Abstract
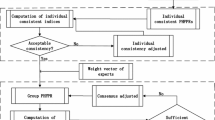
This paper studies the consistency and consensus models with local adjustment strategy for hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations (HFLPRs). A consistency and consensus reaching model with local adjustment strategy is devised. In the consistency improving process, only the most inconsistent preferences are suggested to be modified toward the preferences in the consistent HFLPR. In the consensus reaching process, an individual to group consensus index and a group consensus index are introduced to measure the consensus degree for the individual and the group. Meanwhile, only those HFLPRs whose consensus degrees are not within the predefined threshold are suggested to be modified, and only the preferences in these HFLPRs which have the largest distances from the preferences in group HFLPR are suggested to be revised by the group’s preference values. For both the consistency and consensus reaching processes, the improved preference values are still using the original linguistic terms. Finally, an example is illustrated to show the effectiveness of the proposed method, and comparative analyses with the existing methods are offered to show the advantages of the proposed method.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herrera-Viedma, E., Cabrerizo, F.J., Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W.: A review of soft consensus models in a fuzzy environment. Inf. Fusion 17, 4–13 (2014)
Palomares, I., Estrella, F.J., Martínez, L., Herrera, F.: Consensus under a fuzzy context: taxonomy, analysis framework AFRYCA and experimental case of study. Inf. Fusion 20, 252–271 (2014)
Torra, V.: Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 25, 529–539 (2010)
Rodríguez, R.M., Martínez, L., Herrera, F.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 20, 109–119 (2012)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J.: Distance and similarity measure for hesitant fuzzy linguistic terms sets and their application in multi-criteria decision making. Inf. Sci. 271, 125–142 (2014)
Chen, Z.S., Chin, K.S., Li, Y.L., Yang, Y.: Proportional hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set for multiple criteria group decision making. Inf. Sci. 357, 61–87 (2016)
Gou, X.J., Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Herrera, F.: Double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set and MULTIMOORA method: a case of study to evaluate the implementation status of haze controlling measures. Inf. Fusion 38, 22–34 (2017)
Rodríguez, R.M., Martínez, L., Herrera, F.: A group decision making model dealing with comparative linguistic expressions based on hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Inf. Sci. 241, 28–42 (2013)
Liu, H.B., Rodríguez, R.M.: A fuzzy envelope for hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set and its application to multicriteria decision making. Inf. Sci. 258, 220–238 (2014)
Wei, C.P., Zhao, N., Tang, X.J.: Operators and comparisons of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22, 575–585 (2014)
Wang, H.: Extended hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and their aggregation in group decision making. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 8, 14–33 (2015)
Xu, Y.J., Xu, A.W., Wang, H.M.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic linear programming technique for multidimensional analysis of preference for multi-attribute group decision making. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybernet. 7, 845–855 (2016)
Zhai, Y.L., Xu, Z.S., Liao, H.C.: Probabilistic linguistic vector-term set and its application in group decision making with multi-granular linguistic information. Appl. Soft Comput. 49, 801–816 (2016)
Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F., Li, H.Y.: On consistency measures of linguistic preference relations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 189, 430–444 (2008)
Zhu, B., Xu, Z.S.: Consistency measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22, 35–45 (2014)
Wang, H., Xu, Z.S.: Interactive algorithms for improving incomplete linguistic preference relations based on consistency measures. Appl. Soft Comput. 42, 66–79 (2016)
Dong, Y.C., Chen, X., Herrera, F.: Minimizing adjusted simple terms in the consensus reaching process with hesitant linguistic assessments in group decision making. Inf. Sci. 297, 95–117 (2015)
Zhang, Z.M., Wu, C.: A decision support model for group decision making with hesitant multiplicative preference relations. Inf. Sci. 282, 136–166 (2014)
Xu, Y.J., Cabrerizo, F.J., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A consensus model for hesitant fuzzy preference relations and its application in water allocation management. Appl. Soft Comput. 58, 265–284 (2017)
Ben-Arieh, D., Chen, Z.F.: Linguistic-labels aggregation and consensus measure for autocratic decision making using group recommendations. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 36, 558–568 (2006)
Mata, F., Martínez, L., Herrera-Viedma, E.: An adaptive consensus support model for group decision-making problems in a multigranular fuzzy linguistic context. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 17, 279–290 (2009)
Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F., Li, H.Y., Feng, B.: The OWA-based consensus operator under linguistic representation models using position indexes. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 203, 455–463 (2010)
Wu, Z.B., Xu, J.P.: A concise consensus support model for group decision making with reciprocal preference relations based on deviation measures. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 206, 58–73 (2012)
Alonso, S., Perez, I.J., Cabrerizo, F.J., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A linguistic consensus model for Web 2.0 communities. Appl. Soft Comput. 13, 149–157 (2013)
Xu, Y.J., Li, K.W., Wang, H.M.: Distance-based consensus models for fuzzy and multiplicative preference relations. Inf. Sci. 253, 56–73 (2013)
Liu, Y.J., Liang, C.Y., Chiclana, F., Wu, J.: A trust induced recommendation mechanism for reaching consensus in group decision making. Knowl. Based Syst. 11, 221–231 (2017)
Wu, J., Chiclana, F., Fujita, H., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A visual interaction consensus model for social network group decision making with trust propagation. Knowl. Based Syst. 122, 39–50 (2017)
Zadeh, L.A.: The Concept of a Linguistic Variable and Its Application to Approximate Reasoning. Springer, New York (1974)
Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., Verdegay, J.L.: A sequential selection process in group decision making with a linguistic assessment approach. Inf. Sci. 85, 223–239 (1995)
Xu, Z.S.: A method based on linguistic aggregation operators for group decision making with linguistic preference relations. Inf. Sci. 166, 19–30 (2004)
Xu, Z.S., Wang, H.: On the syntax and semantics of virtual linguistic terms for information fusion in decision making. Inf. Fusion 34, 43–48 (2017)
Xu, Z.S.: Deviation measures of linguistic preference relations in group decision making. Omega 33, 249–254 (2005)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic VIKOR method and its application in qualitative multiple criteria decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23, 1343–1355 (2015)
Xu, Y.J., Zhang, W.C., Wang, H.M.: A conflict-eliminating approach for emergency group decision of unconventional incidents. Knowl. Based Syst. 83, 92–104 (2015)
Zhang, G.Q., Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F.: Consistency and consensus measures for linguistic preference relations based on distribution assessments. Inf. Fusion 17, 46–55 (2014)
Pang, Q., Wang, H., Xu, Z.S.: Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Inf. Sci. 369, 128–143 (2016)
Bai, C.Z., Zhang, R., Qian, L.X., Wu, Y.N.: Comparisons of probabilistic linguistic term sets for multi-criteria decision making. Knowl. Based Syst. 119, 284–291 (2017)
Xu, Y.J., Chen, L., Rodríguez, R.M., Herrera, F., Wang, H.M.: Deriving the priority weights from incomplete hesitant fuzzy preference relations in group decision making. Knowl. Based Syst. 99, 71–78 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the Key Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 71633002), sponsored by Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Wen, X., Sun, H. et al. Consistency and Consensus Models with Local Adjustment Strategy for Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Preference Relations. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20, 2216–2233 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0438-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0438-3