Abstract
Purpose
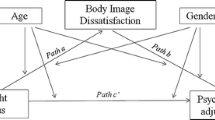
Examine whether unhealthy and extreme weight control behaviors (WCBs) mediate the relationship between youth weight status and disease-specific health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in treatment-seeking youth who are overweight and obese (OV/OB).
Method
82 youth 10–17 years of age who were OV/OB and attending an outpatient obesity-related medical appointment completed measures assessing unhealthy and extreme WCBs and disease-specific HRQOL. Parents completed a demographic questionnaire and medical staff measured youth height and weight.
Results
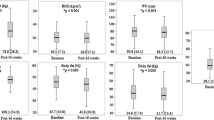
Regression analyses revealed that unhealthy WCBs mediated the associations between youth weight status and emotional and social avoidance disease-specific HRQOL, such that higher body mass index (BMI) predicted unhealthy WCBs, which were ultimately associated with poorer emotional and social HRQOL. Mediation analyses were not significant for total, physical, teasing/marginalization, and positive attributes disease-specific HRQOL. In addition, extreme WCBs did not mediate the association between youth weight status and any subscales of the disease-specific HRQOL measure.
Discussion
Weight status is an important predictor of disease-specific HRQOL in OV/OB youth; however, the association with emotional and social HRQOL is partially accounted for by youth engagement in unhealthy WCBs. Clinicians and researchers should assess WCBs and further research should explore and evaluate appropriate intervention strategies to address unhealthy WCBs in pediatric weight management prevention and treatment efforts.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL et al (2014) Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011–2012. JAMA 311(8):806–814. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.732
Daniels SR (2006) The consequences of childhood overweight and obesity. Future Child 16(1):47–67
Zeller MH et al (2006) Health-related quality of life and depressive symptoms in adolescents with extreme obesity presenting for bariatric surgery. Pediatrics 117(4):1155–1161. doi:10.1542/peds.2005-1141
Puhl RM, Luedicke J, Heuer C (2011) Weight-based victimization toward overweight adolescents: observations and reactions of peers. J Sch Health 81(11):696–703. doi:10.1111/j.1746-1561.2011.00646.x
Singh AS et al (2008) Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obes Rev 9(5):474–488. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2008.00475.x
Reilly JJ, Kelly J (2011) Long-term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: systematic review. Int J Obes 35(7):891–898. doi:10.1038/ijo.2010.222
Wang Y et al (2008) Will all Americans become overweight or obese? Estimating the progression and cost of the US obesity epidemic. Obesity 16(10):2323–2330. doi:10.1038/oby.2008.351
Palermo TM et al (2008) Evidence-based assessment of health-related quality of life and functional impairment in pediatric psychology. J Pediatr Psychol 33(9):983–996. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jsn038 (discussion 997–8)
Panepinto JA et al (2005) Health-related quality of life in children with sickle cell disease: child and parent perception. Br J Haematol 130(3):437–444. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05622.x
Schwimmer JB, Burwinkle TM, Varni JW (2003) Health-related quality of life of severely obese children and adolescents. JAMA 289(14):1813–1819. doi:10.1001/jama.289.14.1813
Janicke DM et al (2007) Impact of psychosocial factors on quality of life in overweight youth. Obesity 15(7):1799–1807. doi:10.1038/oby.2007.214
Zeller MH, Modi AC (2006) Predictors of health-related quality of life in obese youth. Obesity 14(1):122–130. doi:10.1038/oby.2006.15
Gowey MA et al (2014) Disordered eating and health-related quality of life in overweight and obese children. J Pediatr Psychol 39(5):552–561. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jsu012
Modi AC, Zeller MH (2011) The IWQOL-Kids©: establishing minimal clinically important difference scores and test-retest reliability. Int J Pediatr Obes 6(2–2):e94–e96. doi:10.3109/17477166.2010.500391
Teixeira PJ et al (2004) Pretreatment predictors of attrition and successful weight management in women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 28(9):1124–1133. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802727
Cushing CC, Steele RG (2012) Psychometric properties of sizing me up in a community sample of 4th and 5th grade students with overweight and obesity. J Pediatr Psychol 37(9):1012–1022. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jss075
Zeller MH, Modi AC (2009) Development and initial validation of an obesity-specific quality-of-life measure for children: sizing me up. Obesity 17(6):1171–1177. doi:10.1038/oby.2009.47
Kolodziejczyk JK et al (2015) Influence of specific individual and environmental variables on the relationship between body mass index and health-related quality of life in overweight and obese adolescents. Qual Life Res 24(1):251–261. doi:10.1007/s11136-014-0745-1
Guilfoyle SM, Zeller MH, Modi AC (2010) Parenting stress impacts obesity-specific health-related quality of life in a pediatric obesity treatment-seeking sample. J Dev Behav Pediatr 31(1):17–25. doi:10.1097/DBP.0b013e3181c73641
Herzer M et al (2011) Perceived social support and its association with obesity-specific health-related quality of life. J Dev Behav Pediatr 32(3):188–195. doi:10.1097/DBP.0b013e318208f576
Neumark-Sztainer D et al (2003) Correlates of unhealthy weight-control behaviors among adolescents: implications for prevention programs. Health Psychol 22(1):88–98
Neumark-Sztainer D et al (2012) Dieting and unhealthy weight control behaviors during adolescence: associations with 10-year changes in body mass index. J Adolesc Health 50(1):80–86. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2011.05.010
Neumark-Sztainer D et al (2002) Overweight status and eating patterns among adolescents: where do youths stand in comparison with the healthy people 2010 objectives? Am J Public Health 92(5):844–851
Goldschmidt AB et al (2008) Disordered eating attitudes and behaviors in overweight youth. Obesity 16(2):257–264. doi:10.1038/oby.2007.48
Neumark-Sztainer D et al (2002) Weight-related concerns and behaviors among overweight and nonoverweight adolescents: implications for preventing weight-related disorders. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 156(2):171–178
Kuczmarski RJ et al (2000) CDC growth charts: United States. Adv Data 314:1–27
Neumark-Sztainer D et al (2006) Does body satisfaction matter? Five-year longitudinal associations between body satisfaction and health behaviors in adolescent females and males. J Adolesc Health 39(2):244–251. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2005.12.001
Neumark-Sztainer D et al (2008) Family meals and disordered eating in adolescents: longitudinal findings from project EAT. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 162(1):17–22. doi:10.1001/archpediatrics.2007.9
Hayes AF (2013) Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis. Guilford Press, New York
Preacher KJ, Rucker DD, Hayes AF (2007) Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivar Behav Res 42:185–227
Neumark-Sztainer D (2005) Can we simultaneously work toward the prevention of obesity and eating disorders in children and adolescents? Int J Eat Disord 38(3):220–227. doi:10.1002/eat.20181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted in compliance with the American Psychological Association Ethics Code. This study was reviewed and approved by the governing Institutional Review Board.
Informed consent
All participants gave informed consent/assent prior to participating in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, C.S., Gowey, M.A., Cohen, M.J. et al. Unhealthy weight control behaviors mediate the association between weight status and weight-specific health-related quality of life in treatment-seeking youth who are obese. Eat Weight Disord 22, 125–132 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-016-0262-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-016-0262-z