Abstract
Introduction
Renal impairment may have a significant impact on the pharmacokinetics of drugs. Ad hoc studies in subjects with renal impairment are required by the regulatory authorities to propose dose adjustments in these subjects, to find a dosing regimen able to provide a systemic exposure similar to those in subjects with a normal renal function given the relevant clinical dose.
Methods
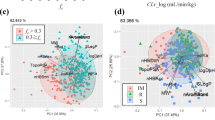
To evaluate the main descriptors and establish a predictive model of the effect of renal impairment on the exposure of new drugs, we considered 73 marketed drugs, for which studies in subjects with different degrees of renal impairment were available in the literature. Multivariate analysis was performed using the main pharmacokinetic parameters. Other approaches, including data mining and machine learning techniques, were tested to propose models based on a categorical definition of the exposure changes.
Results
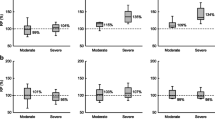
Stepwise multivariate regression analyses revealed, as expected, that the fraction of dose excreted unchanged in urine and plasma protein binding were the factors primarily related to the change in exposure between subjects with normal and impaired renal function. Data mining techniques provided similar results.
Discussion
The pharmacokinetic predictions were however not always satisfactory, especially for drugs which, despite the negligible renal excretion, are characterized by significant increases in the systemic exposure in subjects with renal impairment. This phenomenon, interpreted considering the accumulation of endogenous metabolism inhibitors in subjects with moderate and severe renal disease (uremic toxins), cannot be fully captured and described, likely owing to an incomplete understanding of the pathophysiological phenomena and to some limitations of the available database of clinical studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowland Yeo K, Aarabi M, Jamei M, et al. Modeling and predicting drug pharmacokinetics in patients with renal impairment. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2011;4(2):261–74.
Velenosi TJ, Urquhart BL. Pharmacokinetic considerations in chronic kidney disease and patients requiring dialysis. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2014;10(8):1131–43.
Verbeeck RK, Musuamba FT. Pharmacokinetics and dosage adjustment in patients with renal dysfunction. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;65:757–73.
Poggesi I, Benedetti MS, Whomsley R, et al. Pharmacokinetics in special populations. Drug Metab Rev. 2009;41(3):422–54.
Levey AS, Eckardt KU, Tsukamoto Y, et al. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from Kidney Disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005;67:2089–100.
Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298:2038–47.
Schlondorff DO. Overview of factors contributing to the pathophysiology of progressive renal disease. Kidney Int. 2008;74(7):860–6.
Eknoyan G, Levin A, Levin NW. Bone metabolism and disease in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42:1–201.
Kliger AS, Foley RN, Goldfarb DS, et al. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(5):849–59.
US Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Pharmacokinetics in patients with impaired renal function: study design, data analysis, and impact on dosing and labeling. Draft FDA guidance. 2010. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidances/UCM204959.pdf. Accessed 20 Mar 2017.
US National Library of Medicine. DailyMed. Bethesda (MD): U.S. National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, Health and Human Services; 2005. http://purl.access.gpo.gov/GPO/LPS81632. Accessed 20 Mar 2017.
Dowell JA, Stogniew M, Krause D, et al. Anidulafungin does not require dosage adjustment in subjects with varying degrees of hepatic or renal impairment. J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;47(4):461–70.
Mallikaarjun S, Shoaf SE, Boulton DW, et al. Effects of hepatic or renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of aripiprazole. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008;47(8):533–42.
Drusano GL, Weir M, Forrest A, et al. Pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered ciprofloxacin in patients with various degrees of renal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987;31(6):860–4.
Roy MJ, Erdman KA, Abeyratne AT, et al. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous conivaptan in subjects with hepatic or renal impairment. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013;52(5):385–95.
Boike SC, Pue MA, Freed MI, et al. Pharmacokinetics of famciclovir in subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1994;55(4):418–26.
Johnson MA, Verpooten GA, Daniel MJ, et al. Single dose pharmacokinetics of lamivudine in subjects with impaired renal function and the effect of haemodialysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998;46(1):21–7.
Wootton R, Soul-Lawton J, Rolan PE, et al. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine in patients with chronic renal failure and healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1997;43(1):23–7.
Delhotal-Landes B, Flouvat B, Duchier J, et al. Pharmacokinetics of lansoprazole in patients with renal or liver disease of varying severity. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1993;45(4):367–71.
Christensson BA, Nilsson-Ehle I, Hutchison M, et al. Pharmacokinetics of meropenem in subjects with various degrees of renal impairment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992;36(7):1532–7.
Snoeck E, van Peer A, Mannens G, et al. Influence of age, renal and liver impairment on the pharmacokinetics of risperidone in man. Psychopharmacology. 1995;122(3):223–9.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W, et al. Effects of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of rivaroxaban, an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;70(5):703–12.
Boulton D, Li L, Frevert EU, et al. Influence of renal or hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011;50(4):253–65.
Germani M, Crivori P, Rocchetti M, et al. Evaluation of a basic physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for simulating the first-time-in-animal study. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2007;31(3–4):190–201.
Bastien P, Tenenhaus M. PLS regression and multiple imputations. In: Vilares M, et al. (eds), Proceedings of the PLS’03 international symposium. Paris: CISIA; 2003: pp. 497–8. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/a547/464f9e10a6101a5e75ba5504fe9e2cc905b0.pdf. Accessed 22 Jun 2017.
Abdi H. Partial least squares regression and projection on latent structure regression (PLS regression). Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Stat. 2010;2(1):97–106.
Preda C, Saporta G, Hedi M, et al. The NIPALS algorithm for missing functional data. Rom J Pure Appl Math. 2010;55(4):315–26. http://cedric.cnam.fr/fichiers/art_2223.pdf. Accessed 20 Mar 2017.
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2014. http://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 20 Mar 2017.
Fung G. A comprehensive overview of basic clustering algorithms. 2001. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/b7cd/0a4e0a129b55b76b7a0faf8ec73a5ebd1645.pdf. Accessed 20 Mar 2017.
Demsar J, Curk T, Erjavec A, et al. Orange: data mining toolbox in Python. J Mach Learn Res. 2013;14:2349–53.
Chen N, Lau H, Kong L, et al. Pharmacokinetics of lenalidomide in subjects with various degrees of renal impairment and in subjects on hemodialysis. J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;47(12):1466–75.
Stangier J, Rathgen K, Stähle H, et al. Influence of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral dabigatran etexilate. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010;49(4):259–68.
Poole C, Gardiner J, Twelves C, et al. Effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics and tolerability of capecitabine (Xeloda) in cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2002;49(3):225–34.
Jannuzzo MG, Poggesi I, Spinelli R, et al. The effects of degree of hepatic or renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of exemestane in postmenopausal women. Cancer Chemoth Pharm. 2004;53(6):475–81.
Yoshida K, Sun B, Zhang L, et al. Systematic and quantitative assessment of the effect of chronic kidney disease on CYP2D6 and CYP3A4/5. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016;100(1):75–87.
Joy MS, Frye RF, Nolin TD, et al. In vivo alterations in drug metabolism and transport pathways in patients with chronic kidney diseases. Pharmacotherapy. 2014;34:114–22.
Thomson BK, Nolin TD, Velenosi TJ, et al. Effect of CKD and dialysis modality on exposure to drugs cleared by nonrenal mechanisms. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;65(4):574–82.
Yeung CK, Yoshida K, Kusama M, et al. Organ impairment-drug-drug interaction database: a tool for evaluating the impact of renal or hepatic impairment and pharmacologic inhibition on the systemic exposure of drugs. CPT Pharmacomet Syst Pharmacol. 2015;4:489–94.
Hsu V, de L T Vieira M, Zhao P, et al. Towards quantitation of the effects of renal impairment and probenecid inhibition on kidney uptake and efflux transporters, using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling and simulations. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2014;53(3):283–93.
Lu C, Suri A, Shyu WC, et al. Assessment of cytochrome P450-mediated drug–drug interaction potential of orteronel and exposure changes in patients with renal impairment using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2014;35(9):543–52.
Grillo JA, Zhao P, Bullock J, et al. Utility of a physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling approach to quantitatively predict a complex drug-drug-disease interaction scenario for rivaroxaban during the drug review process: implications for clinical practice. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2012;33(2):99–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No external funding was used in the preparation of this article.
Conflict of Interest
Elisa Borella and Paolo Magni have no conflicts of interest directly relevant to the content of this article. Italo Poggesi is an employee at Janssen R&D.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borella, E., Poggesi, I. & Magni, P. Prediction of the Effect of Renal Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics of New Drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet 57, 505–514 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-017-0574-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-017-0574-9