Abstract
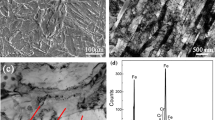
The corrosion behavior of high-strength steel used for flexible riser exposed to CO2-saturated saline solution and CO2-saturated vapor environments was studied through immersion experiment and electrochemical corrosion experiment. The corrosion behavior and mechanism of the tested steel were analyzed on the basis of corrosion kinetics, nature of corrosion products, corrosion product morphology, elemental distribution and polarization curves. The experimental results showed that the microstructure of the tested steel was bainitic microstructure. The corrosive activity of the tested steel exposed to CO2-saturated vapor environment was significantly lower than that exposed to CO2-saturated saline solution environment. On prolonging the exposure time, the corrosion rate gradually decreased, the corrosion heterogeneity increased, and the dimensions of FeCO3 crystals gradually became small. At later stages of corrosion, the corrosion current density decreased significantly and the anodic Tafel slope increased, indicating that the corrosion process was strongly inhibited. The corrosion mechanism of low-alloy steel with bainitic microstructure was proposed based on experimental results.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.R. Linter, G.T. Burstein, Corros. Sci. 117, 41 (1999)
J.D. Laumb, K.A. Glazewski, J.A. Hamling, A. Azenkeng, N. Kalenze, T.L. Watson, Energy Procedia 5173, 114 (2017)
X. Yang, S. Saevik, L. Sun, Ocean Eng. 594, 108 (2015)
I.S. Cole, P. Corrigan, S. Sim, N. Birbilis, Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 749, 5 (2011)
Z.-L. Zhang, L.-Q. Wang, H.-Y. Ci, Ocean Eng. 386, 106 (2015)
S.M. O’Halloran, A.D. Connaire, A.M. Harte, S.B. Leen, Tribol. Int. 306, 100 (2016)
M.A. Vaz, N.A.S. Rizzo, Mar. Struct. 275, 24 (2011)
N.H. Østergaard, A. Lyckegaard, J.H. Andreasen, Mar. Struct. 64, 27 (2012)
Z. Liu, X. Gao, L. Du, J. Li, X. Zhou, X. Wang, Y. Wang, C. Liu, G. Xu, R.D.K. Misra, Appl. Surf. Sci. 974, 440 (2018)
Y. Bai, T. Liu, W. Ruan, W. Chen, Compos. Struct. 1, 170 (2017)
C. Taravel-Condat, N. Desamais, Qualification of high strength carbon steel wires for use in specific annulus environment of flexible pipes containing CO2 and H2S. Paper presented at the 25th international conference on offshore mechanics and Arctic engineering, Hamburg, Germany, 4–9 June 2006
D.A. Lopez, T. Perez, S.N. Simison, Mater. Des. 561, 24 (2003)
S. Sim, I.S. Cole, F. Bocher, P. Corrigan, R.P. Gamage, N. Ukwattage, N. Birbilis, Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 534, 17 (2013)
R.M. Moreira, C.V. Franco, C.J.B.M. Joia, S. Giordana, O.R. Mattos, Corros. Sci. 2987, 46 (2004)
J.L. Li, H.X. Ma, S.D. Zhu, C.T. Qu, Z.F. Yin, Corros. Sci. 101, 86 (2014)
G.A. Zhang, Y.F. Cheng, Corros. Sci. 87, 51 (2009)
L. Xu, B. Wang, J. Zhu, W. Li, Z. Zheng, Appl. Surf. Sci. 39, 379 (2016)
Y. Zhou, J. Chen, Y. Xu, Z. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 168, 29 (2013)
S. Guo, L. Xu, L. Zhang, W. Chang, M. Lu, Corros. Sci. 123, 110 (2016)
Z. Liu, X. Gao, J. Li, L. Du, C. Yu, P. Li, X. Bai, Electrochim. Acta 842, 213 (2016)
Q.Y. Liu, L.J. Mao, S.W. Zhou, Corros. Sci. 165, 84 (2014)
Z. Liu, X. Gao, L. Du, J. Li, Y. Kuang, B. Wu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 610, 351 (2015)
S. Sim, I.S. Cole, Y.-S. Choi, N. Birbilis, Int. J. Greenh. Gas Contol 185, 29 (2014)
L. Wei, X. Pang, C. Liu, K. Gao, Corros. Sci. 404, 100 (2015)
H. Cano, D. Neff, M. Morcillo, P. Dillmann, I. Diaz, D. de la Fuente, Corros. Sci. 438, 87 (2014)
Z.J. Cheng, D. Song, J.Y. Jiang, J.H. Jiang, X.L. Ma, K. You, A.B. Ma, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 1281, 23 (2016)
G.A. Zhang, Y.F. Cheng, Corros. Sci. 1589, 51 (2009)
F.F. Eliyan, A. Alfantazi, Corros. Sci. 380, 85 (2014)
F.F. Eliyan, F. Mohammadi, A. Alfantazi, Corros. Sci. 37, 64 (2012)
A. Kahyarian, M. Singer, S. Nesic, J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 530, 29 (2016)
M. Gao, X. Pang, K. Gao, Corros. Sci. 557, 53 (2011)
N. Zhang, D. Zeng, G. Xiao, J. Shang, Y. Liu, D. Long, Q. He, Ambrish Singh, J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 444, 30 (2016)
J.L. Mora-Mendoza, S. Turgoose, Corros. Sci. 1223, 44 (2002)
L. Wei, K. Gao, Q. Li, Appl. Surf. Sci. 524, 440 (2018)
G.A. Zhang, D. Liu, Y.Z. Li, X.P. Guo, Corros. Sci. 107, 120 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out with financial support from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2015AA03A501) and Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Jiangsu University of Science and Technology (1062931702).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Available online at http://link.springer.com/journal/40195
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, DZ., Gao, XH., Du, LX. et al. Corrosion Behavior of High-Strength Steel for Flexible Riser Exposed to CO2-Saturated Saline Solution and CO2-Saturated Vapor Environments. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 32, 607–617 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-018-0825-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-018-0825-2