Abstract
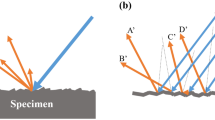
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a process of developing prototypes by depositing layers of material according to predetermined cross sectional geometry. Quality of the produced part is highly dependent on surface finish. This work describes a methodology to calculate the surface roughness of part manufactured using FDM process. The surface roughness values are measured using conventional stylus instrument and light sectioning vision system. In conventional stylus instrument method, diamond tipped stylus destroys the surface topography. Light sectioning method is non-contact method hence it overcomes this problem. In light sectioning method microscope and light source are arranged in such a manner, as both are inclined at an angle of 45° to the normal plane. The light section is projected on surface of profile at an incident angle of 45°. The reflected light can be observed using microscope. The camera is connected with microscope to capture the micrograph. These images are analyzed and processed using various image processing techniques. Experimental results are validated by comparing final results with conventional system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Xu, H. Hu, Development of non-contact surface roughness measurement in last decades, in International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (2009)
R.I. Campbell, M. Martorelli, H.S. Lee, Surface roughness visualization for rapid prototyping models. Comput. Aided Des. 34, 717–725 (2002)
P.M. Pandey, N.V. Reddy, S.G. Dhangle, Improvement of surface finish by staircase machining in fused deposition modeling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 132, 323–331 (2003)
T. Jeyapoovan, M. Murugan, Surface roughness classification using image processing. Measurement 46, 2065–2072 (2013)
M.B. Kiran, B. Ramamoorthy, V. Radhakrishnan, Evaluation of surface roughness by vision system. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 38(5–6), 685–690 (1998)
G.D. Babu, K.S. Babu, B.U.M. Gowd, Evaluation of Surface Roughness Using Machine Vision (IEEE, Piscataway, 2010)
G. Schmaltz, Technische Oberflächenkunde (Springer, Berlin, 1936), pp. 5–8
O.B. Aboulatta, 3D surface roughness measurement using light sectioning vision system, in WCE, vol. 1 (2010)
D. Yang, M.R. Jackson, R.M. Parkin, Inspection of wood surface waviness defects using the light sectioning method. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. I 220(7), 617 (2006)
W. Wang, P.L. Wong, The dynamic measurement of surface topography using a light-section technique. Tribotest 9(4), 305–316 (2003)
Acknowledgment
This paper is a revised and expanded version of an article entitled “Surface Roughness Measurement of Parts Manufactured by FDM Process using Light Sectioning Vision System” presented in “International Conference on Additive Manufacturing, 3D printing and 3D Scanning” held at Chennai, India during February 6–7, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelkar, A.S., Kumbhar, N.N. & Mulay, A.V. Surface Roughness Measurement of Parts Manufactured by FDM Process using Light Sectioning Vision System. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. C 99, 429–433 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-016-0341-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-016-0341-y