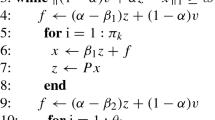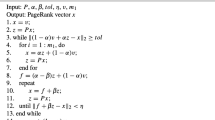Abstract
In this paper, we extend the two-step matrix splitting iteration approach by introducing a new relaxation parameter. The main idea is based on the inner–outer iteration for solving the PageRank problems proposed by Gleich et al. (J Sci Comput 32(1): 349–371, 2010) and Bai (Numer Algebra Cont Optim 2(4): 855–862, 2012) and the two-step splitting iteration presented by Gu et al. (Appl Math Comput 271: 337–343, 2015). The theoretical analysis results show that the proposed method is efficient. Numerical experiments demonstrate that the convergence performances of the method are better than the existing methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Z-Z, Golub GH, Lu L-Z, Yin J-F (2004) Block triangular and skew-Hermitian splitting methods for positive-definite linear systems. SIAM J Sci Comput 26(3):844–863
Bai Z-Z (2012) On convergence of the inner-outer iteration method for computing PageRank. Numer Algebra Cont Optim 2(4):855–862
Bai Z-Z, Sun J-C, Wang D-R (1996) A unified framework for the construction of various matrix multisplitting iterative methods for large sparse system of linear equations. Comput Math Appl 32(12):51–76
Berkhin P (2005) A survey on PageRank computing. Internet Math 2(1):73–120
Capizzano SS (2005) Jordan canonical form of the Google matrix: a potential contribution to the PageRank computation. SIAM J Matrix Anal Appl 27(2):305–312
Cottle RW, Dantzig G (1968) Complementary pivot theory of mathematical programming. Linear Algebra Appl 1:103–125
Cottle RW, Pang J-S, Stone RE (1992) The linear complementarity problem. Academic Press, New York
Fan C, Simpson O (2015) Distributed algorithms for finding local clusters using heat kernel pagerank, algorithms and models for the web graph. Springer International Publishing, pp 177–189
Gleich DF, Gray AP, Greif C, Lau T (2010) An inner-outer iteration for computing PageRank. SIAM J Sci Comput 32(1):349–371
Golub GH, Greif C (2006) An Arnoldi-type algorithm for computing PageRank. BIT 46(4):759–771
Golub GH, Van Loan C (1996) Matrix computations, 3rd edn. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Gu C-Q, Xie F, Zhang K (2015) A two-step matrix splitting iteration for computing PageRank. J Comput Appl Math 278(15):19–28
Huang N, Ma C-F (2015) Parallel multisplitting iteration methods based on M-splitting for the PageRank problem. Appl Math Comput 271:337–343
Jia Z-X (1997) Refined iterative algorithms based on Arnoldis process for large unsymmetric eigenproblems. Linear Algebra Appl 259(1):1–23
Kamvar S, Haveliwala T, Manning C, Golub GH (2003) Extrapolation methods for accelerating PageRank computations. In: Twelfth International World Wide Web Conference, Budapest, Hungary, pp 261–270
Kamvar S, Haveliwala T, Golub GH (2004) Adaptive methods for the computation of PageRank. Linear Algebra Appl 386(15):51–65
Kamvar S, Haveliwala T, Manning C, Golub GH (2003) Exploiting the block structure of the web for computing PageRank. Technical Report, Stanford
Langville AN, Meyer CD (2005) A survey of eigenvector methods for Web information retrieval. SIAM Rev 47(1):135–161
Langville A, Meyer C (2006) Googles PageRank and beyond: the science of search engine rankings. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Langville A, Meyer C (2006) A reordering for the PageRank problem. SIAM J Sci Comput 27(6):2112–2120
Mangasarian OL, Meyer RR (2006) Absolute value equations. Linear Algebra Appl 419(2):359–367
Mangasarian OL (2007) Absolute value programming. Comput Optim Appl 36(1):43–53
Morrison JL, Breitling R, Higham DJ, Gilbert DR (2005) GeneRank: using search engine technology for the analysis of microarray experiments. BMC Bioinform 6:233
Moosaei H, Ketabchi S, Noor MA (2015) Some techniques for solving absolute value equations. Appl Math Comput 268:696–705
Page L, Brin S, Motwani R, Winograd T (1999) The PageRank citation ranking: bringing order to the web, Stanford Digital Libraries SIDL-WP-1999-0120, Stanford
Rohn J (2012) An algorithm for computing all solutions of an absolute value equation. Optim Lett 6(5):851–856
Sauer T (2005) Numerical analysis. Addison Wesley Publication, USA
Skardal PS, Taylor D, Sun J, Arenas A (2015) Collective frequency variation in complex networks and Google’s PageRank, arXiv preprint arXiv:1510.02018
Stewart W (1994) Introduction to the numerical solution of Markov chains. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Wu G, Wei Y-M (2007) A power-Arnoldi algorithm for computing PageRank. Numer Linear Algebra Appl 14(7):521–546
Yin J-F, Yin G-J, Ng MK (2012) On adaptively accelerated Arnoldi method for computing PageRank. Numer Linear Algebra Appl 19(1):73–85
Yong L-Q (2016) A smoothing newton method for absolute value equation. Int J Control Autom 9(2):119–132
Yong L-Q, Liu S-Y, Zhang S-M (2011) A new method for absolute value equations based on harmony search algorithm. ICIC Express Lett Part B Appl 2:1231–1236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jinyun Yuan.
The Project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11071041, 11201074), Fujian Natural Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 2016J01005, 2015J01578), and Outstanding Young Training Plan of Fujian Province universities (Grant No. 15kxtz13, 2015).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, YJ., Ma, CF. A relaxed two-step splitting iteration method for computing PageRank. Comp. Appl. Math. 37, 221–233 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-016-0338-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-016-0338-4