Abstract
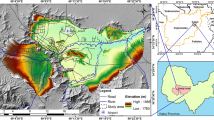
Due to the climate change and global warming, water shortage is known as a serious worldwide issue particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. Utilization of subsurface dams (SSD) could be a solution to this matter, but finding a suitable site for construction of a SSD is an engineering challenge. Selection of the optimum location is carried out by evaluating different positive and negative criteria. Criteria are combined by means of multi-criteria decision-making methods (MCDM), such as AHP, ANP, TOPSIS and other well-known methods. In these research, because of the complexity of the decision and this fact that the results in other MCDM methods are very similar to each other, we choose ELECTRE method which is performed for site selection of SSDs. 10 regions out of 50 are studied as SSD alternatives in Isfahan province of Iran. For performing ELECTRE method, 14 criteria have been defined based on four different aspects of SSD construction that are hydrogeology, socio-economy, geology and climate change. The most important criteria include average annual rainfall, area of upper basin, distance from villages and stream slope. The modified ELECTRE III method was used to rank the alternatives from the most suitable choice for constructing a subsurface dam to the least. Hoseinabad area was finally selected to construct the sub-surface dam. Application of an advanced MCDM method like ELECTRE reduces some uncertainties in SSD site selection and this developed methodology can be used as a base for more detailed field investigations.

(modified after Foster et al. 2008)

(modified after Safinejad and Dadras 2000)






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini M, Khademi H, Afyuni M, Abbaspour KC (2005) Variability of available cadmium in relation to soil properties and landuse in an arid region in central Iran Water. Air Soil Pollut 162:205–218
Benayoun R, Roy B, Sussman N (1966) Manual de reference du programme electre Note de synthese et Formation 25
Brans J-P, Vincke P, Mareschal B (1986) How to select and how to rank projects: the PROMETHEE method. Eur J Oper Res 24:228–238
Charnes A, Cooper WW (1957) Management models and industrial applications of linear programming. Manag Sci 4:38–91
Cooper WW, Seiford LM, Tone K (2007) Data envelopment analysis: a comprehensive text with models, applications, references and DEA-solver software. Springer, New York
Deng J-L (1989) Introduction to grey system theory. J Grey Syst 1:1–24
Forzieri G, Gardenti M, Caparrini F, Castelli F (2008) A methodology for the pre-selection of suitable sites for surface and underground small dams in arid areas: a case study in the region of Kidal, Mali. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/B/C 33(1–2):74–85
Foster S, Tuinhof A, Garduño H (2008) Groundwater in sub-saharan africa: a strategic overview of developmental issues. In: Adelana SMA, MacDonald AM (eds) Applied groundwater studies in Africa. Taylor & Francis, London, pp 9–21
Frankl A, Nyssen J, De Dapper M, Haile M, Billi P, Munro N, Deckers J, Poesen J (2011) Linking long-term gully and river channel dynamics to environmental change using repeat photography (Northern Ethiopia). Geomorphology 129:238–251
Hanson G, Nilsson Å (1986) Ground-water dams for rural-water supplies in developing countries. Groundwater 24:497–506
Hyde KM, Maier HR, Colby CB (2005) A distance-based uncertainty analysis approach to multi-criteria decision analysis for water resource decision making. J Environ Manag 77:278–290
Ishida S, Tsuchihara T, Yoshimoto S, Imaizumi M (2011) Sustainable use of groundwater with underground dams. Japan Agric Res Q 45:51–61
Jamali IA, Olofsson B, Mörtberg U (2013) Locating suitable sites for the construction of subsurface dams using GIS. Environ Earth Sci 70:2511–2525
Jamali IA, Mörtberg U, Olofsson B, Shafique M (2014) A spatial multi-criteria analysis approach for locating suitable sites for construction of subsurface dams in Northern Pakistan. Water Resour Manag 28:5157–5174
Jamali AA, Randhir TO, Nosrati J (2018) Site suitability analysis for subsurface dams using boolean and fuzzy logic in arid watersheds. J Water Resour Plan Manag 144(8):04018047
Janssen R (1992) Multiobjective decision support for environmental management, vol 2. Springer, New York
Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Ansari M, Mehr MR, Kaabi H, Kermani M (2015) Macronutrients and trace metals in soil and food crops of Isfahan Province, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 187:1–22
Khosravi H (2005) Application of MEDALUS model in desertification of Kashan
Lalehzari R, Tabatabaei SH (2015) Simulating the impact of subsurface dam construction on the change of nitrate distribution. Environ Earth Sci 74:3241–3249
Li H-F, Wang J-J (2007) An improved ranking method for ELECTRE III. In: 2007, pp 6659–6662
Mobarakabadi MK (2012) Model for determination the optimum location of subsurface dam using analytical hierarchy process AHP. Adv Environ Biol 6(3):1292–1297
Moghaddasi M, Araghinejad S, Morid S (2013) Water management of irrigation dams considering climate variation: case study of Zayandeh-rud reservoir, Iran. Water Resour Manag 27:1651–1660
Nagarajan R, Rajmohan N, Mahendran U, Senthamilkumar S (2010) Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in Thanjavur city, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 171:289–308
Onder H, Yilmaz M (2005) Underground dams: a tool of sustainable development and management of groundwater resources. Eur Water 11(12):35–45
Opricovic S (1998) Multicriteria optimization of civil engineering systems Faculty of Civil Engineering. Belgrade 2:5–21
Opricovic S, Tzeng GH (2002) Multicriteria planning of post-earthquake sustainable reconstruction. Comput Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 17:211–220
Raju NJ, Reddy TVK, Munirathnam P (2006) Subsurface dams to harvest rainwater—a case study of the Swarnamukhi River basin, Southern India. Hydrogeol J 14:526–531
Rezaei P, Rezaie K, Nazari-Shirkouhi S, JamalizadehTajabadi MR (2013) Application of fuzzy multi-criteria decision making analysis for evaluating and selecting the best location for construction of underground dam. Acta Polytech Hungar 10(7):187–205
Roy B (1978) ELECTRE III: algorithme de classement basé sur une représentation des préférence en présence de critères multiples. Cahiers du CERO 21:3–24
Roy B, Bertier P (1973) La Méthode ELECTRE II(Une application au média-planning
Saaty TL (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48:9–26
Saaty TL, Tran LT (2007) On the invalidity of fuzzifying numerical judgments in the analytic hierarchy process. Math Comput Model 46(7–8):962–975
Safinejad J, Dadras B (2000) Underground dam in Vazvan-Meimeh Qanat in Isfahan. National Water Iran Museum, Iran
Singh LK, Jha MK, Chowdary VM (2017) Multi-criteria analysis and GIS modeling for identifying prospective water harvesting and artificial recharge sites for sustainable water supply. J Clean Product 142(4):1436–1456
Stevanović Z (2016) Damming underground flow to enhance recharge of karst aquifers in the arid and semi-arid worlds. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–14
Tzimopoulos C, Balioti V, Evangelides C (2013) Fuzzy multi-criteria decision making method for dam selection. In: Proceedings of the 13th international conference on environmental science and technology, CEST Athens
VSF (2006) SubSurface Dams: a simple, safe and affordable technology for pastoralists: a manual on subSurface dams construction based on an experience of Vétérinaires sans Frontières in Turkana District (Kenya). Vétérinaires sans Frontières (VSF), Brussels
Yasser M, Jahangir K, Mohmmad A (2013) Earth dam site selection using the analytic hierarchy process (AHP): a case study in the west of Iran. Arabian J Geosci 6:3417–3426
Yoon KP, Hwang C-L (1995) Multiple attribute decision making: an introduction, vol 104. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks
Zehtabian G (2003) The effect of artificial recharge with flood spreading on groundwater resources and arid lands. In: Paper presented at the 7th international conference on development of dry lands, Tehran, Iran
Zehtabian G, Khosravi H, Ghodsi M (2010) High demand in a land of water scarcity: Iran. In: Water and sustainability in arid regions. Springer, New York, pp 75–86
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the member of Isfahan Centre for Research of Agricultural Science and Natural Resources and Experts who gave the authors help during the survey. We are very grateful to anonymous reviewers who helped us and gave valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Article impact statement
Subsurface dam constructions especially in arid and semiarid regions are a way for optimized use of groundwater. Site selection of these kind of dam depends on many factors. In this study, a knowledge-driven method called ELECTRE III was employed to deal with this challenge.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dortaj, A., Maghsoudy, S., Doulati Ardejani, F. et al. Locating suitable sites for construction of subsurface dams in semiarid region of Iran: using modified ELECTRE III. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 6, 7 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00362-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00362-2