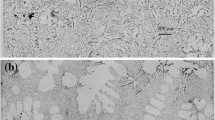
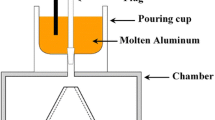
Abstract
Sr-modified Al–Si alloys are promising for automotive and aerospace industrial applications. However, Sr modifier increases the porosity level and deteriorates the performance of the castings, which has confused foundrymen for several decades. Many researchers have studied the phenomenon, but there is no unified explanation. In this study, two types of Sr modifier (50 ppm and 250 ppm) are applied to explore the effect of Sr modification on the surface oxide film and the porosity of the castings. The results of optical emission spectrometer and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) reveal that the surface oxide film has some degree of Sr segregation. Combining the high-resolution XPS spectrums with electron probe microanalysis–wavelength-dispersive spectroscopic (EPMA–WDS), it can be found that a small amount of SrO is distributed on the Al2O3 film. Further analyzing the surface oxide film by scanning electron microscopy and EPMA mapping, it can be concluded that the compact Al2O3 film is fractured by congregated SrO and then some new Al2O3 films and oxide inclusions are formed in the cracks. Those can cause the increase in the porosity. And the result of reduced pressure test (RPT) shows that the densities of RPT samples are decreasing with the increase in Sr content. It means that Sr modification dose increase the porosity of the A356 alloy castings.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Tenekedjiev, J.E. Gruzleski, Hypereutectic aluminum–silicon casting alloys—a review. Cast Metals 3(2), 96–105 (1990)
G.K. Sigworth, Fundamentals of solidification in aluminum castings. Int. J. Metalcast. 8(1), 7–20 (2014)
J. Campbell, Metal casting processes, metallurgy techniques and design complete, Casting Handbook, 2nd edn. (Elsevier Ltd, Amsterdam, 2011), pp. 269–300
A. Pacz, Alloy U.S. Patent No. 1, 387, 900 (1921)
S. Hegde, K.N. Prabhu, Modification of eutectic silicon in Al–Si alloys. Mater. Sci. 43(9), 3009–3027 (2008)
F. Zu, X. Li, Functions and mechanism of modification elements in eutectic solidification of Al–Si alloys: a brief review. China Foundry 11(4), 287–295 (2014)
A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, Porosity formation in al–si sand mold castings. Int. J. Metalcast. 11(4), 812–822 (2017)
H. Liao, W. Song, Q. Wang, L. Zhao, R. Fan, F. Jia, Effect of Sr addition on porosity formation in directionally solidified A356 alloy. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 26(4), 201–208 (2013)
G. Sigworth, Understanding quality in aluminum castings. Int. J. Metalcast. 5(1), 7–22 (2011)
D. Emadi, J.E. Gruzleski, J.M. Toguri, The effect of Na and Sr modification on surface tension and volumetric shrinkage of A 356 alloy and their influence on porosity formation. Metall. Trans. B 24(6), 1055–1063 (1993)
X. Bian, Z. Zhang, X. Liu, Effect of strontium modification on hydrogen content and porosity shape of al–si alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 331–337, 361–366 (2000)
D. Argo, J.E. Gruzleski, Porosity in modified aluminum alloy castings. Trans. Am. Foundrym. Soc. 96, 65–74 (1988)
A.K. Dahle, K. Nogita, S.D. Mcdonald, C. Dinnis, L. Lu, Eutectic modification and microstructure development in Al–Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 413–414(6), 243–248 (2005)
S. Akhtar, L. Arnberg, M. Sabatino, D. Dispinar, M. Syvertsen, A comparative study of porosity and pore morphology in a directionally solidified a356 alloy. Int. J. Metalcast. 3(1), 39–52 (2009)
D. Dispinar, J. Campbell, Critical assessment of reduced pressure test. Part 1: porosity phenomena. Int. J. Cast Metals Res. 17(5), 280–286 (2015)
G.K. Sigworth, C. Wang, H. Huang, J.T. Berry, Porosity formation in modified and unmodified Al–Si alloy castings. Trans. Am. Foundrym. Soc. 102, 245–262 (1994)
S.M. Miresmaeili, J. Campbell, S.G. Shabestari, S.M.A. Boutorabi, Precipitation of Sr-rich intermetallic particles and their influence on pore formation in Sr-modified A356 alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36(9), 2341–2349 (2005)
J. Gruzleski, W. La Orchan, H. Mulazimoglu, New reduced pressure test quantifies hydrogen content. Mod. Cast. 85(9), 47–49 (1995)
S.W. Hudson, D. Apelian, Inclusion detection in molten aluminum: current art and new avenues for in situ analysis. Int. J. Metalcast. 10(3), 289–305 (2016)
M.H. Mulazimoglu, N. Handiak, Some observation on the reduced pressure test and hydrogen concertation of modified A356 alloy. Trans. Am. Foundrym. Soc. 97, 225–232 (1989)
Z. Zhang, X. Bian, Y. Wang, X. Liu, Microstructures and modification performance of melt-spun Al-10 Sr alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 37(20), 4473–4480 (2002)
B. Closset, H. Dugas, M. Pekguleryuz, J.E. Gruzleski, The aluminum–strontium phase diagram. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 17(7), 1250–1253 (1986)
C.B. Alcock, V.P. Itkin, The Al–Sr (aluminum–strontium) system. Bull. Alloy Ph. Diagr. 10(6), 624–630 (1989)
K.J. Brondyke, P.D. Hess, Interpretation of vacuum gas test results for aluminum alloys. Trans. TMS-AIME 230, 1542–1546 (1964)
J.F. Moulder, W.F. Stickle, P.E. Sobol, K.D. Bomben, J. Chastain, in Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: A Reference Book of Standard Spectra for Identification and Interpretation of XPS Data, ed. by J. Chastain (Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Waltham, 1992), pp. 54–55
T.P. Hanusa, Strontium physical and chemical properties, in Encyclopedia of Metalloproteins, ed. by R.H. Kretsinger, V.N. Uversky, E.A. Permyakov (Springer, New York, 2013), pp. 2141–2149
C. Xu, W. Gao, Pilling–Bedworth ratio for oxidation of alloys. Mater. Res. Innov. 3(4), 231–235 (2000)
R. Bedworth, N. Pilling, The oxidation of metals at high temperatures. J. Inst. Metals 29(3), 529–582 (1923)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the assistance from State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing and Material Analysis and Testing Center of Shaanxi Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Hao, Q. & Yu, W. Effect of Strontium Modification on Porosity Formation in A356 Alloy. Inter Metalcast 13, 944–952 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-00300-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-00300-1