Abstract
Purpose
The aim of the current study was to assess the psychometric proprieties of the Italian version of the latest edition of the Questionnaire of Eating and Weight Patterns (QEWP-5), evaluating its accuracy in screening patients with binge-eating disorder (BED).
Methods
The Italian translation of the tool was administered to 604 Italian-speaking adults seeking treatment for obesity. The clinical sample was given the Eating Disorder Examination interview to assess for BED. Participants also completed the Symptom Checklist 90, the Obesity-Related Well-Being and the Binge-Eating Scale.
Results
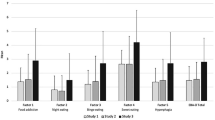
The sensitivity of the QEWP-5 was 0.49, and its specificity 0.93. The positive and negative predictive values were 0.34 and 0.96, respectively. Agreement between QEWP-5 and EDE using Cohen’s kappa was 0.35. Nevertheless, among patients with an EDE diagnosis of no BED, those ‘QEWP-5-positive’ for BED displayed higher eating-disorder and general psychopathology scores, poorer weight-related quality of life, and greater severity of binge-eating behaviours than those ‘QEWP-5-negative’ for BED.
Conclusion
Despite the low concordance with the EDE interview in terms of detecting the presence of BED, the QEWP-5 may be a useful initial screening tool for the clinical assessment of adults seeking treatment for obesity.
Level of evidence
Level V, Descriptive study.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5™). American Psychiatric Publishing, Arlington
Udo T, Grilo CM (2018) Prevalence and Correlates of DSM-5-Defined Eating Disorders in a Nationally Representative Sample of U.S Adults. Biol Psychiatry 84(5):345–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.03.014
Erskine HE, Whiteford HA (2018) Epidemiology of binge eating disorder. Curr Opin Psychiatry 31(6):462–470. https://doi.org/10.1097/yco.0000000000000449
Machado PP, Goncalves S, Hoek HW (2013) DSM-5 reduces the proportion of EDNOS cases: evidence from community samples. Int J Eat Disord 46(1):60–65. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22040
Solmi F, Hotopf M, Hatch SL, Treasure J, Micali N (2016) Eating disorders in a multi-ethnic inner-city UK sample: prevalence, comorbidity and service use. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 51(3):369–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-015-1146-7
Gorin AA, Niemeier HM, Hogan P, Coday M, Davis C, DiLillo VG, Gluck ME, Wadden TA, West DS, Williamson D, Yanovski SZ (2008) Binge eating and weight loss outcomes in overweight and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes: results from the Look AHEAD trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65(12):1447–1455. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.65.12.1447
Allison KC, Crow SJ, Reeves RR, West DS, Foreyt JP, Dilillo VG, Wadden TA, Jeffery RW, Van Dorsten B, Stunkard AJ (2007) Binge eating disorder and night eating syndrome in adults with type 2 diabetes. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md) 15(5):1287–1293. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2007.150
Ricca V, Mannucci E, Moretti S, Di Bernardo M, Zucchi T, Cabras PL, Rotella CM (2000) Screening for binge eating disorder in obese outpatients. Compr Psychiatry 41(2):111–115
Pace CS, Muzi S (2019) Binge-eating symptoms, emotional-behavioral problems and gender differences among adolescents: a brief report. Mediterr J Clini Psychol 7(2):1–9
Kessler RC, Berglund PA, Chiu WT, Deitz AC, Hudson JI, Shahly V, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, Alonso J, Angermeyer MC, Benjet C, Bruffaerts R, de Girolamo G, de Graaf R, Maria Haro J, Kovess-Masfety V, O’Neill S, Posada-Villa J, Sasu C, Scott K, Viana MC, Xavier M (2013) The prevalence and correlates of binge eating disorder in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. Biol Psychiat 73(9):904–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.11.020
Citrome L (2017) Binge-eating disorder and comorbid conditions: differential diagnosis and implications for treatment. J Clin Psychiatry 78(Suppl 1):9–13. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.sh16003su1c.02
Marcus MD, Wing RR, Hopkins J (1988) Obese binge eaters: affect, cognitions, and response to behavioural weight control. J Consult Clin Psychol 56(3):433–439
Sherwood NE, Jeffery RW, Wing RR (1999) Binge status as a predictor of weight loss treatment outcome. Int J Obes Relat Metabol Disord 23(5):485–493
Vamado PJ, Williamson DA, Bentz BG, Ryan DH, Rhodes SK, O’Neil PM, Sebastian SB, Barker SE (1997) Prevalence of binge eating disorder in obese adults seeking weight loss treatment. Eat Weight Disord 2(3):117–124
Allison KC, Wadden TA, Sarwer DB, Fabricatore AN, Crerand CE, Gibbons LM, Stack RM, Stunkard AJ, Williams NN (2006) Night eating syndrome and binge eating disorder among persons seeking bariatric surgery: prevalence and related features. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2(2):153–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soard.2006.03.014
Yanovski SZ, Marcus MD, Wadden TA, Walsh BT (2015) The Questionnaire on eating and weight patterns-5 (QEWP-5): an updated screening instrument for binge eating disorder. Int J Eat Disord 48(3):259–261. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22372
Spitzer RL, Devlin M, Walsh BT, Hasin D, Wing R, Marcus MD, Stunkard A, Wadden T, Yanovski S, Agras S, Mitchell J, Nonas CA (1992) Binge eating disorder: a multisite trial of the diagnostic criteria. Int J Eat Disord 11:191–203
Spitzer RL, Yanovski SZ, Marcus MD (1994) Questionnaire on eating and weight patterns. Behavioral Measurement Database Services, Pittsburgh
de Zwaan M, Mitchell JE, Specker SM, Pyle RL, Mussell MP, Seim HC (1993) Diagnosing binge eating disorder: level of agreement between self-report and expert-rating. Int J Eat Disord 14(3):289–295
Dymek-Valentine M, Rienecke-Hoste R, Alverdy J (2004) Assessment of binge eating disorder in morbidly obese patients evaluated for gastric bypass: SCID versus QEWP-R. Eat Weight Disord 9(3):211–216
Celio AA, Wilfley DE, Crow SJ, Mitchell J, Walsh BT (2004) A comparison of the binge eating scale, questionnaire for eating and weight patterns-revised, and eating disorder examination questionnaire with instructions with the eating disorder examination in the assessment of binge eating disorder and its symptoms. Int J Eat Disord 36(4):434–444. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20057
Johnson WG, Kirk AA, Reed AE (2001) Adolescent version of the questionnaire of eating and weight patterns: reliability and gender differences. Int J Eat Disord 29(1):94–96
Garcia Diaz E, Martin Folgueras T, Morcillo Herrera L, Jimenez Sosa A (2012) Diagnostic and psychopathologic evaluation of binge eating disorder in gastric bypass patients. Nutr Hosp 27(2):553–557. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0212-16112012000200031
Borges MB, Morgan CM, Claudino AM, da Silveira DX (2005) Validation of the Portuguese version of the Questionnaire on Eating and Weight Patterns-Revised (QEWP-R) for the screening of binge eating disorder. Revista brasileira de psiquiatria 27(4):319–322
Hilton A, Skrutkowski M (2002) Translating instruments into other languages: development and testing processes. Cancer Nurs 25(1):1–7
Fairburn CG, Beglin SJ (2008) Cognitive behavior therapy and eating disorders. In: Fairburn CG (ed) Eating disorder examination questionnaire (EDE-Q 6.0). Guiford Press, New York, pp 309–313
Calugi S, Ricca V, Castellini G, Lo Sauro C, Ruocco A, Chignola E, El Ghoch M, Dalle Grave R (2015) The eating disorder examination: reliability and validity of the Italian version. Eat Weight Disord 20(4):505–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-015-0191-2
Derogatis LR, Savitz KL (1999) The SCL-90-R, brief symptom inventory, and matching clinical rating scales. In: Maruish ME (ed) The use of psychological testing for treatment planning and outcomes assessment. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers, Mahwah, pp 679–724
Prunas A, Sarno I, Preti E, Madeddu F, Perugini M (2012) Psychometric properties of the Italian version of the SCL-90-R: a study on a large community sample. Eur Psychiatry 27(8):591–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2010.12.006
Mannucci E, Ricca V, Barciulli E, Di Bernardo M, Travaglini R, Cabras PL, Rotella CM (1999) Quality of life and overweight: the obesity related well-being (Orwell 97) questionnaire. Addict Behav 24(3):345–357
Gormally J, Black S, Daston S, Rardin D (1982) The assessment of binge eating severity among obese persons. Addict Behav 7(1):47–55
Di Bernardo M, Barciulli E, Ricca V, Mannucci E, Moretti S, Cabras PL, Rotella CM (1998) Binge Eating Scale in obese patients: validation of the Italian version. Minerva Psichiatr 39(3):125–130
Imperatori C, Innamorati M, Lamis DA, Contardi A, Continisio M, Castelnuovo G, Manzoni GM, Fabbricatore M (2016) Factor structure of the binge eating scale in a large sample of obese and overweight patients attending low energy diet therapy. Eur Eat Disord Rev 24(2):174–178. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.2384
Brody ML, Walsh BT, Devlin MJ (1994) Binge eating disorder: reliability and validity of a new diagnostic category. J Consult Clin Psychol 62(2):381–386
Greeno CG, Marcus MD, Wing RR (1995) Diagnosis of binge eating disorder: discrepancies between a questionnaire and clinical interview. Int J Eat Disord 17(2):153–160
Gladis MM, Wadden TA, Foster GD, Vogt RA, Wingate BJ (1998) A comparison of two approaches to the assessment of binge eating in obesity. Int J Eat Disord 23(1):17–26
Wilfley DE, Schwartz MB, Spurrell EB, Fairburn CG (1997) Assessing the specific psychopathology of binge eating disorder patients: interview or self-report? Behav Res Ther 35(12):1151–1159
Fairburn CG, Beglin SJ (1994) Assessment of eating disorders: interview or self-report questionnaire? Int J Eat Disord 16(4):363–370
Acknowledgements
We thank Marsha Marcus, Ph.D. for her help in the translation process of the Italian version of the QEWP-5.
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedure performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calugi, S., Pace, C.S., Muzi, S. et al. Psychometric proprieties of the Italian version of the questionnaire on eating and weight patterns (QEWP-5) and its accuracy in screening for binge-eating disorder in patients seeking treatment for obesity. Eat Weight Disord 25, 1739–1745 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-019-00818-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-019-00818-1