Abstract
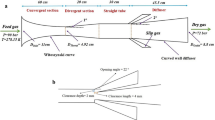
Taking vapor–liquid separators used in marine desalination as objects, a novel kind of plate-type vapor–liquid separator with groove is designed to achieve a more prominent separation effect. The Eulerian–Lagrangian approach is applied to simulate the two-phase flow in the separator. The SST κ–ω turbulence model is utilized to simulate the continuous phase, and discrete phase model (DPM) is employed to calculate the water droplet distribution and the corresponding trajectories, which is verified by the experimental results from the literature. The impacts from the groove height, width and depth on the separator performance are studied. Furthermore, to acquire the optimal geometry of the separators with groove, a dimensionless objective function considering the space size, separation efficiency and pressure drop is proposed, and the corresponding prediction model is established based on the response surface methodology. Compared to the traditional type, the computational fluid dynamic (CFD) simulation results show that a higher velocity and bigger circulation region contribute to a much more comprehensive performance in the proposed separator. After determining the optimal values for all the parameters, a discrepancy value of 5.2% between the simulation results and the prediction value is attained, which indicates that the prediction model is applicable to guide the design of the separator. Further study shows that the optimal novel separator guarantees the separation efficiency with much smaller size compared with the original one.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Lateral area (mm2)
- a 1 ,a 2 ,a 3 :
-
Constants
- C D :
-
Drag force coefficient
- D :
-
Groove depth (mm)
- D ω :
-
Cross-diffusion term(kg/m3s2)
- d :
-
Diameter (mm)
- e :
-
Error
- F :
-
Additional force per particle mass (N)
- g :
-
Gravity acceleration (m/s2)
- G κ :
-
Generation of κ (kg/ms2)
- G ω :
-
Generation of ω (kg/m3s2)
- H :
-
Groove height (mm)
- m :
-
Mass (kg)
- Ob1 :
-
The difference of η and Δp
- Ob2 :
-
Objective function
- Δp :
-
Pressure drop (Pa)
- P :
-
Plate pitch (mm)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- Re p :
-
Relative Reynolds number
- S κ :
-
Source terms of κ (kg/ms2)
- S ω :
-
Source terms of ω (1/s)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- u, v :
-
Velocity (m/s)
- x, y :
-
Directions
- X :
-
Variables
- Y κ :
-
Dissipation of κ (kg/ms2)
- Y ω :
-
Dissipation of ω (kg/m3s2)
- α :
-
Turning angle (°)
- β :
-
Coefficient
- η :
-
Separation efficiency
- κ :
-
Turbulence kinetic energy (m2/s2)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (Pa s)
- μ t :
-
Turbulent viscosity (Pa s)
- σ κ :
-
Turbulent Prandtl number of κ
- σ ω :
-
Turbulent Prandtl number of ω
- ω:
-
Specific dissipation rate of κ (1/s)
- ρ :
-
Density(kg/m3)
- p:
-
Particle
- i,j,k :
-
Indexes
- max:
-
Maximum
References
Chen Q, Li Y, Chua KJ (2016) On the thermodynamic analysis of a novel low-grade heat driven desalination system. Energy Convers Manage 128:145–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.09.070
Shu G, Liang Y, Wei H et al (2013) A review of waste heat recovery on two-stroke IC engine aboard ships. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 19(1):385–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.11.034
Liu Y, Yu D, Jiang J et al (2017) Experimental and numerical evaluation of the performance of a novel compound demister. Desalination 409:115–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.01.022
Miao C, Xie CG, Feng HJ et al (2011) Development status and research proposals on seawater desalination technology for ships. Ship Eng 33:6–9. https://doi.org/10.13788/j.cnki.cbgc.2011.06.011
Venkatesan G, Kulasekharan N, Iniyan S (2014) Numerical analysis of curved vane demisters in estimating water droplet separation efficiency. Desalination 339:40–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2014.02.013
Josang AI (2002) Numerical and experimental studies of droplet-gas flow, Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Technology. Dissertation, Telemark University
Ghetti S (2003) Investigation of entrainment phenomena in inertial separators. Dissertation, University of Pisa
Li J, Huang S, Wang X (2007) Numerical study of steam-water separators with wave-type vanes. Chin J Chem Eng 15(4):492–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1004-9541(07)60114-1
Estakhrsar MHH, Rafee R (2016) Effects of wavelength and number of bends on the performance of zigzag demisters with drainage channels. Appl Math Model 40:685–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2015.08.023
Galletti C, Brunazzi E, Tognotti L (2008) A numerical model for gas flow and droplet motion in wave-plate mist eliminators with drainage channels. Chem Eng Sci 63:5639–5652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2008.08.013
Rafee R, Rahimzadeh H, Ahmadi G (2010) Numerical simulations of airflow and droplet transport in a wave-plate mist eliminator. Chem Eng Res Des 88:1393–1404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2010.03.001
James PW, Wang Y, Azzopardi BJ et al (2003) The role of drainage channels in the performance of wave-plate mist eliminators. Trans IChemE, Part A, Chem Eng Res Design 81(6):639–648. https://doi.org/10.1205/026387603322150499
Estakhrsar MHH, Rafee R (2013) Effect of drainage channel dimensions on the performance of wave-plate mist eliminators. Korean J Chem Eng 30(6):1301–1311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0032-9
Abdolhossein S, Rahimzadeh H, Rafee R (2010) Determination of minimum pressure drop at different plate spacings and air velocity in a wave-plate mist eliminator. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 7(4):590–597. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.611
Venkatesan G, Kulasekharan N, Iniyan S (2014) Design and selection of curved vane demisters using Taguchi based CFD analysis. Desalination 339:40–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2014.09.018
Narimani E, Shahhoseini S (2011) Optimization of vane mist eliminators. Appl Therm Eng 31:188–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2010.08.031
Zhao J, Jin B, Zhong Z (2007) Study of the separation efficiency of a demister vane with response surface methodology. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.046
Kavousi F, Behjat Y, Shahhoseini S (2013) Optimal design of drainage channel geometry parameters in vane demister liquid–gas separators. Chem Eng Res Des 91(7):1212–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2013.01.012
Cai ZF, Zhao JM, Zhao P, Wang Y (2014) Manufacture of the corrugated plate of a new and high efficient vapor-liquid separation dryer. Chem Eng Mach 41(3):381–383. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0254-6094.2014.03.029
Menter FR (1994) Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J 32(8):1598–1605. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.12149
Zamora B, Kaiser AS (2010) Comparative efficiency evaluations of four types of cooling tower drift eliminator, by numerical investigation. Chem Eng Sci 66:1232–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2010.12.023
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51406081) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2016M601801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Celso Kazuyuki Morooka.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, L., Han, D., He, W. et al. Performance analysis of plate-type vapor–liquid separators with groove used in marine desalination. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 40, 243 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1104-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1104-x