Abstract
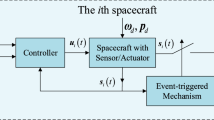
Attitude control is a requirement always present in spacecraft design. Several kinds of actuators exist to accomplish this control, being momentum wheels one of the most employed. Usually satellites carry redundant momentum wheels to handle any possible single failure, but the controller remains as a single centralized element, posing problems in case of failures. In this work a decentralized agent-based event-driven algorithm for attitude control is presented as a possible solution. Several agents based in momentum wheels will interact among them to accomplish the satellite control. A simulation environment has been developed to analyze the behavior of this architecture. This environment has been made available through the web page http://www.dia.uned.es.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kristiansen, R., et al.: A comparative study of actuator configurations for satellite attitude control. Model. Identif. Control 26(4), 201–219 (2005)
Astolfi, A, Rapaport, A.: Robust stabilization of the angular velocity of a rigid body. Syst. Control Lett. 34, 256–264 (1998)
Guyot, P., et al.: Flywheel power and attitude control systems (FACS). In: Proceedings of the 4th ESA International Conference Spacecraft Guidance, Navigation and Control Systems, pp. 18–21. ESTEC, Noordwijk (1999)
Jiang, T., Khorasani, K.: A fault detection, isolation and reconstruction strategy for a satellite’s attitude control subsystem with redundant reaction wheels. In: IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, pp. 3146–3152, (ISIC, 2007), 7–10 Oct 2007
Karami, M.A., Sassani, F.: Spacecraft momentum dumping using less than three external control torques. In: IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, pp. 4031–4039, (ISIC, 2007), 7–10 Oct 2007
YI, B.-J., et al.: A five-bar finger mechanism involving redundant actuators: analysis and its applications. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 15(6), 12–13 (1999)
Tsiotras, P.: New control laws for the attitude stabilisation of rigid bodies. In: 13th IFAC Symposium on automatic control in aerospace (IFAC, 1994)
Meyer, G.: Design and global analysis of spacecraft attitude control systems (NASA Technical Report, 1971)
Tsiotras, P., Longuski, J.M.: A new parametrization of attitude kinematics. J. Astronaut. Sci. 43(3), 243–262 (1995)
Tsiotras, P.: Stabilization and optimality results for the attitude control problem. J. Guid., Control Dyn. 19(4), 56–57 (1996)
Thawar, T.A.: Adaptive control of rigid body satellite. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 5, 296–306 (2008)
Gawthrop, P.J., Wang, L.: Event driven intermittent control. Int. J. Control 4, 1–14 (2009)
Gawthrop, P.J., Wang, L.: Constrained intermittent model predictive control. Int. J. Control 5, 1–10 (2009)
Galdun, J., et al.: Distributed control systems reliability: Consideration of multi-agent behavior. In: 6th International Symposium on Applied Machine Intelligence and Informatics, 2008, (SAMI, 2008), pp. 157–162
Davies, J., et al.: Multiagent control of high redundancy actuation. In: UKACC Control Conference (Manchester), pp. 2–4 Sept
Olfati-Saber, R., et al.: Consensus and cooperation in networked multi-agent systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 0018-92192007 IEEE 95, No. 1 (2007)
Tabuada, P.: Event-triggered real-time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 52(9), 40 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia, J.L., Moreno, J.S. Multiagent Attitude Control System for Satellites Based in Momentum Wheels and Event-Driven Synchronization. J of Astronaut Sci 59, 726–746 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40295-014-0010-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40295-014-0010-4