Abstract
Several publications deal with the influence of the initial fiber orientation in joining parts on the weld strength of fiber-reinforced thermoplastics. The welding partners have been sawn before welding. Preparing the joining parts after injection molding is not suitable since it is an additional manufacturing step. Since injection molding results in a non-uniform fiber orientation, there is a possibility that the position of the weld influences weld characteristics. The influence of the initial fiber orientation was investigated by preparing parts with longitudinal or transverse initial fiber orientation. Short and long glass fiber-reinforced thermoplastics with a glass fiber content of 30% have been welded by hot-plate and vibration welding. The initial fiber orientation in non-welded parts influences the weld strength: longitudinal fibers are more advantageous for the weld strength than transverse fibers. The influence of the position of the weld in injection-molded parts was investigated by welding the plates at the end of the flow path, at the sawn gate, and at the lateral side. The weld strength is similar at the gate or at the end of the flow path. For PA-GF30, the weld strength at the gate is even higher. Positioning the weld at the lateral side in injection-molded parts results in significantly lower weld strengths for short and long glass fiber-reinforced thermoplastics in hot-plate and vibration welding.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
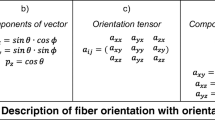
- a :
-
Amplitude
- ABS:
-
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene
- a xx, a yy, a zz :
-
Component of orientation tensor
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- d:
-
Thickness
- DVS:
-
German Welding Association
- FRP:
-
Fiber-reinforced plastics
- GF:
-
Glass fiber-reinforced
- HP:
-
Hot plate (welding)
- LGF:
-
Long glass fiber-reinforced
- L 0 :
-
Melt-layer thickness after heating
- P:
-
Unit vector
- PA:
-
Polyamide
- PP:
-
Polypropylene
- p W :
-
Welding pressure
- p x, p y, p z :
-
Component of the unit vector P
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- s J :
-
Joining displacement
- T HP :
-
Hot-plate temperature
- v J :
-
Joining velocity
- Vib:
-
Vibration welding
- σW :
-
Weld strength
References
Advani SG, Tucker CL (1987) The use of tensors to describe and predict fiber orientation in short fiber composites. J Rheol 31(8):751–784 John Wiley & Sons
Baudrit B (2014) Entwicklung innovativer Technologien zum Heizelementstumpf- und Infrarot-Schweißen von mineralgefüllten und faserverstärkten Kunststoffen. Forschungsbericht der SKZ - KFE gGmbH Kunststoff-Forschung und -Entwicklung zu dem AiF-geförderten Vorhaben 17303 N
Bates P, Couzens D, Kendall J Vibration welding of continuously reinforced thermoplastic composites. J Reinf Plast Compos, Vol. 14, July 2001, Sage Publications, pp. 344–354, 2001
Bucknall CB, Drinkwater IC, Smith GR (1980) Hot plate welding of plastics: factors affecting weld strength. Polymer engineering and science, April 1980, Vol. 20, no. 6, pp. 432–440. Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim
Brüßel A (1999) Fertigungstechnische und werkstoffspezifische Aspekte zum Fügen von Thermoplasten mittels Heizelement. Universität-Gesamthochschule Paderborn, Dissertation
Dierig T, Becker B, Reinhart C, Günther T (2012) Fiber composite material analysis in aerospace using CT data. 4th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace, 13.-15. November 2012, Augsburg,
DVS (August 2010) Prüfen von Schweißverbindungen an Tafeln und Rohren aus thermoplastischen Kunststoffen. Richtlinie DVS:2203–2202
Fiebig I, Schöppner V (2016) Investigation on factors influencing fiber orientation in welding of fiber reinforced thermoplastics. 69th annual assembly of the International Institute of Welding (IIW). In: Melbourne (Australien)
Fiebig I, Schöppner V (2016) Influence of the initial fiber orientation on the weld strength in welding of glass fiber reinforced thermoplastics. Int J Polymer Sci 2016
Fiebig I, Schöppner V (2018) Factors influencing the fiber orientation in welding of fiber-reinforced thermoplastics. Welding in the World (2018) 62:997–1012
Gehde M, Giese M, Ehrenstein GW (1997) Welding of thermoplastics reinforced with random glass mat. Polym Eng Sci, April 1997, Vol. 37, No. 4, pp. 702–714, Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim
Kagan V, Bednarczyk C, Siu-Ching L, Smith GR (1999) US-patent 5.874.146: performance of vibration welded thermoplastic joints
Kamal MR, Chung Y-M, Gomez R Three-dimensional fiber orientation in vibration welded joints of glass fiber reinforced polyamide-6. Polym Compos, 2008, Vol. 20, No. 9, Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim, pp. 954–963, 2008
Krause F, Linder T (2016) Mehr Leistung beim Kunststoffschweißen – Vier neue Polyamidtypen für Bauteile unter der Motorhaube. Kunststoffe 9 (2016), Carl Hanser Verlag, München, S. 202–204
Rudolf R, Neitzel M, Strohfuss W (1997) Interaction of variables in welding of continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastics. 29th International SAMPE Technical Conference 29:462–474
Acknowledgements
The IGF Project 18702 N of the research association “Forschungsvereinigung Schweißen und verwandte Verfahren e. V. des DVS. Aachener Straße 172. 40223 Düsseldorf” was on the basis of a resolution of the German Bundestag, promoted by the German Ministry of Economic Affairs and Energy via AiF within the framework of the program for the promotion of joint industrial research and development (IGF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended for publication by Commission XVI - Polymer Joining and Adhesive Technology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiebig, I., Schoeppner, V. Influence of fiber orientation and weld position in welding injection-molded fiber-reinforced thermoplastics. Weld World 62, 1301–1309 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-018-0649-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-018-0649-8