Abstract
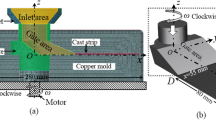
The effects of different casting parameters on porosity defects between the horizontal and vertical shot sleeve processes are quantitatively studied based on experiments and simulations. The castings made using the two processes are characterized in terms of porosity defects by X-ray radiographic inspection and blistering formation by T4 heat treatment process. Experimental results indicate that much fewer porosities and blisters are formed in the castings made using the vertical process than those made using the horizontal one. Meanwhile, numerical simulations have been performed to quantitatively investigate the flow dynamics behavior of molten metal in the horizontal and vertical shot sleeves. The simulation results demonstrate that compared with the conventional horizontal process, the vertical shot sleeve process is more efficient in elimination of waves and reduction of air entrapment and oxide formation. Moreover, the vertical process needs a lower pouring temperature which can decrease hydrogen solubility in the molten metal; it has a smaller temperature gradient of molten melt which can reduce the formation of cold flakes and pre-solidified materials. Therefore, the vertical shot sleeve process is more competitive in improving the internal integrity of die castings.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.J. Nikroo, M. Akhlaghi, M.A. Najafabadi, Simulation and analysis of flow in the injection chamber of die casting machine during the slow shot phase. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 41, 31–41 (2009)
D. Sui, Z. Cui, R. Wang, S. Hao, Q. Han, Effect of cooling process on porosity in the aluminum alloy automotive wheel during low-pressure die casting. Int. J. Metalcast. 10(1), 32–42 (2016)
T.C. Tszeng, Y.L. Chu, A study of wave formation in shot sleeve of a die casting machine. J. Eng. Ind. 116, 175–182 (1994)
Z. Ignaszak, J. Hajkowski, Contribution to the identification of porosity type in AlSiCu high-pressure-die-castings by experimental and virtual way. Arch. Foundry Eng. 15, 143–151 (2015)
Y. Liu, W. Jie, Z. Gao, Y. Zheng, Investigation on the formation of microporosity in aluminum alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 629, 221–229 (2015)
C. Tian, J. Law, J. Touw, M. Murray, J.Y. Yao, D. Graham, D. John, Effect of melt cleanliness on the formation of porosity defects in automotive aluminium high pressure die castings. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 122, 82–93 (2002)
V.D. Tsoukalas, The effect of die casting machine parameters on porosity of aluminium die castings. Int. J. Cast Metals Res. 15, 581–588 (2003)
S.G. Lee, A.M. Gokhale, G.R. Patel, M. Evans, Effect of process parameters on porosity distributions in high-pressure die-cast AM50 Mg-alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 427, 99–111 (2006)
D. Dispinar, S. Akhtar, A. Nordmark, M. Di Sabatino, L. Arnberg, Degassing, hydrogen and porosity phenomena in A356. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527, 3719–3725 (2010)
J. Lopez, J. Hernandez, F. Faura, G. Trapaga, Shot sleeve wave dynamics in the slow phase of die casting injection. J. Fluids Eng. 122, 349–356 (2000)
J. Lopez, F. Faura, J. Hernandez, P. Gomez, On the optimum plunger acceleration law in the slow shot phase of pressure die casting machines. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 125, 529–537 (2003)
F. Faura, J. Lopez, J. Hernandez, On the critical plunger speed and three-dimensional effects in high-pressure die casting injection chambers. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 41, 173–191 (2001)
J. Hernandez, J. Lopez, F. Faura, P. Gomez, Analysis of the flow in a high-pressure die casting injection chamber. J. Fluids Eng. 125, 315–324 (2003)
R. Zamora, F. Faura, J. Lopez, J. Hernandez, Experimental verification of numerical predictions for the optimum plunger speed in the slow phase of a high-pressure die casting machine. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 33, 266–276 (2007)
R. Zamora, J.J. Hernandez-Ortega, F. Faura, J. Lopez, Experimental investigation of porosity formation during the slow injection phase in high-pressure die-casting processes. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 10, 1–10 (2008)
A.I.N. Korti, S. Abboudi, Numerical simulation of the interface molten metal air in the shot sleeve chambre and mold cavity of a die casting machine. Heat Mass Transf. 47, 1465–1478 (2011)
A.I.N. Korti, M.C. Korti, S. Abboudi, Thermal effect in minimizing air entrainment in the 3D shot sleeve during injection stage of the HPDC machine. Int. J. Fluid Mech. Res. 43, 1–17 (2016)
A.I.N. Korti, S. Abboudi, Effects of shot sleeve filling on evolution of the free surface and solidification in the high-pressure die casting machine. Int. J. Metalcast. 11(2), 223–239 (2017)
E. Florese, F. bonollo, Plunder kinematic parameters affecting quality of high-pressure die-cast aluminum alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47A, 3731–3743 (2016)
E. Fiorese, D. Richiedei, F. Bonollo, Improving the quality of die castings through optimal plunger motion planning: analytical computation and experimental validation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 88, 1475–1484 (2017)
L. Wang, T. Nguyen, G. Savage, C. Davidson, Thermal and flow modelling of ladling and injection in high pressure die casting process. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 16, 409–417 (2003)
M.R. Barkhudarov, Minimizing air entrainment in a shot sleeve during slow-shot stage. Die Cast. Eng. 5, 34–37 (2009)
M. Frings, M. Behr, S. Elgeti, Study on objective functions for the slow shot phase in high-pressure die casting. AIP Conf. Proc. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4963423, (2016)
M. Ichimura, H. Katsuta, Y. Sasajima, M. Imabayashi, Hydrogen and deuterium solubility in aluminum with voids. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 49, 1259–1267 (1988)
G. Jiang, Y. Li, Y. Liu, Calculation of hydrogen solubility in molten alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 21, 1130–1135 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from Fiat Chrysler Automobiles LLC under the R&D project Agreement No. 00059689.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sui, D., Han, Q. Effects of Different Parameters on Porosity Defects Between the Horizontal and Vertical Shot Sleeve Processes. Inter Metalcast 13, 417–425 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-0267-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-0267-7