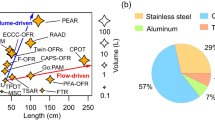
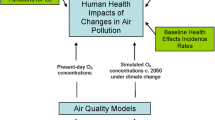
Abstract
Although the discovery of ammonia might trace to earlier Greek or Iranian alchemy, negative consequences of atmospheric ammonia to humans and the environment have only been discovered in the last decades. The global ammonia emissions have irrepressibly increased with the growth of population and anthropogenic activities. Fortunately, extensive research has been conducted with the goal to mitigate the anthropogenic sources of ammonia. The volatilization of nitrogen fertilizers is believed to be the most important anthropogenic source. However, atmospheric ammonia from urban areas has been attributed to vehicles or ammonia slip. Therefore, source apportionment of this trace atmospheric compound is a prerequisite to achieve ammonia mitigation. This review summarizes the current methods applied to source apportionment of atmospheric ammonia including in situ measurement of emission flux, emission inventory, satellite observation, and stable isotope signature. The advantages and drawbacks of these methods are discussed. The reliability of these methods depends on the scale in the field and the characteristics of emission sources. A combination of these methods is necessary to develop reliable models of atmospheric physics and chemistry.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreae MO, Merlet P. Emission of trace gases and aerosols from biomass burning. Glob Biogeochem Cycles. 2001;15(4):955–66.
Bash JO, Cooter EJ, Dennis RL, Walker JT, Pleim JE. Evaluation of a regional air-quality model with bidirectional NH3 exchange coupled to an agroecosystem model. Biogeosciences. 2013;10(3):1635–45.
Battye W, Aneja VP, Roelle PA. Evaluation and improvement of ammonia emissions inventories. Atmos Environ. 2003;37(27):3873–83.
Battye WH, Bray CD, Aneja VP, Tong D, Lee P, Tang Y. Evaluating ammonia (NH3) predictions in the NOAA National Air Quality Forecast Capability (NAQFC) using in situ aircraft, ground-level, and satellite measurements from the DISCOVER-AQ Colorado campaign. Atmos Environ. 2016;140:342–51.
Beer R, Shephard MW, Kulawik SS, Clough SA, Eldering A, Bowman KW, et al. First satellite observations of lower tropospheric ammonia and methanol. Geophys Res Lett. 2008;35(9):L09801. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL033642.
Behera SN, Sharma M, Aneja VP, Balasubramanian R. Ammonia in the atmosphere: a review on emission sources, atmospheric chemistry and deposition on terrestrial bodies. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2013;20(11):8092–131.
Bianchi F, Trostl J, Junninen H, Frege C, Henne S, Hoyle CR, et al. New particle formation in the free troposphere: a question of chemistry and timing. Science. 2016;352(6289):1109–12.
Bouwman AF, Lee DS, Asman WAH, Dentener FJ, Vander Hoek KW, Olivier JGJ. A global high-resolution emission inventory for ammonia. Glob Biogeochem Cycles. 1997;11(4):561–87.
Boyle E. Nitrogen pollution knows no bounds. Science. 2017;356(6339):700–1.
Bray CD, Battye W, Aneja VP, Tong D, Lee P, Tang Y, et al. Evaluating ammonia (NH3) predictions in the NOAA National Air Quality Forecast Capability (NAQFC) using in-situ aircraft and satellite measurements from the CalNex2010 campaign. Atmos Environ. 2017;163:65–76.
Buzek F, Cejkova B, Hellebrandova L, Jackova I, Lollek V, Lnenickova Z, et al. Isotope composition of NH3, NOx and SO2 air pollution in the Moravia-Silesian region, Czech Republic. Atmos Pollut Res. 2017;8(2):221–32.
Chang YH, Liu XJ, Deng CR, Dore AJ, Zhuang GS. Source apportionment of atmospheric ammonia before, during, and after the 2014 APEC summit in Beijing using stable nitrogen isotope signatures. Atmos Chem Phys. 2016;16(18):11635–47.
Ciezka M, Modelska M, Gorka M, Trojanowska-Olichwer A, Widory D. Chemical and isotopic interpretation of major ion compositions from precipitation: a one-year temporal monitoring study in Wroclaw, SW Poland. J Atmos Chem. 2016;73(1):61–80.
Clarisse L, Clerbaux C, Dentener F, Hurtmans D, Coheur PF. Global ammonia distribution derived from infrared satellite observations. Nat Geosci. 2009;2(7):479–83.
Clarisse L, Shephard MW, Dentener F, Hurtmans D, Cady-Pereira K, Karagulian F, et al. Satellite monitoring of ammonia: a case study of the San Joaquin Valley. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 2010;115(D13):D13302.
Clark CM, Tilman D. Loss of plant species after chronic low-level nitrogen deposition to prairie grasslands. Nature. 2008;451(7179):712–5.
Dammers E, Palm M, Van Damme M, Vigouroux C, Smale D, Conway S, et al. An evaluation of IASI-NH3 with ground-based Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy measurements. Atmos Chem Phys. 2016;16(16):10351–68.
Dammers E, Shephard MW, Palm M, Cady-Pereira K, Capps S, Lutsch E, et al. Validation of the CrIS fast physical NH3 retrieval with ground-based FTIR. Atmos Meas Tech. 2017;10(7):2645–67.
Dunne EM, Gordon H, Kurten A, Almeida J, Duplissy J, Williamson C, et al. Global atmospheric particle formation from CERN CLOUD measurements. Science. 2016;354(6316):1119–24.
European Environment Agency. Ammonia (NH3) emissions. 2011; https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/eea-32-ammonia-nh3-emissions-1/assessment-4. Accessed 18 June 2018.
Environmental Protection Agency. National Emissions Inventory (NEI) Data. United States 2011; https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories/2011-national-emissions-inventory-nei-data. Accessed 15 June 2018.
Faulkner WB, Powell JJ, Lange JM, Shaw BW, Lacey RE, Parnell CB. Comparison of dispersion models for ammonia emissions from a ground-level area source. Trans ASABE. 2007;50(6):2189–97.
Felix JD, Elliott EM, Gish T, Maghirang R, Cambal L, Clougherty J. Examining the transport of ammonia emissions across landscapes using nitrogen isotope ratios. Atmos Environ. 2014;95:563–70.
Felix JD, Elliott EM, Gish TJ, McConnell LL, Shaw SL. Characterizing the isotopic composition of atmospheric ammonia emission sources using passive samplers and a combined oxidation-bacterial denitrifier approach. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2013;27(20):2239–46.
Fowler D, Coyle M, Skiba U, Sutton MA, Cape JN, Reis S, et al. The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci. 2013;368(1621):20130164.
Fukuzaki N, Hayasaka H. Seasonal variations of nitrogen isotopic ratios of ammonium and nitrate in precipitations collected in the Yahiko-Kakuda Mountains area in Niigata Prefecture, Japan. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009;203(1–4):391–7.
Hastings MG, Sigman DM, Lipschultz F. Isotopic evidence for source changes of nitrate in rain at Bermuda. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 2003;108(D24):4790. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JD003789.
Hautier Y, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Adler PB, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, et al. Eutrophication weakens stabilizing effects of diversity in natural grasslands. Nature. 2014;508(7497):521–5.
Heald CL, Collett JL Jr, Lee T, Benedict KB, Schwandner FM, Li Y, et al. Atmospheric ammonia and particulate inorganic nitrogen over the United States. Atmos Chem Phys. 2012;12(21):10295–312.
Hendriks C, Kranenburg R, Kuenen JJP, Van den Bril B, Verguts V, Schaap M. Ammonia emission time profiles based on manure transport data improve ammonia modelling across north western Europe. Atmos Environ. 2016;131:83–96.
Huang RJ, Zhang YL, Bozzetti C, Ho KF, Cao JJ, Han YM, et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature. 2014;514(7521):218–22.
Huang X, Song Y, Li M, Li J, Huo Q, Cai X, et al. A high-resolution ammonia emission inventory in China. Glob Biogeochem Cycles. 2012;26(1):GB1030. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GB004161.
Hutchings NJ, Sommer SG, Andersen JM, Asman WAH. A detailed ammonia emission inventory for Denmark. Atmos Environ. 2001;35(11):1959–68.
Hyde BP, Carton OT, O'Toole P, Misselbrook TH. A new inventory of ammonia emissions from Irish agriculture. Atmos Environ. 2003;37(1):55–62.
Kang YN, Liu MX, Song Y, Huang X, Yao H, Cai XH, et al. High-resolution ammonia emissions inventories in China from 1980 to 2012. Atmos Chem Phys. 2016;16(4):2043–58.
Kirkby J, Curtius J, Almeida J, Dunne E, Duplissy J, Ehrhart S, et al. Role of sulphuric acid, ammonia and galactic cosmic rays in atmospheric aerosol nucleation. Nature. 2011;476(7361):429–U77.
Kulmala M, Kontkanen J, Junninen H, Lehtipalo K, Manninen HE, Nieminen T, et al. Direct observations of atmospheric aerosol nucleation. Science. 2013;339(6122):943–6.
Kulmala M, Pirjola U, Makela JM. Stable sulphate clusters as a source of new atmospheric particles. Nature. 2000;404(6773):66–9.
Li X, Wang S, Duan L, Hao J, Li C, Chen Y, et al. Particulate and trace gas emissions from open burning of wheat straw and corn stover in China. Environ Sci Technol. 2007;41(17):6052–8.
Liu J, Zhang Y, Liu X, Tang A, Qiu H, Zhang F. Concentrations and isotopic characteristics of atmospheric reactive nitrogen around typical sources in Beijing, China. J Arid Land. 2016;8(6):910–20.
Liu T, Wang X, Wang B, Ding X, Deng W, Lu S, et al. Emission factor of ammonia (NH3) from on-road vehicles in China: tunnel tests in urban Guangzhou. Environ Res Lett. 2014;9(6):064027. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/9/6/064027.
Lonsdale CR, Hegarty JD, Cady-Pereira KE, Alvarado MJ, Henze DK, Turner MD, et al. Modeling the diurnal variability of agricultural ammonia in Bakersfield, California, during the CalNex campaign. Atmos Chem Phys. 2017;17(4):2721–39.
Luo M, Shephard MW, Cady-Pereira KE, Henze DK, Zhu L, Bash JO, et al. Satellite observations of tropospheric ammonia and carbon monoxide: global distributions, regional correlations and comparisons to model simulations. Atmos Environ. 2015;106:262–77.
Malm WC, Schichtel BA, Barna MG, Gebhart KA, Rodriguez MA, Collett JL Jr, et al. Aerosol species concentrations and source apportionment of ammonia at Rocky Mountain National Park. J Air Waste Manage Assoc. 2013;63(11):1245–63.
Martinelli LA, Victoria RL, Sternberg LSL, Ribeiro A, Moreira MZ. Using stable isotopes to determine sources of evaporated water to the atmosphere in the Amazon basin. J Hydrol. 1996;183(3–4):191–204.
McFarlane DA, Keeler RC, Mizutani H. Ammonia volatilization in a Mexican bat cave ecosystem. Biogeochemistry. 1995;30(1):1–8.
Meng W, Zhong Q, Yun X, Zhu X, Huang T, Shen H, et al. Improvement of a global high-resolution ammonia emission inventory for combustion and industrial sources with new data from the residential and transportation sectors. Environ Sci Technol. 2017;51(5):2821–9.
Miller DJ, Sun K, Tao L, Pan D, Zondlo MA, Nowak JB, et al. Ammonia and methane dairy emission plumes in the San Joaquin Valley of California from individual feedlot to regional scales. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 2015;120(18):9718–38.
Norman AL, Barrie LA, Toom-Sauntry D, Sirois A, Krouse HR, Li SM, et al. Sources of aerosol sulphate at alert: apportionment using stable isotopes. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 1999;104(D9):11619–31.
Nowak JB, Neuman JA, Bahreini R, Middlebrook AM, Holloway JS, McKeen SA, et al. Ammonia sources in the California South Coast Air Basin and their impact on ammonium nitrate formation. Geophys Res Lett. 2012;39(7):102-14.
Pan Y, Tian S, Zhao Y, Zhang L, Zhu X, Gao J, et al. Identifying ammonia hotspots in China using a national observation network. Environ Sci Technol. 2018;52(7):3926–34.
Pan YP, Tian SL, Liu DW, Fang YT, Zhu XY, Zhang Q, et al. Fossil fuel combustion-related emissions dominate atmospheric ammonia sources during severe haze episodes: evidence from 15N-stable isotope in size-resolved aerosol ammonium. Environ Sci Technol. 2016;50(15):8049–56.
Paulot F, Jacob DJ, Pinder RW, Bash JO, Travis K, Henze DK. Ammonia emissions in the United States, European Union, and China derived by high-resolution inversion of ammonium wet deposition data: interpretation with a new agricultural emissions inventory (MASAGE_NH3). J Geophys Res-Atmos. 2014;119(7):4343–64.
Pinder RW, Walker JT, Bash JO, Cady-Pereira KE, Henze DK, Luo MZ, et al. Quantifying spatial and seasonal variability in atmospheric ammonia with in situ and space-based observations. Geophys Res Lett. 2011;38:L04802. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL046146.
Sarwar G, Corsi RL, Kinney KA, Banks JA, Torres VM, Schmidt C. Measurements of ammonia emissions from oak and pine forests and development of a non-industrial ammonia emissions inventory in Texas. Atmos Environ. 2005;39(37):7137–53.
Savard MM, Cole A, Smirnoff A, Vet R. Delta N-15 values of atmospheric N species simultaneously collected using sector-based samplers distant from sources—isotopic inheritance and fractionation. Atmos Environ. 2017;162:11–22.
Schiferl LD, Heald CL, Van Damme M, Clarisse L, Clerbaux C, Coheur P-F, et al. Interannual variability of ammonia concentrations over the United States: sources and implications. Atmos Chem Phys. 2016;16(18):12305–28.
Shephard MW, Cady-Pereira KE. Cross-track Infrared Sounder (CrIS) satellite observations of tropospheric ammonia. Atmos Meas Tech. 2015;8(3):1323–36.
Shephard MW, Cady-Pereira KE, Luo M, Henze DK, Pinder RW, Walker JT, et al. TES ammonia retrieval strategy and global observations of the spatial and seasonal variability of ammonia. Atmos Chem Phys. 2011;11(20):10743–63.
Skinner R, Ineson P, Jones H, Sleep D, Theobald M. Sampling systems for isotope-ratio mass spectrometry of atmospheric ammonia. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2006;20(2):81–8.
Smith AM, Keene WC, Maben JR, Pszenny AAP, Fischer E, Stohl A. Ammonia sources, transport, transformation, and deposition in coastal New England during summer. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 2007;112:D10S08. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD007574.
Stein LY, Yung YL. Production, isotopic composition, and atmospheric fate of biologically produced nitrous oxide. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci. 2003;31:329–56.
Sun L, Liu Y, Wang J, Khalil MAK, Zou J, Xiong Z. Atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus deposition at three sites in Nanjing, China, and possible links to nitrogen deposition sources. Clean Soil Air Water. 2014;42(11):1650–9.
Sutton MA, Erisman JW, Dentener F, Moeller D. Ammonia in the environment: from ancient times to the present. Environ Pollut. 2008;156(3):583–604.
Sutton MA, Nemitz E, Milford C, Fowler D, Moreno J, San Jose R, et al. Micrometeorological measurements of net ammonia fluxes over oilseed rape during two vegetation periods. Agric For Meteorol. 2000;105(4):351–69.
Sutton MA, Reis S, Riddick SN, Dragosits U, Nemitz E, Theobald MR, et al. Towards a climate-dependent paradigm of ammonia emission and deposition. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci. 2013;368(1621):13.
Tyler SC. Stable carbon isotope ratios in atmospheric methane and some of its sources. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 1986;91(D12):3232–8.
Van Damme M, Clarisse L, Dammers E, Liu X, Nowak JB, Clerbaux C, et al. Towards validation of ammonia (NH3) measurements from the IASI satellite. Atmos Meas Tech. 2015;8(3):1575–91.
Velthof GL, Lesschen JP, Webb J, Pietrzak S, Miatkowski Z, Pinto M, et al. The impact of the nitrates directive on nitrogen emissions from agriculture in the EU-27 during 2000–2008. Sci Total Environ. 2014;468:1225–33.
Walker JM, Philip S, Martin RV, Seinfeld JH. Simulation of nitrate, sulfate, and ammonium aerosols over the United States. Atmos Chem Phys. 2012;12(22):11213–27.
Walker JT, Jones MR, Bash JO, Myles L, Meyers T, Schwede D, et al. Processes of ammonia air-surface exchange in a fertilized Zea mays canopy. Biogeosciences. 2013;10(2):981–98.
Walters WW, Hastings MG. Collection of ammonia for high time-resolved nitrogen isotopic characterization utilizing an acid-coated honeycomb denuder. Anal Chem. 2018;90(13):8051-7.
Wentworth GR, Murphy JG, Benedict KB, Bangs EJ, Collett JL Jr. The role of dew as a night-time reservoir and morning source for atmospheric ammonia. Atmos Chem Phys. 2016;16(11):7435–49.
Xiao HW, Xiao HY, Long AM, Liu CQ. δ15N-NH4 + variations of rainwater: application of the Rayleigh model. Atmos Res. 2015;157:49–55.
Xiao HW, Xiao HY, Long AM, Wang YL. Who controls the monthly variations of NH4 + nitrogen isotope composition in precipitation? Atmos Environ. 2012;54:201–6.
Zhang XM, Wu YY, Liu XJ, Reis S, Jin JX, Dragosits U, et al. Ammonia emissions may be substantially underestimated in China. Environ Sci Technol. 2017;51(21):12089–96.
Zhang Y, Dore AJ, Ma L, Liu XJ, Ma WQ, Cape JN, et al. Agricultural ammonia emissions inventory and spatial distribution in the North China Plain. Environ Pollut. 2010;158(2):490–501.
Zhao DW, Wang AP. Estimation of anthropogenic ammonia emissions in Asia. Atmos Environ. 1994;28(4):689–94.
Zheng JY, Yin SS, Kang DW, Che WW, Zhong LJ. Development and uncertainty analysis of a high-resolution NH3 emissions inventory and its implications with precipitation over the Pearl River Delta region, China. Atmos Chem Phys. 2012;12(15):7041–58.
Zhou Y, Cheng S, Lang J, Chen D, Zhao B, Liu C, et al. A comprehensive ammonia emission inventory with high-resolution and its evaluation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region, China. Atmos Environ. 2015;106:305–17.
Zhu L, Henze DK, Bash JO, Cady-Pereira KE, Shephard MW, Luo M, et al. Sources and impacts of atmospheric NH3: current understanding and frontiers for modeling, measurements, and remote sensing in North America. Curr Pollut Rep. 2015;1(2):95–116.
Zhu L, Henze DK, Cady-Pereira KE, Shephard MW, Luo M, Pinder RW, et al. Constraining U.S. ammonia emissions using TES remote sensing observations and the GEOS-Chem adjoint model. J Geophys Res-Atmos. 2013;118(8):3355–68.
Zipf EC, Prasad SS. Evidence for new sources of NOx in the lower atmosphere. Science. 1998;279(5348):211–3.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant 2017YFC0210100), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 41405144, 21777085, 21607094), the Shandong Natural Science Foundation (ZR2016BQ29), and the Foundation of Shandong University (11440076614091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Air Pollution
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Y., Tian, S. & Pan, Y. Revealing the Sources of Atmospheric Ammonia: a Review. Curr Pollution Rep 4, 189–197 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-018-0096-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-018-0096-6