Abstract
Background and Objective
Sonidegib is a potent, selective and orally bioavailable inhibitor of the Hedgehog signaling pathway, primarily metabolized by the liver. In order to make dose recommendations for patients with hepatic impairment, we have assessed here the pharmacokinetics (PKs) and safety of sonidegib in subjects with varying degrees of hepatic function.
Methods
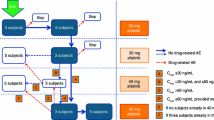
The primary objective of this phase I, multicenter, open-label study was to evaluate the PKs of a single oral 800 mg dose of sonidegib in subjects with impaired hepatic function compared with healthy subjects. PK parameters (e.g. area under the concentration–time curve from time zero to infinity [AUCinf], area under the concentration–time curve from time zero to the last measurable concentration [AUClast], maximum concentration [C max], apparent clearance [CL/F], and terminal half-life [t ½]) for parent drug and the metabolite were compared with the normal group, as the reference. Metabolite ratio, unbound PK parameters, and the relationship between specific PK parameters and liver function parameters were assessed.
Results
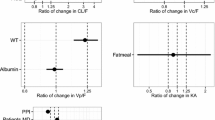
In total, 33 subjects entered the study and received sonidegib. Plasma concentrations peaked at approximately 2–3 h in all groups after dosing. Compared with the normal group, AUClast decreased by 35 and 23% and increased by 14% in the mild, severe, and moderate hepatic impairment groups, respectively. The C max values were lower in all groups with respect to the normal group (decreases of 20, 21 and 60% in the mild, moderate and severe hepatic impairment groups, respectively). Protein binding was independent of hepatic function, and similar trends in the PK parameters were observed for unbound sonidegib and the metabolite. Protein binding was similar across all groups. Weak to no correlation between specific PK and hepatic function parameters was found.
Conclusions
Overall, sonidegib exposures were similar or decreased in the hepatic impairment groups compared with the normal group, and sonidegib was generally well-tolerated in all subjects. Dose adjustment is not considered necessary for subjects with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Low JA, de Sauvage FJ. Clinical experience with Hedgehog pathway inhibitors. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:5321–6.
Otsuka A, Levesque MP, Dummer R, Kabashima K. Hedgehog signaling in basal cell carcinoma. J Dermatol Sci. 2015;78:95–100.
Zollinger M, Lozac’h F, Hurh E, Emotte C, Bauly H, Swart P. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of (1)(4)C-sonidegib (LDE225) in healthy volunteers. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014;74:63–75.
Novartis. Odomzo prescribing information. Novartis. 2016. https://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/sites/www.pharma.us.novartis.com/files/odomzo.pdf. Accessed 19 May 2017.
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646–9.
US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/ucm072123.pdf. Accessed 19 May 2017.
European Medicines Agency. Guideline on the evaluation of the pharmacokinetics of medicinal products in patients with impaired hepatic function. London: Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP); 2005.
Goel V, Hurh E, Stein A, Nedelman J, Zhou J, Chiparus O, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of sonidegib (LDE225), an oral inhibitor of hedgehog pathway signaling, in healthy subjects and in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016;77:745–55.
European Medicines Agency. Odomzo. Assessment report, 25 June 2015. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002839/WC500192972.pdf. Accessed 3 Apr 2017.
Yin OQ, Gallagher N, Tanaka C, Fisher D, Sethuraman V, Zhou W, et al. Effects of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of nilotinib: an open-label, single-dose, parallel-group study. Clin Ther. 2009;31(Pt 2):2459–69.
Mallikaarjun S, Shoaf SE, Boulton DW, Bramer SL. Effects of hepatic or renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of aripiprazole. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008;47:533–42.
Graefe-Mody U, Rose P, Retlich S, Ring A, Waldhauser L, Cinca R, et al. Pharmacokinetics of linagliptin in subjects with hepatic impairment. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;74:75–85.
Zhou J, Quinlan M, Glenn K, Boss H, Picard F, Castro H, et al. Effect of esomeprazole, a proton pump inhibitor on the pharmacokinetics of sonidegib in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;82:1022–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Tina Patrick, PhD, of Novartis Ireland Ltd, for providing medical writing and editorial support, which was funded by Novartis AG in accordance with Good Publication Practice (GPP3) guidelines (http://www.ismpp.org/gpp3). They would also like to thank Dr. Tycho Heimbach for his scientific input during manuscript revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was sponsored and designed by Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland, EudraCT no. 2011-005876-40. Dr. Horsmans, the primary investigator, conducted the study and collected the data; the sponsor and the authors analyzed and interpreted the data; and the sponsor wrote the study report. The authors and the sponsor jointly agreed to submit the manuscript for publication.
Conflict of interest
Yves Horsmans has received consulting fees from Novartis Pharma AG as the principal investigator of the study. Corinne Emotte and Hildegard Boss are employees at Novartis Pharma AG. Henry Castro was an employee at Novartis Pharma AG during the study and is currently employed by Bristol Myers Squibb. Michelle Quinlan, Dalila Sellami, and Jocelyn Zhou are employees of Novartis Pharmaceuticals, and Dalila Sellami owns Novartis stock. Richard A. Preston received a research grant from the University of Miami, Division of Clinical Pharmacology, to conduct this study. Mateva Liudmila, George Golor and Oren Shibolet declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
40262_2017_560_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 1: The mean (SD) concentration-time profiles of LGE899 for 0-56 days by hepatic group (TIFF 323 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horsmans, Y., Zhou, J., Liudmila, M. et al. Effects of Mild to Severe Hepatic Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics of Sonidegib: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Parallel-Group Study. Clin Pharmacokinet 57, 345–354 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-017-0560-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-017-0560-2