP-based BCI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 55(1), 361–364 (2008)
Murguialday, A.R., et al.: Brain–computer interface for a prosthetic hand using local machine control and haptic feedback. In: 2007 IEEE 10th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, ICORR 2007, 2007
Nicolas-Alonso, L.F., Gomez-Gil, J.: Brain computer interfaces, a review. Sensors 12(2), 1211–1279 (2012)
Nirenberg, L.M., Hanley, J., Stear, E.B.: A new approach to prosthetic control: eeg motor signal tracking with an adaptively designed phase-locked loop. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 18(6), 389–398 (1971)
Ofner, P., Muller-Putz, G.R.: Decoding of velocities and positions of 3D arm movement from EEG. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2012, 6406–6409 (2012)
Pfurtscheller, G., et al.: Self-paced operation of an SSVEP-based orthosis with and without an imagery-based “brain switch:” a feasibility study towards a hybrid BCI. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 18(4), 409–414 (2010)
Royer, A.S., et al.: EEG control of a virtual helicopter in 3-dimensional space using intelligent control strategies. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 18(6), 581–589 (2010)
Schalk, G., et al.: BCI2000: a general-purpose brain-computer interface (BCI) system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51(6), 1034–1043 (2004)
Schalk, G., et al.: Two-dimensional movement control using electrocorticographic signals in humans. J. Neural Eng. 5(1), 75 (2008)
Schultz, A.E., Kuiken, T.A.: Neural interfaces for control of upper limb prostheses: the state of the art and future possibilities. PM&R 3(1), 55–67 (2011)
Sequeira, S., Diogo, C., Ferreira, F.J.T.E.: EEG-signals based control strategy for prosthetic drive systems. In: 2013 IEEE 3rd Portuguese Meeting in Bioengineering (ENBENG), 2013
Slutzky, M.W., Flint, R.D.: Physiological properties of brain-machine interface input signals. J. Neurophysiol. 118(2), 1329–1343 (2017)
Taylor, D.M., Tillery, S.I.H., Schwartz, A.B.: Direct cortical control of 3D neuroprosthetic devices. Science 296(5574), 1829–1832 (2002)
Ubeda, A., et al.: Linear decoding of 2D hand movements for target selection tasks using a non-invasive BCI system. In: Systems Conference (SysCon), 2013 IEEE International. 2013
Velliste, M., et al.: Cortical control of a prosthetic arm for self-feeding. Nature 453(7198), 1098–1101 (2008)
Vidaurre, C., Blankertz, B.: Towards a cure for BCI illiteracy. Brain Topogr. 23(2), 194–198 (2010)
Vidaurre, C., et al.: EEG-based BCI for the linear control of an upper-limb neuroprosthesis. Med. Eng. Phys. 38(11), 1195–1204 (2016)
Vogel, J., et al.: An assistive decision-and-control architecture for force-sensitive hand–arm systems driven by human–machine interfaces. Int. J. Robot. Res. 34(6), 763–780 (2015)
Wolpaw, J.R., McFarland, D.J.: Control of a two-dimensional movement signal by a noninvasive brain-computer interface in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101(51), 17849–17854 (2004)
Wolpaw, J.R., et al.: An EEG-based brain-computer interface for cursor control. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 78(3), 252–259 (1991)
Wright, J., et al.: A Review of control strategies in closed-loop neuroprosthetic systems. Front. Neurosci. 10, 312 (2016)
Xia, B., et al.: A combination strategy based brain–computer interface for two-dimensional movement control. J. Neural Eng. 12(4), 046021 (2015)
Yuan, H., He, B.: Brain–computer interfaces using sensorimotor rhythms: current state and future perspectives. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61(5), 1425–1435 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was in part supported by a NeuroNET seed grant to XZ; and in part by the NIH under grants NIH P30 AG028383 to the UK Sanders-Brown Center on Aging, NIH AG00986 to YJ, and NIH NCRR UL1TR000117 to the UK Center for Clinical and Translational Science. JK’s work was partially supported through a summer internship from the Office of Undergraduate Research at The University of Tennessee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 24822 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilmarx, J., Abiri, R., Borhani, S. et al. Sequence-based manipulation of robotic arm control in brain machine interface. Int J Intell Robot Appl 2, 149–160 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-018-0049-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-018-0049-7