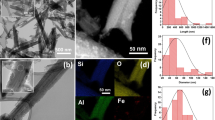
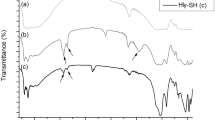
Abstract
Halloysite nanotubes are inorganic clay minerals of kaolin group. Halloysite possess unique morphology, chemical composition, cation exchange capacity and charge properties making them ideal candidate for various industrial application. In the present study, an attempt was made to functionalize the exterior surface of halloysite nanocontainer. The surface of halloysite nanocontainer was modified using tetrabutylammonium chloride (TBAC). Further an attempt was made to employ these functionalized nanocontainers to uptake and release the active molecule (dye Acid Red1). TBAC-modified nanocontainer indicated higher adsorption capacity of 4.54 mg/g as compared to unmodified nanocontainer (3.08 mg/g). The release behaviour of active molecule from loaded nanocontainers was found with change in pH and temperature. Since the loading characteristics of functionalized nanocontainers were found to be adsorption dependent, parameters such as effect of time, loading, pH, initial concentration were studied for analysing the loading characteristics. The dye release from 0.5 g dye-loaded TBAC-modified nanocontainers at pH 11 and at 32 °C was found to be 92%. Lastly, the release readings were analysed for the best fit (97%) using permeation kinetic model (Peppa’s model).















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
Acid Red 1 (dye)
- CH3COOH:
-
Acetic acid
- CH3COONa:
-
Sodium acetate
- DI:
-
Deionized water
- HCl:
-
Hydrochloric acid
- HDTMA:
-
Hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide
- HNT:
-
Halloysite nanotubes
- Na2HPO4 :
-
Disodium hydrogen phosphate
- NaCl:
-
Sodium chloride
- NaH2PO4 :
-
Monosodium phosphate
- TBAC:
-
Tetrabutylammonium chloride
- C 0 :
-
Initial solution concentration in ppm
- C e :
-
Solution concentration at equilibrium in ppm
- C ed :
-
Equilibrium concentration of the dye in the solution in (mg/L)
- k ad1 :
-
Rate constant of pseudo-first-order adsorption (min−1)
- k ad2 :
-
Rate constant of pseudo-second-order adsorption (g mg−1 min−1)
- K f and n :
-
Physical constants of the Freundlich adsorption isotherm
- k t :
-
Release rate constant
- M :
-
Mass of nanocontainers in g
- n :
-
Release exponent indicating transport mechanism
- q 0 :
-
Amount of dye release in the solution at time t = 0
- q e :
-
Amount of adsorbed dye on the adsorbent surface in (mg/g) at equilibrium
- q t :
-
Amount of dye release in the solution at time t
- Q max :
-
Maximum adsorption capacity (mg/g)
- Q t :
-
Amount of dye release in given time
- V :
-
Volume of solution in litre
- β :
-
Signifies the constant related to the energy of adsorption
References
A.G. Skirtach, O. Kreft, Stimuli sensitive nanotechnology for drug delivery, in Nanotechnology in drug delivery, vol. 10, ed. by M.M. Devilliers, et al. (Springer, New York, 2009), pp. 545–578
S.M. Moghimi, A.C. Hunter, J.C. Murray, Nanomedicine: current status and future prospects. J. Fed. Amer. Soc. Exp. Biol. 19, 311–330 (2005)
D. Borisova, H. Mohwald, D. Shchukin, Influence of embedded nanocontainers on the efficiency of active anticorrosive coatings for aluminum alloys part I: influence of nanocontainer concentration. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 2931–2939 (2012)
S.A. Ghodke, S.H. Sonawane, B.A. Bhanvase, S. Mishra, K.S. Joshi, Studies on fragrance delivery from inorganic nanocontainers: encapsulation, release and modeling studies. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. E 96(1), 45–53 (2015)
M. Zhou, T.S.H. Leong, S. Melino, F. Cavalieri, M. Ashokkumar, S. Kentish, Sonochemical synthesis of liquid-encapsulated lysozyme microspheres. Ultrason. Sonochem. 17, 333–337 (2010)
A. Kumar, L.D. Stephenson, J.N. Murray, Self-healing coatings for steel. Prog. Org. Coat. 55, 244–253 (2006)
S.H. Sonawane, B.A. Bhanvase, A.A. Jamali, S.K. Dubey, S.S. Kale, D.V. Pinjari, A.B. Pandit, Improved active anticorrosion coatings using layer-by-layer assembled ZnO nanocontainers with benzotriazole. Chem. Eng. J. 189–190, 464–472 (2012)
D. Quintanar, E. Allémann, H. Fessi, E. Doelker, Preparation techniques and mechanisms of formation of biodegradable nanoparticles from preformed polymers. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 24, 1113–1128 (1998)
C.E. Mora-Huertas, H. Fessi, A. Elaissari, Polymer-based nanocapsules for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 385, 113–142 (2010)
E. Fleige, M.A. Quadir, R. Haag, Stimuli-responsive polymeric nanocarriers for the controlled transport of active compounds: concepts and applications. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 64, 866–884 (2012)
G.V. Joshi, B.D. Kevadiya, H.C. Bajaj, Design and evaluation of controlled drug delivery system of buspirone using inorganic layered clay mineral. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 132(3), 526–530 (2010)
Z. Zhong Zhang, D.L. Sparks, N.C. Scrivner, Sorptlon and desorption of quaternary amine cations on clays. Environ. Sci. Technol. 27, 1625–1631 (1993)
M.G. Apps, A.J. Ammit, A. Gu, N.J. Wheate, Analysis of montmorillonite clay as a vehicle in platinum anticancer drug delivery. Inorg. Chimica. Acta. 421, 513–518 (2014)
S.A. Boyd, M.M. Mortland, C.T. Chiou, Sorption characteristic of organic compounds on hexadecyltrimethylammonium-smectite. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 52, 652–657 (1998)
S.H. Sonawane, P.L. Chaudhari, S.A. Ghodke, S. Ambade, A. Mirikar, A. Bane, S. Gulig, Combined effect of ultrasound and nanoclay on adsorption of phenol. Ultrason. Sonochem. 15, 1033–1037 (2008)
M.I. Carretero, M. Pozo, Clay and non-clay minerals in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. Part II Active ingredients. Appl. Clay. Sci. 47, 171–181 (2010)
C. Vettori, D. Paffetti, G. Pieramellara, E. Stotzky, E. Gallori, Amplification of bacterial DNA bound on clay minerals by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) technique. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 20, 251–260 (1996)
M.A. Osman, M. Ploetze, U.W. Suter, Surface treatment of clay minerals thermal stability, basal-plane spacing and surface coverage. J. Mater. Chem. 13(9), 2359–2366 (2003)
H.Y. Wei, N. Li, D.S. Tong, C.H. Zhou, C.X. Lin, C.Y. Xu, Adsorption of proteins and nucleic acids on clay minerals and their interactions: a review. Appl. Clay Sci. 80–81, 443–452 (2013)
E. Abdullayev, R. Price, D. Shchukin, Y. Lvov, Halloysite tubes as nanocontainers for anticorrosion coating with benzotriazole. Appl. Mater. Interf. 1(7), 1437–1443 (2009)
V. Vergaro, Y.M. Lvov, S. Leporatti, Halloysite clay nanotubes for resveratrol delivery to cancer cells. Macromol. Biosci. 12(9), 1265–1271 (2012)
H. Hemmatpour, V. Haddadi-Asl, H. Roghani-Mamaqani, Synthesis of pH-sensitive poly (N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate)-grafted halloysite nanotubes for adsorption and controlled release of DPH and DS drugs. Polymer 65, 143–153 (2015)
E. Joussein, S. Petit, J. Churchman, B. Delvaux, B. Theng, D. Righi, Halloysite clay minerals—a review. Clay Miner. 40, 383–426 (2005)
E. Abdullayev, Y. Lvov, Clay nanotubes for corrosion inhibitor encapsulation: release control with end stoppers. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 6681–6687 (2010)
Y.M. Lvov, D.G. Shchukin, H. Mohwald, R.R. Price, Halloysite clay nanotubes for controlled release of protective agents. ACS Nano 2(5), 814–820 (2008)
S.R. Levis, P.B. Deasy, Characterisation of halloysite for use as a microtubular drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 243, 125–134 (2002)
Q. Wang, J. Zhang, A. Wang, Alkali activation of halloysite for adsorption and release of ofloxacin, Alkali activation of halloysite for adsorption and release of ofloxacin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 287, 54–61 (2013)
A. Zhang, L. Pan, H. Zhang, S. Liu, Y. Ye, M. Xia, X. Chen, Effects of acid treatment on the physico-chemical and pore characteristics of halloysite. Colloids Surf. B 396, 182–188 (2012)
E. Abdullayev, A. Joshi, W. Wei, Y. Zhao, Y. Lvov, Enlargement of halloysite clay nanotube lumen by selective etching of aluminum oxide. ACS Nano 6(8), 7216–7226 (2012)
W.O. Yah, A. Takahara, Y.M. Lvov, Selective modification of halloysite lumen with octadecyl phosphonic acid: new inorganic tubular micelle. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 1853–1859 (2012)
E. Horvath, J. Kristof, R. Kurdi, E. Mako, V. Khunova, Study of urea intercalation into halloysite by thermoanalytical and spectroscopic techniques. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 105, 53–59 (2011)
P. Yuan, S.J. Antill, P.D. Southon, Z. Liu, C.J. Kepert, M.E.R. Green, J.M. Hook, Functionalization of halloysite clay nanotubes by grafting with γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 15742–15751 (2008)
W. Jinhua, Z. Xiang, Z. Bing, Z. Yafei, Z. Rui, L. Jindun, C. Rongfeng, Rapid adsorption of Cr(VI) on modified halloysite nanotubes. Desalination 259, 22–28 (2010)
M.M. Mortland, S. Shaobai, S.A. Boyd, Clay-organic complexes as adsorbents for phenol and chlorophenols. Clays Clay Miner. 34(5), 581–585 (1986)
I.M.C. Lo, R.K.M. Mak, S.C.H. Lee, Modified clays for waste containment and pollutant attenuation. J. Environ. Eng. 123(1), 25–32 (1997)
P. Luo, Y. Zhao, B. Zhang, J. Liu, Y. Yang, J. Liu, Study on the adsorption of Neutral Red from aqueous solution onto halloysite nanotubes. Water Res. 44, 1489–1497 (2010)
K.P. Nicolini, C.R. Fukamachi, F. Wypych, A.S. Mangrich, Dehydrated halloysite intercalated mechanochemically with urea: thermal behavior and structural aspects. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 338, 474–479 (2009)
Q. He, D. Yang, X. Deng, Q. Wu, R. Li, Y. Zhai, L. Zhang, Preparation, characterization and application of N-2-Pyridylsuccinamic acid-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for solid-phase extraction of Pb(II). Water Res. 47, 3976–3983 (2013)
S. Lagergren, About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Svenska Vetensk Handl. 24, 1–39 (1898)
Y. Zhao, B. Zhang, X. Zhang, J. Wang, J. Liu, R. Chen, Preparation of highly ordered cubic NaA zeolite from halloysite mineral for adsorption of ammonium ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 178(1–3), 658–664 (2010)
S. Rangabhashiyam, N. Selvaraju, Efficacy of unmodified and chemically modified Swietenia mahagoni shells for the removal of hexavalent chromium from simulated wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 209, 487–497 (2015)
E. Nakkeeran, S. Rangabhashiyam, M.S. Giri Nandagopal, N. Selvaraju, Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using Strychnos nux-vomica shell as an adsorbent. Desalin. Water Treat. 57(50), 23951–23964 (2016)
S. Rangabhashiyam, M.S. Giri Nandagopal, E. Nakkeeran, N. Selvaraju, Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from synthetic and electroplating effluent on chemically modified Swietenia mahagoni shell in a packed bed column. J. Environ. Monitor. 188(7), 1–13 (2016)
F. Kiani, M. Dostali, A. Rostami, A.R. Khataee, Adsorption studies on the removal of Malachite Green from aqueous solutions onto halloysite nanotubes. Appl. Clay Sci. 54, 34–39 (2011)
G. Crini, H.N. Peindy, Adsorption of CI Basic Blue 9 on cyclodextrin-based material containing carboxylic groups. Dyes Pigm. 70, 204–211 (2006)
S. Rangabhashiyam, E. Nakkeeran, N. Anu, N. Selvaraju, Biosorption potentials of a novel Ficus auriculata leaves powder for the sequestration of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions. Res. Chem. Intermed. 41(11), 8405–8424 (2015)
E. Nakkeeran, N. Saranya, M.S. Giri Nandagopal, A. Santhiagu, N. Selvaraju, Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solutions by a novel powder prepared from Colocasia esculenta leaves. Int. J. Phytoremediation. 18(8), 812–821 (2016)
S. Li, Removal of crystal violet from aqueous solution by sorption into semi interpenetrated networks hydrogels constituted of poly(acrylic acid-acrylamide methacylate) and amylase. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 2197–2202 (2010)
N. Emad, J. Qada, G. Stephen, Adsorption of methylene blue onto activated carbon produced from steam activated bituminous coal: a study of equilibrium adsorption isotherm. Chem. Eng. J. 124, 103–110 (2006)
V.N. Ravella, R.R. Nadendla, N.C. Kesari, Design and evaluation of sustained release pellets of aceclofenac. J. Pharm. Res. 6, 525–531 (2013)
P. Costa, J.M.S. Lobo, Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 13, 123–133 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghodke, S.A., Sonawane, S.H., Bhanvase, B.A. et al. Functionalization, Uptake and Release Studies of Active Molecules Using Halloysite Nanocontainers. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. E 100, 59–70 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-019-00140-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-019-00140-6