Abstract
Purpose
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that significantly affects quality of life and interpersonal relationships.
Objective
Our objective was to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of herbal dietary supplements in the treatment of ED.
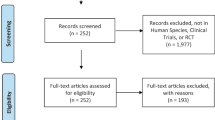
Materials and Methods
We searched five databases to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that evaluated the clinical efficacy of herbal medicines in ED. Quality was assessed and risk of bias was estimated using the Jadad score and the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool.
Results
In total, 24 RCTs, including 2080 patients with ED, were identified. Among these, 12 evaluated monopreparations (five ginseng [n = 399], three saffron [n = 397], two Tribulus terrestris [n = 202], and one each Pinus pinaster [n = 21] and Lepidium meyenii [n = 50]), seven evaluated formulations (n = 544), and five investigated dietary supplements in combination with pure compounds (n = 410). Ginseng significantly improved erectile function (International Index of Erectile Function [IIEF]-5 score: 140 ginseng, 96 placebo; standardized mean difference [SMD] 0.43; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.15–0.70; P < 0.01; I2 = 0), P. pinaster and L. meyenii showed very preliminary positive results, and saffron and T. terrestris treatment produced mixed results. Several herbal formulations were associated with a decrease of IIEF-5 or IIEF-15, although the results were preliminary. The quality of the included studies varied, with only seven having a prevalent low risk of bias. The median methodological quality Jadad score was three out of a maximum of five. Adverse events were recorded in 19 of 24 trials, with no significant differences between placebo and verum in placebo-controlled studies.
Conclusions
Encouraging evidence suggests that ginseng may be an effective herbal treatment for ED. However, further, larger, and high-quality studies are required before firm conclusions can be drawn. Promising (although very preliminary) results have also been generated for some herbal formulations. Overall, more research in the field, adhering to the CONSORT statement extension for reporting trials, is justified before the use of herbal products in ED can be recommended.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCabe MP, Sharlip ID, Lewis R, Atalla E, Balon R, Fisher AD, et al. Incidence and prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women and men: a Consensus Statement from the Fourth International Consultation on Sexual Medicine 2015. J Sex Med. 2016;13:144–52.
Baumann F, Hehli D, Makaloski V, Schumacher M, Schönhofen H, Diehm N. Erectile dysfunction—overview from a cardiovascular perspective. Vasa. 2017;10:1–7.
Eisenberg ML, Meldrum D. Effects of age on fertility and sexual function. Fertil Steril. 2017;107:301–4.
Nguyen HMT, Gabrielson AT, Hellstrom WJG. Erectile dysfunction in young men-a review of the prevalence and risk factors. Sex Med Rev. 2017;5:508–20.
Hsu B, Hirani V, Naganathan V, Blyth FM, Le Couteur DG, Seibel MJ, et al. Sexual function and mortality in older men: the concord health and ageing in men project. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017;72:520–7.
Hatzimouratidis K, Salonia A, Adaikan G, Buvat J, Carrier S, El-Meliegy A, et al. Pharmacotherapy for Erectile dysfunction: recommendations from the fourth international Consultation for Sexual Medicine (ICSM 2015). J Sex Med. 2016;13:465–88.
Doumas M, Lazaridis A, Katsiki N, Athyros V. PDE-5 inhibitors: clinical points. Curr Drug Targets. 2015;16:420–6.
Evans JD, Pace K, Evans EW. Natural therapies used by adult men for the treatment of erectile dysfunction, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and for augmenting exercise performance. J Pharm Pract. 2011;24:323–31.
Chauhan NS, Sharma V, Dixit VK, Thakur M. A review on plants used for improvement of sexual performance and virility. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:868062.
Cui T, Kovell RC, Brooks DC, Terlecki RP. A urologist’s guide to ingredients found in top-selling nutraceuticals for men’s sexual health. J Sex Med. 2015;12:2105–17.
Marcus DM. Dietary supplements: what’s in a name? What’s in the bottle? Drug Test Anal. 2016;8:410–2.
Izzo AA, Hoon-Kim S, Radhakrishnan R, et al. A critical approach to evaluating clinical efficacy, adverse events and drug interactions of herbal remedies. Phytother Res. 2016;30:691–700.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:b2535.
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17:1–12.
Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. http://handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21:1539–58.
Follmann D, Elliot P, Suh I, Cutler J. Variance imputation for overviews of clinical trials with continuous response. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992;45:769–73.
Cherdshewasart W, Nimsakul N. Clinical trial of Butea superba, an alternative herbal treatment for erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl. 2003;5:243–6.
Dording CM, Fisher L, Papakostas G, Farabaugh A, Sonawalla S, Fava M, et al. A double-blind, randomized, pilot dose-finding study of maca root(L. meyenii) for the management of SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008;14:182–91.
Shamsa A, Hosseinzadeh H, Molaei M, Shakeri MT, Rajabi O. Evaluation of Crocus sativus L. (saffron) on male erectile dysfunction: a pilot study. Phytomedicine. 2009;16:690–3.
Aldemir M, Okulu E, Neşelioğlu S, Erel O, Kayıgil O. Pistachio diet improves erectile function parameters and serum lipid profiles in patients with erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2011;23:32–8.
Kobori Y, Suzuki K, Iwahata T, Shin T, Sadaoka Y, Sato R, et al. Improvement of seminal quality and sexual function of men with oligoasthenoteratozoospermia syndrome following supplementation with l-arginine and Pycnogenol®. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2015;87:190–3.
Ito T, Kawahara K, Das A, Strudwick W. The effects of ArginMax, a natural dietary supplement for enhancement of male sexual function. Hawaii Med J. 1998;57:741–4.
Adimoelja A, Ganeshan P. Protodioscin from herbal plant Tribulus terrestris L improves the male sexual functions, probably via DHEA. Int. J. Impot Res. 1997;9(Supp 1):S1–70.
Ashton AK, Ahrens K, Gupta S, Masand PS. Antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction and Ginkgo Biloba. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:836–7.
Cohen AJ, Bartlik B. Ginkgo biloba for antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction. J Sex Marital Ther. 1998;24:139–43.
Cortés-González JR, Arratia-Maqueo JA, Gómez-Guerra LS, Holmberg AR. The use of Butea superba (Roxb.) compared to sildenafil for treating erectile dysfunction. BJU Int. 2010;105:225–8.
Aoki H, Nagao J, Ueda T, Strong JM, Schonlau F, Yu-Jing S, et al. Clinical assessment of a supplement of Pycnogenol® and l-arginine in Japanese patients with mild to moderate erectile dysfunction. Phytother Res. 2012;26:204–7.
Asare GA, Afriyie D, Ngala RA, Appiah AA, Anang Y, Musah I, et al. Shrinkage of prostate and improved quality of life: management of BPH patients with croton membranaceus ethanolic root extract. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:365205.
Roaiah MF, El Khayat YI, GamalEl Din SF, Abd El Salam MA. Pilot study on the effect of botanical medicine (Tribulus terrestris) on Serum Testosterone Level and Erectile Function in Aging Males With Partial Androgen Deficiency (PADAM). J Sex Marital Ther. 2016;42:297–301.
Kang BJ, Lee SJ, Kim MD, Cho MJ. A placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of Ginkgo biloba for antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2002;17:279–84.
Wheatley D. Triple-blind, placebo-controlled trial of Ginkgo biloba in sexual dysfunction due to antidepressant drugs. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2004;19:545–8.
Iacono F, Prezioso D, Illiano E, Romeo G, Ruffo A, Amato B. Sexual asthenia: tradamixina versus Tadalafil 5 mg daily. BMC Surg. 2012;12:S23.
Ismail SB, Wan Mohammad WM, George A, Nik Hussain NH, Musthapa Kamal ZM, Liske E. Randomized clinical trial on the use of PHYSTA freeze-dried water extract of Eurycoma longifolia for the improvement of quality of life and sexual well-being in Men. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:429268.
Choi HK, Seong DH, Rha KH. Clinical efficacy of Korean red ginseng for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 1995;7:181–6.
Hong B, Ji YH, Hong JH, Nam KY, Ahn TY. A double-blind crossover study evaluating the efficacy of korean red ginseng in patients with erectile dysfunction: a preliminary report. J Urol. 2002;168:2070–3.
de Andrade E, de Mesquita AA, Claro Jde A, de Andrade PM, Ortiz V, Paranhos M, et al. Study of the efficacy of Korean Red Ginseng in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl. 2007;9:241–4.
Kim TH, Jeon SH, Hahn EJ, Paek KY, Park JK, Youn NY, et al. Effects of tissue-cultured mountain ginseng (Panax ginseng CA Meyer) extract on male patients with erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl. 2009;11:356–61.
Choi YD, Park CW, Jang J, Kim SH, Jeon HY, Kim WG, et al. Effects of Korean ginseng berry extract on sexual function in men with erectile dysfunction: a multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical study. Int J Impot Res. 2013;25:45–50.
Safarinejad MR, Shafiei N, Safarinejad S. An open label, randomized, fixed-dose, crossover study comparing efficacy and safety of sildenafil citrate and saffron (Crocus sativus Linn.) for treating erectile dysfunction in men naïve to treatment. Int J Impot Res. 2010;22:240–50.
Modabbernia A, Sohrabi H, Nasehi AA, Raisi F, Saroukhani S, Jamshidi A, et al. Effect of saffron on fluoxetine-induced sexual impairment in men: randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Psychopharmacology. 2012;223:381–8.
Mohammadzadeh-Moghadam H, Nazari SM, Shamsa A, Kamalinejad M, Esmaeeli H, Asadpour AA, et al. Effects of a topical saffron (Crocus sativus L) gel on erectile dysfunction in diabetics: a randomized, parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2015;20:283–6.
Santos CA Jr, Reis LO, Destro-Saade R, Luiza-Reis A, Fregonesi A. Tribulus terrestris versus placebo in the treatment of erectile dysfunction: a prospective, randomized, double blind study. Actas Urol Esp. 2014;38:244–8.
Kamenov Z, Fileva S, Kalinov K, Jannini EA. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of Tribulus terrestris in male sexual dysfunction—a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Maturitas. 2017;99:20–6.
Duračková Z, Trebatický B, Novotný V, Žitňanová I, Breza J. Lipid metabolism and erectile function improvement by pycnogenol®, extract from the bark of pinus pinaster in patients suffering from erectile dysfunction-a pilot study. Nutr Res 2003;23:1189–98.
Zenico T, Cicero AF, Valmorri L, Mercuriali M, Bercovich E. Subjective effects of Lepidium meyenii (Maca) extract on well-being and sexual performances in patients with mild erectile dysfunction: a randomised, double-blind clinical trial. Andrologia. 2009;41:95–9.
Kulkarni MP, Shinde BS, Chaudhari MK, Avhad GM, Pensalwar SV, Prasad BS, et al. Efficacy and safety of two polyherbal combinations: E-MA-H and E-MA-HP in male sexual dysfunction. Am J Ther. 2011;18:162–9.
Shah GR, Chaudhari MV, Patankar SB, Pensalwar SV, Sabale VP, Sonawane NA. Evaluation of a multi-herb supplement for erectile dysfunction: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012;12:155.
Punyawudho B, Puttilerpong C, Wirotsaengthong S, Aramwit P. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study of Cappra® for the treatment of mild or mild to moderate erectile dysfunction in Thai male. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012;10:310–5.
Cai T, Morgia G, Carrieri G, Terrone C, Imbimbo C, Verze P, et al. IDIProst® Gold Study Group. An improvement in sexual function is related to better quality of life, regardless of urinary function improvement: results from the IDIProst® Gold Study. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2013;85:184–9.
Nishimatsu H, Kitamura T, Yamada D, Nomiya A, Niimi A, Suzuki M, et al. Improvement of symptoms of aging in males by a preparation LEOPIN ROYAL containing aged garlic extract and other five of natural medicines - comparison with traditional herbal medicines (Kampo). Aging Male. 2014;17:112–6.
Udani JK, George AA, Musthapa M, Pakdaman MN, Abas A. Effects of a proprietary freeze-dried water extract of Eurycoma longifolia (Physta) and polygonum minus on sexual performance and well-being in men: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:179529.
Hsieh CH, Tsai HC, Hsu GL, Chen CC, Hsu CY. Herb formula enhances treatment of impotent patients after penile venous stripping: a randomised clinical trials. Andrologia. 2016;48:754–60.
Stanislavov R, Nikolova V, Rohdewald P. Improvement of erectile function with Prelox: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Int J Impot Res. 2008;20:173–80.
Ledda A, Belcaro G, Cesarone MR, Dugall M, Schönlau F. Investigation of a complex plant extract for mild to moderate erectile dysfunction in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-arm study. BJU Int. 2010;106:1030–3.
Paulis G, Cavallini G, Brancato T, Alvaro R. Peironimev-Plus® in the treatment of chronic inflammation of tunica albuginea (Peyronie’s disease). results of a controlled study. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2013;12:61–7.
Sansalone S, Leonardi R, Antonini G, Vitarelli A, Vespasiani G, Basic D, et al. Alga Ecklonia bicyclis, Tribulus terrestris, and glucosamine oligosaccharide improve erectile function, sexual quality of life, and ejaculation function in patients with moderate mild-moderate erectile dysfunction: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blinded study. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:121396.
Stanislavov R, Rohdewald P. Improvement of erectile function by a combination of French maritime pine bark and roburins with aminoacids. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2015;67:27–32.
Andrew R, Izzo AA. Principles of pharmacological research of nutraceuticals. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174:1177–94.
Patel S, Rauf A. Adaptogenic herb ginseng (Panax) as medical food: status quo and future prospects. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;85:120–7.
Jang DJ, Lee MS, Shin BC, Lee YC, Ernst E. Red ginseng for treating erectile dysfunction: a systematic review. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;66:444–50.
Shergis JL, Zhang AL, Zhou W, Xue CC. Panax ginseng in randomised controlled trials: a systematic review. Phytother Res. 2013;27:949–65.
Fink HA, MacDonald R, Rutks IR, Wilt TJ. Trazodone for erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJU Int. 2003;92:441–6.
Lee HS, Lee YJ, Chung YH, Lee MY, Kim ST, Ko SK, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of tissue-cultured mountain ginseng on penile erection. J Ginseng Res. 2016;40:334–43.
Kim SD, Kim YJ, Huh JS, Kim SW, Sohn DW. Improvement of erectile function by Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) in a male rat model of metabolic syndrome. Asian J Androl. 2013;15:395–9.
Achike FI, Kwan CY. Nitric oxide, human diseases and the herbal products that affect the nitric oxide signalling pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2003;30:605–15.
Neychev V, Mitev V. Pro-sexual and androgen enhancing effects of Tribulus terrestris L.: fact or Fiction. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;179:345–55.
Schoonees A, Visser J, Musekiwa A, Volmink J. Pycnogenol® (extract of French maritime pine bark) for the treatment of chronic disorders. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;4:CD008294.
Beharry S, Heinrich M. Is the hype around the reproductive health claims of maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.) justified? J Ethnopharmacol. 2018;211:126–70.
Lee MS, Lee HW, You S, Ha KT. The use of maca (Lepidium meyenii) to improve semen quality: a systematic review. Maturitas. 2016;92:64–9.
Lee MS, Shin BC, Yang EJ, Lim HJ, Ernst E. Maca (Lepidium meyenii) for treatment of menopausal symptoms: a systematic review. Maturitas. 2011;70:227–33.
Xiong G, Li B, Wang K, Li H. Chinese herb formulae for treatment of erectile dysfunction: a systematic review of randomised controlled clinical trials. Andrologia. 2014;46:201–23.
Coon JT, Ernst E. Panax ginseng: a systematic review of adverse effects and drug interactions. Drug Saf. 2002;25:323–44.
Pavan V. The old made new: natural compounds against erectile dysfunction. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2015;348:607–14.
Tam SW, Worcel M, Wyllie M. Yohimbine: a clinical review. Pharmacol Ther. 2001;91:215–43.
Ernst E, Pittler MH. Alternative therapy bias. Nature. 1997;385:480.
Choi J, Kim TH, Choi TY, Lee MS. Ginseng for health care: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials in Korean literature. PLoS One. 2013;8:e59978.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors collectively planned the study. FB and AAI drafted the systematic review manuscript. FB and AAI assessed the eligibility of included articles and extracted data. DD, MI, and CC assessed the quality of the studies. All authors served as adjudicators for disagreements. CC performed the meta-analysis. All authors reviewed the manuscript for intellectual content and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Francesca Borrelli, Cristiano Colalto, Domenico V. Delfino, Marcello Iriti, and Angelo A. Izzo have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this manuscript.
Funding
No funding was received in the preparation of this systematic review.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borrelli, F., Colalto, C., Delfino, D.V. et al. Herbal Dietary Supplements for Erectile Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Drugs 78, 643–673 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-018-0897-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-018-0897-3