Abstract
Introduction
Fenofibrate is an effective and safe treatment for hypertriglyceridemia. However, after TG reduction a residual dyslipidemia could appear and require further treatment.
Aim
To comparatively evaluate the short-term tolerability and efficacy of a combined lipid-lowering nutraceutical and pravastatin 40 mg in fenofibrate treated patients.
Method
We prospectively enrolled 40 patients well-tolerating treatment with micronized fenofibrate 145 mg/day and with residual dyslipidemia (LDL-C > 115 mg/dL and TG > 150 mg/dL). Exclusion criteria have been type 2 diabetes, Familial Hypercholesterolemia, previous cardiovascular diseases and severe chronic kidney disease. Then, we have randomly assigned the patients to treatment with pravastatin 40 mg or a combined lipid-lowering nutraceutical (Armolipid Plus®, containing monacolin 3 mg and berberine 500 mg).
Results
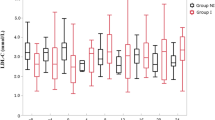
After 8 weeks of treatment, 80% of pravastatin treated patients (N. 16/20) and 75% of those treated with Armolipid Plus® (N. 15/20) reached the desired LDL-C target, while 50% of pravastatin treated patients (N. 10/20) and 80% of the Armolipid Plus® treated ones reached the desired TG target (N. 16/20). No one adverse event has been registered during Armolipid Plus®, while 1 patient claimed myalgia and 1 reported significant increase of CPK (> 3 ULN) during pravastatin treatment. Both patients were then treated with Armolipid Plus® with resolution of symptoms and CPK increase, respectively.
Conclusion
In hypertriglyceridemic patients treated with fenofibrate, the association with a combined lipid lowering nutraceutical seem to be more effective in optimizing residual hypertriglyceridemia than pravastatin 40 mg, while being more tolerable and having similar effect on LDL-C plasma level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Budoff M. Triglycerides and triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in the causal pathway of cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2016;118(1):138–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2016.04.004.
Maki KC, Guyton JR, Orringer CE, Hamilton-Craig I, Alexander DD, Davidson MH. Triglyceride-lowering therapies reduce cardiovascular disease event risk in subjects with hypertriglyceridemia. J Clin Lipidol. 2016;10(4):905–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacl.2016.03.008.
Catapano AL, Graham I, De Backer G, Wiklund O, Chapman MJ, Drexel H, Hoes AW, Jennings CS, Landmesser U, Pedersen TR, Reiner Ž, Riccardi G, Taskinen MR, Tokgozoglu L, Verschuren WM, Vlachopoulos C, Wood DA, Zamorano JL. 2016 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of dyslipidaemias: the task force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) developed with the special contribution of the European Assocciation for Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation (EACPR). Atherosclerosis. 2016;253:281–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.08.018.
Geng Q, Ren J, Chen H, Lee C, Liang W. Adverse events following statin-fenofibrate therapy versus statin alone: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013;40(3):219–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12053.
Derosa G, Maffioli P, Sahebkar A. Plasma uric acid concentrations are reduced by fenofibrate: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Pharmacol Res. 2015;102:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2015.09.012.
Sahebkar A, Giua R, Pedone C, Ray KK, Vallejo-Vaz AJ, Costanzo L. Fibrate therapy and flow-mediated dilation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Pharmacol Res. 2016;111:163–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.06.011.
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Böhm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Galderisi M, Grobbee DE, Jaarsma T, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, Ruilope LM, Schmieder RE, Sirnes PA, Sleight P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Zannad F, Redon J, Dominiczak A, Narkiewicz K, Nilsson PM, Burnier M, Viigimaa M, Ambrosioni E, Caufield M, Coca A, Olsen MH, Schmieder RE, Tsioufis C, van de Borne P, Zamorano JL, Achenbach S, Baumgartner H, Bax JJ, Bueno H, Dean V, Deaton C, Erol C, Fagard R, Ferrari R, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Kirchhof P, Knuuti J, Kolh P, Lancellotti P, Linhart A, Nihoyannopoulos P, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Sirnes PA, Tamargo JL, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Wijns W, Windecker S, Clement DL, Coca A, Gillebert TC, Tendera M, Rosei EA, Ambrosioni E, Anker SD, Bauersachs J, Hitij JB, Caulfield M, De Buyzere M, De Geest S, Derumeaux GA, Erdine S, Farsang C, Funck-Brentano C, Gerc V, Germano G, Gielen S, Haller H, Hoes AW, Jordan J, Kahan T, Komajda M, Lovic D, Mahrholdt H, Olsen MH, Ostergren J, Parati G, Perk J, Polonia J, Popescu BA, Reiner Z, Rydén L, Sirenko Y, Stanton A, Struijker-Boudier H, Tsioufis C, van de Borne P, Vlachopoulos C, Volpe M, Wood DA. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2159–219. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/eht151.
Cicero AF, Fogacci F, Rosticci M, Parini A, Giovannini M, Veronesi M, D’Addato S, Borghi C. Effect of a short-term dietary supplementation with phytosterols, red yeast rice or both on lipid pattern in moderately hypercholesterolemic subjects: a three-arm, double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Nutr Metab. 2017;14:61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-017-0214-2.
Cicero AF, Fogacci F, Morbini M, Colletti A, Bove M, Veronesi M, Giovannini M, Borghi C. Nutraceutical effects on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with impaired fasting glucose: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial on a combined product. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2017;24(3):283–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-017-0206-3.
Filippatos T, Milionis HJ. Treatment of hyperlipidaemia with fenofibrate and related fibrates. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008;17(10):1599–614. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.17.10.1599.
Shinnakasu A, Yamamoto K, Kurano M, Arimura H, Arimura A, Kikuti A, Hashiguchi H, Deguchi T, Nishio Y. The combination therapy of fenofibrate and ezetimibe improved lipid profile and vascular function compared with statins in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017;24(7):735–48. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.39446.
Tarantino N, Santoro F, De Gennaro L, Correale M, Guastafierro F, Gaglione A, Di Biase M, Brunetti ND. Fenofibrate/simvastatin fixed-dose combination in the treatment of mixed dyslipidemia: safety, efficacy, and place in therapy. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2017;13:29–41. https://doi.org/10.2147/VHRM.S95044.
Hernández Mijares A. Combination of pravastatin and fenofibrate (Pravafenix®). Safety studies. Clin Investig Arterioscler. 2014;26(Suppl 1):25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0214-9168(14)70023-3.
Banach M, Patti AM, Giglio RV, Cicero AF, Atanasov AG, Bajraktari G, Bruckert E, Descamps O, Djuric DM, Ezhov M, Fras Z, von Haehling S, Katsiki N, Langlois M, Latkovskis G, Mancini GBJ, Mikhailidis DP, Mitchenko O, Moriarty PM, Muntner P, Nikolic D, Panagiotakos DB, Paragh G, Paulweber B, Pella D, Pitsavos C, Reiner Ž, Rosano GMC, Rosenson RS, Rysz J, Sahebkar A, Serban MC, Vinereanu D, Vrablík M, Watts GF, Wong ND, Rizzo M, International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP). The role of nutraceuticals in statin intolerant patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(1):96–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.04.040.
Pirro M, Mannarino MR, Bianconi V, Simental-Mendía LE, Bagaglia F, Mannarino E, Sahebkar A. The effects of a nutraceutical combination on plasma lipids and glucose: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol Res. 2016;110:76–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.04.021.
Cicero AFG, Colletti A, Bajraktari G, Descamps O, Djuric DM, Ezhov M, Fras Z, Katsiki N, Langlois M, Latkovskis G, Panagiotakos DB, Paragh G, Mikhailidis DP, Mitchenko O, Paulweber B, Pella D, Pitsavos C, Reiner Ž, Ray KK, Rizzo M, Sahebkar A, Serban MC, Sperling LS, Toth PP, Vinereanu D, Vrablík M, Wong ND, Banach M. Lipid lowering nutraceuticals in clinical practice: position paper from an International Lipid Expert Panel. Arch Med Sci. 2017;13(5):965–1005. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2017.69326.
Barrios V, Escobar C, Cicero AF, Burke D, Fasching P, Banach M, Bruckert E. A nutraceutical approach (Armolipid Plus) to reduce total and LDL cholesterol in individuals with mild to moderate dyslipidemia: review of the clinical evidence. Atheroscler Suppl. 2017;24:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosissup.2016.10.003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Human and animal rights statement
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
Dr. Cicero has spoken in Mylan SpA sponsored meetings. Other authors have no direct nor indirect conflict of interest in the publication of this paper.
Additional information
This article is part of the topical collection on Nutraceuticals in Hypertension & Cardiovascular Prevention.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cicero, A.F.G., Fogacci, F., Bove, M. et al. Optimizing Lipid Pattern by Adding a Combined Nutraceutical or Pravastatin to Fenofibrate Treatment in Hypertriglyceridemic Subjects: Single Site, Randomized, Open-Label, Post-Market Clinical Investigation. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 25, 355–359 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-018-0277-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-018-0277-9