Abstract
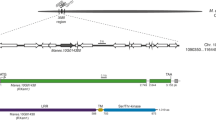
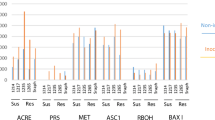
Cassava Bacterial Blight (CBB), caused by Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. manihotis (Xpm), is the most important bacterial disease of cassava (Manihot esculenta). Xpm employs Transcription Activator-Like effectors (TALE) to induce the expression of host susceptibility (S) genes favoring bacterial growth. The identification of resistant and susceptible cassava varieties as well as the identification of the cassava gene MeSweet10a as a target of the effector TAL20, have been conducted on plants grown from mature stem-cuttings. We explored the possibility of using in vitro plants to study cassava-Xpm interactions. Cassava in vitro plants of varieties 60444 and CM6438–14 were susceptible and resistant, respectively, to infection by strain Xpm668. In addition, the expression of MeSweet10a was induced in the susceptible but not in the resistant variety, which was not associated with polymorphisms in the Effector Binding Element (EBE) reported for TAL20. Three other Xpm strains, Xpm531, Xpm681 and Xpm1061, were also able to induce the TAL20 cognate target gene in the susceptible cassava variety 60444. These results demonstrate the usefulness of in vitro plants to study the phenotypic and molecular responses of cassava during Xpm infection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boch J, Scholze H, Schornack S, Landgraf A, Hahn S, Kay S, Lahaye T, Nickstadt A, Bonas A (2009) Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL-type III effectors. Science 326:1509–1512
Castiblanco LF, Gil J, Rojas A, Osorio D, Gutiérrez S, Muñoz A, Perez A, Koebnik R, Szurek B, López C, Restrepo S, Verdier V, Bernal A (2013) TALE1 from Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis acts as a transcriptional activator in plant cells and is important for pathogenicity in cassava plants. Molecular Plant Pathology 14:84–95
Chen L, Hou B, Lalonde S, Takanaga H, Hartung M, Qu X, Guo W, Kim J, Underwood W, Chaudhuri B, Chermak D, Antony G, White F, Somerville S, Mudgett M, Frommer W (2010) Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange and nutrition of pathogens. Nature 468:527–532
Cohn M, Bart RS, Shybut M, Dahlbeck D, Gomez M, Morbitzer R, Hou B-H, Frommer W, Lahaye T, Staskawicz B (2014) Xanthomonas axonopodis virulence is promoted by a transcription activator-like effector-mediated induction of a SWEET sugar transporter in cassava. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 27:1186–1198
Cohn M, Morbitzer R, Lahaye T, Staskawicz B (2016) Comparison of gene activation by two TAL effectors from Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis reveals candidate host susceptibility genes in cassava. Molecular Plant Pathology 17:875–889
Constantin EC, Cleenwerck I, Maes BS, Van Malderghem C, De Vos P, Cottyn B (2016) Genetic characterization of strains named as Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. dieffenbachiae leads to a taxonomic revision of the X. axonopodis species complex. Plant Pathology 65:792–806
Cox KL, Meng F, Wilkins KE, Li F, Wang P, Booher NJ, Carpenter S, Chen L, Zheng H, Gao X, Zheng Y, Fei Z, Yu JZ, Isakeit T, Wheeler T, Frommer WB, He P, Bogdanove AJ, Shan L (2017) TAL effector driven induction of a SWEET gene confers susceptibility to bacterial blight of cotton. Nature Communications 8:155–188
Deng D, Yan C, Pan X, Mahfouz M, Wang J, Zhu J-K, Shi Y, Yan N (2012) Structural basis for sequence-specific recognition of DNA by TAL effectors. Science 335:720–723
Howeler RL, Lutaladio NB, Thomas G (2013) Save and grow: cassava. A guide to sustainable production intensification. FAO, Rome
Hutin M, Al P-Q, Lopez C, Szurek B (2015a) MorTAL Kombat: the story of defense against TAL effectors through loss-of-susceptibility. Frontiers in Plant Science 6:535
Hutin M, Sabot F, Ghesquiere A, Koebnik R, Szurek B (2015b) A knowledge-based molecular screen uncovers a broad-spectrum OsSWEET14 resistance allele to bacterial blight from wild rice. The Plant Journal 84:694–703
Jarvis A, Ramirez J, Herrera B, Navarro C (2012) Is cassava the answer to African climate change adaptation? Tropical Plant Biology 5:9–29
Jorge V, Fregene M, Duque MC, Bonierbale M, Thome J, Verdier V (2000) Genetic mapping of resistance to bacterial blight disease in cassava. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 101:865–872
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Mak A, Bradley P, Cernadas RA, Bogdanove A, Stoddard B (2012) The crystal structure of TAL effector PthXo1 bound to its DNA target. Science 335:716–719
McCallum EJ, Anjanappa RB, Gruissem W (2017) Tackling agriculturally relevant diseases in the staple crop cassava (Manihot esculenta). Current Opinion in Plant Biology 38:50–58
Muñoz BA, Szurek B, López CE (2013) Tell me a tale of TALEs. Molecular Biotechnology 53:228–235
Muñoz A, Perez A, Gomez-Cano F, Gil J, Michelmore R, Bernal A, Szureck B, Lopez C (2014) RNAseq analysis of cassava reveals similar plant responses upon infection with pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis. Plant Cell Reports 33:1901–1912
Mutka AM, Fentress SJ, Sher JW, Berry J, Pretz C, Nusinow D, Bart R (2016) Quantitative, image-based phenotyping methods provide insight into spatial and temporal dimensions of plant disease. Plant Physiology 172:650–660
Norton R (2014) Global starch market outlook and feedstock economics. Cassava World. Africa. Centre for Management Technology (CMT), Lusaka
Pereira A, Carazzolle MF, Abe VY, De Oliveira M, Domingues M, Silva J, Cernadas R, Benedetti C (2014) Identification of putative TAL effector targets of the citrus canker pathogens shows functional convergence underlying disease development and defense response. BMC Genomics 15:157
Restrepo S, Verdier V (1997) Geographical differentiation of the population of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis in Colombia. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 63:4427–4434
Romer P, Hahn S, Jordan T, Straub T, Bonas U, Lahaye T (2007) Plant pathogen recognition mediated by promoter activation of the pepper Bs3 resistance gene. Science 318:645–648
Shaner G, Finney RE (1977) The effect of nitrogen fertilization on the expression of slow-mildewing resistance in Knox wheat. Phytopathology 67:1051–1056
Soto J, Mora R, Mathew B, León J, Gomez F, Ballvora A, López C (2017) Major novel QTL for resistance to cassava bacterial blight identified through a multi-environmental analysis. Frontiers in Plant Science 8:1169
Streubel J, Blucher C, Landgraf A, Boch J (2012) TAL effector RVD specificities and efficiencies. Nature Biotechnology 30:593–595
Streubel J, Pesce C, Hutin M, Koebnik R, Boch J, Szurek B (2013) Five phylogenetically close rice SWEET genes confer TAL effector-mediated susceptibility to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. New Phytologist 200:808–819
Trujillo CA, Ochoa JC, Mideros F, Restrepo S, López C, Bernal A (2014) A complex population structure of the cassava pathogen. Microbial Ecology 68:155–167
Verdier V, Boher B, Maraite H, Geiger JP (1994) Pathological and molecular characterization of Xanthomonas campestris strains causing diseases of cassava (Manihot esculenta). Applied and Environmental Microbiology 60:4478–4486
Wang C, Zhang X, Fan Y, Gao Y, Zhu Q, Zheng C, Qin T, Li Y, Che J, Zhang M, Yang B, Liu Y, Zhao K (2015) XA23 is an executor R protein and confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Molecular Plant 8:290–302
Zhang J, Yin Z, White F (2015) TAL effectors and the executor R genes. Frontiers in Plant Science 6:641
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a Colciencias grant (Contract Number 315-2013) and Dirección de Investigaciones de la Universidad Nacional, sede Bogotá (Proyecto Hermes 37508). The authors thank Adriana Bernal, Boris Szurek and Paula Diaz for fruitful discussions. Special acknowledgments to Adriana Bernal for reviewing and editing the manuscript and Paula Diaz for help in preparing the graphs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Section Editor: Rodrigo Almeida
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mora, R.E., Rodriguez, M.A., Gayosso, L.Y. et al. Using in vitro plants to study the cassava response to Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. manihotis infection. Trop. plant pathol. 44, 423–429 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-019-00296-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-019-00296-x