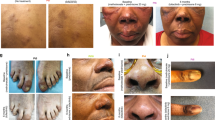
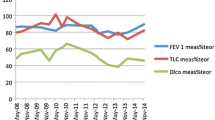
Abstract
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease defined by the presence of non-caseating granulomas. It can affect a number of organ systems, most commonly the lungs, lymph nodes, and skin. Cutaneous manifestations of sarcoidosis can impose a significant detriment to patients’ quality of life. The accepted first-line therapy for cutaneous sarcoidosis consists of intralesional and oral corticosteroids, but these can fail in the face of resistant disease and corticosteroid-induced adverse effects. Second-line agents include tetracyclines, hydroxychloroquine, and methotrexate. Biologics are an emerging treatment option for the management of cutaneous sarcoidosis, but their role in management is not well-defined. In this article, we reviewed the currently available English-language publications on the use of biologics in managing cutaneous sarcoidosis. Although somewhat limited, the data in published studies support the use of both infliximab and adalimumab as third-line treatments for chronic or resistant cutaneous sarcoidosis. There were also scattered reports of etanercept, rituximab, golimumab, and ustekinumab being utilized as third-line agents with varying degrees of success. Larger and more extensive investigations are required to further assess the adverse effect profile and optimal dosing for managing cutaneous sarcoidosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haimovic A, Sanchez M, Judson MA, Prystowsky S. Sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review and update for the dermatologist: part I. Cutaneous disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(5):699 e1–18 (quiz 717–8).
Petit A, Dadzie OE. Multisystemic diseases and ethnicity: a focus on lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, sarcoidosis and Behcet disease. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169(Suppl 3):1–10.
Heath CR, David J, Taylor SC. Sarcoidosis: are there differences in your skin of color patients? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(1):121 e1–14.
Doherty CB, Rosen T. Evidence-based therapy for cutaneous sarcoidosis. Drugs. 2008;68(10):1361–83.
Volden G. Successful treatment of chronic skin diseases with clobetasol propionate and a hydrocolloid occlusive dressing. Acta Dermatovenereol. 1992;72(1):69–71.
Baughman RP, Lower EE. Evidence-based therapy for cutaneous sarcoidosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25(3):334–40.
Fetil E, Ozkan S, Ilknur T, Kavukcu S, Kusku E, Lebe B. Sarcoidosis in a preschooler with only skin and joint involvement. Pediatr Dermatol. 2003;20(5):416–8.
Pariser RJ, Paul J, Hirano S, Torosky C, Smith M. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of adalimumab in the treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68(5):765–73.
Heidelberger V, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Marquet A, Mahevas M, Bessis D, Bouillet L, et al. Efficacy and tolerance of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agents in cutaneous sarcoidosis: a French Study of 46 cases. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153(7):681–5.
Jamilloux Y, Cohen-Aubart F, Chapelon-Abric C, Maucort-Boulch D, Marquet A, Perard L, et al. Efficacy and safety of tumor necrosis factor antagonists in refractory sarcoidosis: a multicenter study of 132 patients. Semin Arthr Rheum. 2017;47(2):288–94.
Judson MA, Baughman RP, Costabel U, Flavin S, Lo KH, Kavuru MS, et al. Efficacy of infliximab in extrapulmonary sarcoidosis: results from a randomised trial. Eur Respir J. 2008;31(6):1189–96.
Baughman RP, Drent M, Kavuru M, Judson MA, Costabel U, du Bois R, et al. Infliximab therapy in patients with chronic sarcoidosis and pulmonary involvement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;174(7):795–802.
Baughman RP, Judson MA, Lower EE, Drent M, Costabel U, Flavin S, et al. Infliximab for chronic cutaneous sarcoidosis: a subset analysis from a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2016;32(4):289–95.
Stagaki E, Mountford WK, Lackland DT, Judson MA. The treatment of lupus pernio: results of 116 treatment courses in 54 patients. Chest. 2009;135(2):468–76.
Baughman RP, Lower EE. Infliximab for refractory sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2001;18(1):70–4.
Mallbris L, Ljungberg A, Hedblad MA, Larsson P, Stahle-Backdahl M. Progressive cutaneous sarcoidosis responding to anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48(2):290–3.
Crouser ED, Lozanski G, Fox CC, Hauswirth DW, Raveendran R, Julian MW. The CD4+ lymphopenic sarcoidosis phenotype is highly responsive to anti-tumor necrosis factor-{alpha} therapy. Chest. 2010;137(6):1432–5.
Saleh S, Ghodsian S, Yakimova V, Henderson J, Sharma OP. Effectiveness of infliximab in treating selected patients with sarcoidosis. Respir Med. 2006;100(11):2053–9.
Chung J, Rosenbach M. Extensive cutaneous sarcoidosis and coexistant Crohn disease with dual response to infliximab: case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J. 2014;21(3).
Tuchinda P, Bremmer M, Gaspari AA. A case series of refractory cutaneous sarcoidosis successfully treated with infliximab. Dermatol Ther. 2012;2(1):11.
Sene T, Juillard C, Rybojad M, Cordoliani F, Lebbe C, Morel P, et al. Infliximab as a steroid-sparing agent in refractory cutaneous sarcoidosis: single-center retrospective study of 9 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(2):328–32.
Cerniglia B, Judson MA. Infliximab-induced hypothyroidism: a novel case and postulations concerning the mechanism. Case Rep Med. 2013;2013:216939.
Tu J, Chan J. Cutaneous sarcoidosis and infliximab: evidence for efficacy in refractory disease. Australas J Dermatol. 2014;55(4):279–81.
Sweiss NJ, Welsch MJ, Curran JJ, Ellman MH. Tumor necrosis factor inhibition as a novel treatment for refractory sarcoidosis. Arthr Rheum. 2005;53(5):788–91.
Rosen T, Doherty C. Successful long-term management of refractory cutaneous and upper airway sarcoidosis with periodic infliximab infusion. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13(3):14.
Blanco R, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Gonzalez-Lopez MA, Fernandez-Llaca H, Gonzalez-Vela MC. Refractory highly disfiguring lupus pernio: a dramatic and prolonged response to infliximab. Int J Dermatol. 2015;54(8):e321–2.
Thielen AM, Barde C, Saurat JH, Laffitte E. Refractory chronic cutaneous sarcoidosis responsive to dose escalation of TNF-alpha antagonists. Dermatology. 2009;219(1):59–62.
Wanat KA, Rosenbach M. Case series demonstrating improvement in chronic cutaneous sarcoidosis following treatment with TNF inhibitors. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148(9):1097–100.
Panselinas E, Rodgers JK, Judson MA. Clinical outcomes in sarcoidosis after cessation of infliximab treatment. Respirology. 2009;14(4):522–8.
Heffernan MP, Anadkat MJ. Recalcitrant cutaneous sarcoidosis responding to infliximab. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141(7):910–1.
Haley H, Cantrell W, Smith K. Infliximab therapy for sarcoidosis (lupus pernio). Br J Dermatol. 2004;150(1):146–9.
Maneiro JR, Salgado E, Gomez-Reino JJ, Carmona L. Efficacy and safety of TNF antagonists in sarcoidosis: data from the Spanish registry of biologics BIOBADASER and a systematic review. Semin Arthr Rheum. 2012;42(1):89–103.
Jounieaux F, Chapelon C, Valeyre D, Israel Biet D, Cottin V, Tazi A, et al. Infliximab treatment for chronic sarcoidosis: a case series (in French). Revue Mal Respir. 2010;27(7):685–92.
Yee AM, Pochapin MB. Treatment of complicated sarcoidosis with infliximab anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(1):27–31.
Heffernan MP, Smith DI. Adalimumab for treatment of cutaneous sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142(1):17–9.
Mirzaei A, Joharimoghadam MM, Zabihiyeganeh M. Adalimumab-responsive refractory sarcoidosis following multiple eyebrow tattoos: a case report. Tanaffos. 2017;16(1):80–3.
Kaiser CA, Cozzio A, Hofbauer GF, Kamarashev J, French LE, Navarini AA. Disfiguring annular sarcoidosis improved by adalimumab. Case Rep Dermatol. 2011;3(2):103–6.
Philips MA, Lynch J, Azmi FH. Ulcerative cutaneous sarcoidosis responding to adalimumab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53(5):917.
Field S, Regan AO, Sheahan K, Collins P. Recalcitrant cutaneous sarcoidosis responding to adalimumab but not to etanercept. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(7):795–6.
Judson MA. Successful treatment of lupus pernio with adalimumab. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147(11):1332–3.
Cohen GF, Wolfe CM. Recalcitrant diffuse cutaneous sarcoidosis with perianal involvement responding to adalimumab. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16(12):1305–6.
Hagan CE, Offiah M, Brodell RT, Jackson JD. Chronic verrucous sarcoidosis associated with human papillomavirus infection: improvement with adalimumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4(9):866–8.
Tuchinda C, Wong HK. Etanercept for chronic progressive cutaneous sarcoidosis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5(6):538–40.
Khanna D, Liebling MR, Louie JS. Etanercept ameliorates sarcoidosis arthritis and skin disease. J Rheumatol. 2003;30(8):1864–7.
Utz JP, Limper AH, Kalra S, Specks U, Scott JP, Vuk-Pavlovic Z, et al. Etanercept for the treatment of stage II and III progressive pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest. 2003;124(1):177–85.
Papp KA. The safety of etanercept for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2007;3(2):245–58.
Judson MA, Baughman RP, Costabel U, Drent M, Gibson KF, Raghu G, et al. Safety and efficacy of ustekinumab or golimumab in patients with chronic sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 2014;44(5):1296–307.
Bomprezzi R, Pati S, Chansakul C, Vollmer T. A case of neurosarcoidosis successfully treated with rituximab. Neurology. 2010;75(6):568–70.
Cinetto F, Compagno N, Scarpa R, Malipiero G, Agostini C. Rituximab in refractory sarcoidosis: a single centre experience. Clin Mol Allergy. 2015;13(1):19.
Lamrock E, Brown P. Development of cutaneous sarcoidosis during treatment with tumour necrosis alpha factor antagonists. Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53(4):e87–90.
Marcella S, Welsh B, Foley P. Development of sarcoidosis during adalimumab therapy for chronic plaque psoriasis. Australas J Dermatol. 2011;52(3):e8–11.
Salvatierra J, Magro-Checa C, Rosales-Alexander JL, Raya-Alvarez E. Acute sarcoidosis as parotid fever in rheumatoid arthritis under anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011;50(7):1346–8.
Bonafede MM, Gandra SR, Watson C, Princic N, Fox KM. Cost per treated patient for etanercept, adalimumab, and infliximab across adult indications: a claims analysis. Adv Ther. 2012;29(3):234–48.
Keijsers RG, Verzijlbergen JF, van Diepen DM, van den Bosch JM, Grutters JC. 18F-FDG PET in sarcoidosis: an observational study in 12 patients treated with infliximab. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2008;25(2):143–9.
Sweiss NJ, Barnathan ES, Lo K, Judson MA, Baughman R. C-reactive protein predicts response to infliximab in patients with chronic sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2010;27(1):49–56.
Damsky W, Thakral D, Emeagwali N, Galan A, King B. Tofacitinib treatment and molecular analysis of cutaneous sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(26):2540–6.
Rotenberg C, Besnard V, Brillet PY, Giraudier S, Nunes H, Valeyre D. Dramatic response of refractory sarcoidosis under ruxolitinib in a patient with associated JAK2-mutated polycythemia. Eur Respir J. 2018;52(6).
Kono M, Kono M, Jodo S. A case of refractory acute sarcoid myopathy successfully treated with intravenous immunoglobulin. Scand J Rheumatol. 2018;47(2):168–9.
Linger MW, van Driel ML, Hollingworth SA. Off-label use of tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors and anakinra at an Australian tertiary hospital. Intern Med J. 2016;46(12):1386–91.
Shenoy N, Tesfaye M, Brown J, Simmons N, Weiss D, Meholli M, et al. Corticosteroid-resistant bulbar neurosarcoidosis responsive to intravenous immunoglobulin. Pract Neurol. 2015;15(4):289–92.
Awano N, Inomata M, Kondoh K, Satake K, Kamiya H, Moriya A, et al. Mixed-type multicentric Castleman’s disease developing during a 17-year follow-up of sarcoidosis. Intern Med. 2012;51(21):3061–6.
Semiz H, Kobak S. Coexistence of sarcoidosis and adult onset Still disease. Reumatol Clin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reuma.2017.04.004 (epub 19 May 2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for the preparation of this review.
Conflict of interest
Christina Dai, Shawn Shih, Ahmed Ansari, and Young Kwak have no conflicts of interest to declare. Naveed Sami was a previous sub-investigator for Centocor clinical trial for sarcoidosis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, C., Shih, S., Ansari, A. et al. Biologic Therapy in the Treatment of Cutaneous Sarcoidosis: A Literature Review. Am J Clin Dermatol 20, 409–422 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-019-00428-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-019-00428-8