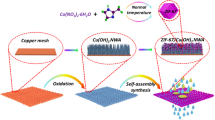
Abstract
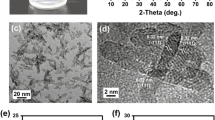
With the possibility of large-area processing, the ZIF-8-coated mesh membranes with rough micro-/nanostructures and underwater superoleophobic properties were successfully fabricated at ambient temperature and pressure. These membranes exhibited excellent separation efficiency over 99.99% for various oil-water mixtures with the residual oil content in the collected water less than 4 ppm, and high water flux of 10.2×104 L m−2 h−1. Furthermore, the ZIF-8-coated mesh membrane displayed outstanding stability towards high temperature and various organic solvents immersion. More importantly, based on its facile fabrication method, this kind of ZIF-8-coated mesh membrane can be easily enlarged, which is critical for the practical oil-water separation applications.
摘要
在常温常压条件下, 以金属网为载体, 成功地制备出表面具有微纳结构的ZIF-8分离膜, 该膜显示出优异的水下超疏油性能. 该方法制备的ZIF-8分离膜, 可以高效地分离多种油水混合物, 油水分离效率高达99.99%, 同时具有较高的水通量10.2×104 L m−2 h−1, 以及耐压性. 进一步, 通过高温处理以及多种常见有机溶剂浸泡, 该膜仍然可以保持高效的油水分离性能, 并且可以循环使用. 由于制备方法简单, 该类ZIF-8油水分离膜可以实现大面积制备, 这对于油水分离的实际应用至关重要.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schrope M. Oil spill: Deep wounds. Nature, 2011, 472: 152–154
Chan YJ, Chong MF, Law CL, et al. A review on anaerobic–aerobic treatment of industrial and municipal wastewater. Chem Eng J, 2009, 155: 1–18
Ge J, Shi LA, Wang YC, et al. Joule-heated graphene-wrapped sponge enables fast clean-up of viscous crude-oil spill. Nat Nanotech, 2017, 12: 434–440
Ge J, Zhao HY, Zhu HW, et al. Advanced sorbents for oil-spill cleanup: recent advances and future perspectives. Adv Mater, 2016, 28: 10459–10490
Gaaseidnes K, Turbeville J. Separation of oil and water in oil spill recovery operations. Pure Appl Chem, 1999, 71: 95–101
Zhang Y, Wei S, Liu F, et al. Superhydrophobic nanoporous polymers as efficient adsorbents for organic compounds. Nano Today, 2009, 4: 135–142
Cheryan M, Rajagopalan N. Membrane processing of oily streams. Wastewater treatment and waste reduction. J Membrane Sci, 1998, 151: 13–28
Kintisch E. An audacious decision in crisis gets cautious praise. Science, 2010, 329: 735–736
Peng Y, Li Y, Ban Y, et al. Metal-organic framework nanosheets as building blocks for molecular sieving membranes. Science, 2014, 346: 1356–1359
Ge Q, Wang Z, Yan Y. High-performance zeolite NAA membranes on polymer-zeolite composite hollow fiber supports. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 17056–17057
Chen L, Shi G, Shen J, et al. Ion sieving in graphene oxide membranes via cationic control of interlayer spacing. Nature, 2017, 550: 380–383
Yu Y, Chen H, Liu Y, et al. Selective separation of oil and water with mesh membranes by capillarity. Adv Colloid Interface Sci, 2016, 235: 46–55
Yu Z, Yun FF, Gong Z, et al. A novel reusable superhydrophilic NiO/Ni mesh produced by a facile fabrication method for superior oil/water separation. J Mater Chem A, 2017, 5: 10821–10826
Dong Y, Li J, Shi L, et al. Underwater superoleophobic graphene oxide coated meshes for the separation of oil and water. Chem Commun, 2014, 50: 5586–5589
Wen Q, Di J, Jiang L, et al. Zeolite-coated mesh film for efficient oil–water separation. Chem Sci, 2013, 4: 591–595
Zhang F, Zhang WB, Shi Z, et al. Nanowire-haired inorganic membranes with superhydrophilicity and underwater ultralow adhesive superoleophobicity for high-efficiency oil/water separation. Adv Mater, 2013, 25: 4192–4198
Crick CR, Gibbins JA, Parkin IP. Superhydrophobic polymercoated copper-mesh; membranes for highly efficient oil–water separation. J Mater Chem A, 2013, 1: 5943–5948
Dunderdale GJ, Urata C, Sato T, et al. Continuous, high-speed, and efficient oil/water separation using meshes with antagonistic wetting properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2015, 7: 18915–18919
Chu Z, Feng Y, Seeger S. Oil/water separation with selective superantiwetting/superwetting surface materials. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2015, 54: 2328–2338
Feng L, Li S, Li Y, et al. Super-hydrophobic surfaces: from natural to artificial. Adv Mater, 2002, 14: 1857–1860
Lu Z, Li Y, Lei X, et al. Nanoarray based “superaerophobic” surfaces for gas evolution reaction electrodes. Mater Horiz, 2015, 2: 294–298
Nakajima A, Hashimoto K, Watanabe T. Recent studies on superhydrophobic films. Monatshefte für Chem, 2001, 132: 31–41
Järn M, Granqvist B, Lindfors J, et al. A critical evaluation of the binary and ternary solid–oil–water and solid–water–oil interaction. Adv Colloid Interface Sci, 2006, 123-126: 137–149
Cassie ABD, Baxter S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans Faraday Soc, 1944, 40: 546–551
Yong J, Chen F, Yang Q, et al. Superoleophobic surfaces. Chem Soc Rev, 2017, 46: 4168–4217
Liu M, Wang S, Wei Z, et al. Bioinspired design of a superoleophobic and low adhesive water/solid interface. Adv Mater, 2009, 21: 665–669
Liu K, Yao X, Jiang L. Recent developments in bio-inspired special wettability. Chem Soc Rev, 2010, 39: 3240
Darmanin T, Guittard F. Superhydrophobic and superoleophobic properties in nature. Mater Today, 2015, 18: 273–285
Ma Q, Cheng H, Yu Y, et al. Preparation of superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic nanofiber-based meshes from waste glass for multifunctional oil/water separation. Small, 2017, 13: 1700391
Gao X, Xu LP, Xue Z, et al. Dual-scaled porous nitrocellulose membranes with underwater superoleophobicity for highly efficient oil/water separation. Adv Mater, 2014, 26: 1771–1775
Zhang JP, Chen XM. Exceptional framework flexibility and sorption behavior of a multifunctional porous cuprous triazolate framework. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130: 6010–6017
Yuan D, Zhao D, Sun D, et al. An isoreticular series of metalorganic frameworks with dendritic hexacarboxylate ligands and exceptionally high gas-uptake capacity. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2010, 49: 5357–5361
Li JR, Sculley J, Zhou HC. Metal–organic frameworks for separations. Chem Rev, 2012, 112: 869–932
Shen K, Zhang L, Chen X, et al. Ordered macro-microporous metal-organic framework single crystals. Science, 2018, 359: 206–210
Ye Y, Zhang L, Peng Q, et al. High anhydrous proton conductivity of imidazole-loaded mesoporous polyimides over a wide range from subzero to moderate temperature. J Am Chem Soc, 2015, 137: 913–918
Sun Q, He H, Gao WY, et al. Imparting amphiphobicity on singlecrystalline porous materials. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 13300
Huang G, Yang Q, Xu Q, et al. Polydimethylsiloxane coating for a palladium/MOF composite: highly improved catalytic performance by surface hydrophobization. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55: 7379–7383
Kim H, Yang S, Rao SR, et al. Water harvesting from air with metal-organic frameworks powered by natural sunlight. Science, 2017, 356: 430–434
Zhao C, Dai X, Yao T, et al. Ionic exchange of metal–organic frameworks to access single nickel sites for efficient electroreduction of CO2. J Am Chem Soc, 2017, 139: 8078–8081
Huang XC, Lin YY, Zhang JP, et al. Ligand-directed strategy for zeolite-type metal–organic frameworks: zinc(II) imidazolates with unusual zeolitic topologies. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2006, 45: 1557–1559
Park KS, Ni Z, Côté AP, et al. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2006, 103: 10186–10191
Qiu S, Xue M, Zhu G. Metal–organic framework membranes: from synthesis to separation application. Chem Soc Rev, 2014, 43: 6116–6140
Yao J, Wang H. Zeolitic imidazolate framework composite membranes and thin films: synthesis and applications. Chem Soc Rev, 2014, 43: 4470–4493
Kang Z, Xue M, Fan L, et al. “Single nickel source” in situ fabrication of a stable homochiral MOF membrane with chiral resolution properties. Chem Commun, 2013, 49: 10569–10571
Liu X, Demir NK, Wu Z, et al. Highly water-stable zirconium metal–organic framework UiO-66 membranes supported on alumina hollow fibers for desalination. J Am Chem Soc, 2015, 137: 6999–7002
Chen Y, Zhang S, Cao S, et al. Roll-to-roll production of metalorganic framework coatings for particulate matter removal. Adv Mater, 2017, 29: 1606221
Zhang G, Zhang J, Su P, et al. Non-activation MOF arrays as a coating layer to fabricate a stable superhydrophobic micro/nano flower-like architecture. Chem Commun, 2017, 53: 8340–8343
Jayaramulu K, Datta KKR, Rösler C, et al. Biomimetic superhydrophobic/superoleophilic highly fluorinated graphene oxide and ZIF-8 composites for oil-water separation. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55: 1178–1182
Kang Z, Wang S, Fan L, et al. Surface wettability switching of metal-organic framework mesh for oil-water separation. Mater Lett, 2017, 189: 82–85
Ma Q, Li G, Liu X, et al. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 film coated stainless steel meshes for highly efficient oil/water separation. Chem Commun, 2018, 54: 5530–5533
Zhang X, Zhao Y, Mu S, et al. UiO-66-coated mesh membrane with underwater superoleophobicity for high-efficiency oil–water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2018, 10: 17301–17308
Cai Y, Chen D, Li N, et al. Nanofibrous metal–organic framework composite membrane for selective efficient oil/water emulsion separation. J Membrane Sci, 2017, 543: 10–17
Guo H, Zhu G, Hewitt IJ, et al. “Twin copper source” growth of metal-organic framework membrane: Cu3(BTC)2 with high permeability and selectivity for recycling H2. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 1646–1647
Kang Z, Xue M, Fan L, et al. Highly selective sieving of small gas molecules by using an ultra-microporous metal–organic framework membrane. Energy Environ Sci, 2014, 7: 4053–4060
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21571076, 21390394, 21571079 and 61701543), “111” project (B07016), the Ministry of Science and Technology of SINOPEC (A381) and Open Projects of State Key Laboratory of Safety and Control for Chemicals (SKL-038). Song M, Zhao Y, and Xue M are inventors of a Chinese patent (CN201810148543.6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mingqiu Song is currently doing her research at the State Key Laboratory of Inorganic Synthesis and Preparative Chemistry, Jilin University, under the supervision of Prof. Shilun Qiu and Prof. Ming Xue. Her research interests mainly focus on the synthesis and design of MOF membranes and their applications.
Yuxin Zhao obtained his BSc degree in chemistry of materials at China University of Petroleum (East) in 2009. He obtained his PhD degree in chemical engineering and technology at China University of Petroleum (East) (2009–2014) in Prof. Zifeng Yan’s group, with Best Undergraduate Thesis Award. In July 2015, Zhao joined SINOPEC Research Institute of Safety Engineering to start his independent academic career. His research interests are in the synthesis of new classes of materials and nanostructures, with an emphasis on their functionality.
Ming Xue received BSc (2003) and PhD (2008) degree from Jilin University (China) in Prof. Shilun Qiu’s group. He joined the University of Texas at San Antonio (USA) during 2007–2008 and 2014–2015 in Prof. Banglin Chen’s group. Currently, he works in State Key Laboratory of Inorganic Synthesis and Preparative Chemistry, Jilin University. His group focuses on the design and synthesis of multifunctional MOF materials and membranes for the applications in adsorption, separation and other advanced applications.
Electronic supplementary material
40843_2018_9345_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
A stable ZIF-8-coated mesh membrane with micro-/nano architectures produced by a facile fabrication method for high-efficiency oil-water separation
Supplementary material, approximately 4.11 MB.
Supplementary material, approximately 2.22 MB.
Supplementary material, approximately 2.22 MB.
Supplementary material, approximately 3.58 MB.
Supplementary material, approximately 3.75 MB.
Supplementary material, approximately 3.33 MB.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, M., Zhao, Y., Mu, S. et al. A stable ZIF-8-coated mesh membrane with micro-/nano architectures produced by a facile fabrication method for high-efficiency oil-water separation. Sci. China Mater. 62, 536–544 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-018-9345-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-018-9345-3