Abstract
Development of a nation is directly related to the accomplishment of public infrastructure projects. They cater to the objectives of sector-specific demand and accrue benefits in other related fields. These architectural engineering projects contribute to the overall development, which is complex to measure in tangible terms alone, but call for establishing indicators for measuring intangible benefits as well. Delay in projects is considered to affect the tangible cost benefits. It is, however, a limited perception of delay consequences. The cost of delay (CoD), therefore, can be determined by considering the overall impact of tangible and intangible benefits of such projects. This paper brings out the framework for determining the CoD for the selected case study of a metro rail project. It reflects the consequences of delay in overall development prospects and high-level infrastructure objectives by establishing the CoD. The cost thus established can serve as the basis for mobilizing additional resources and strategic decision making in the best interest of overall benefits. The outcome of the study creates an opportunity to manage metro rail projects by mitigating the negative consequences of time overruns.

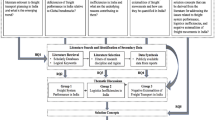
Source: Author
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Patanakul, Y.H. Kwak, O. Zwikael, M. Liu, What impacts the performance of large-scale government projects? Int. J. Proj. Manag. 34(3), 452–466 (2016)
S. Wells, C. Bullen, A near miss: the importance of context in a public health informatics project in a New Zealand case study. J. Am. Med. Inf. Assoc. (JAMIA) 15(5), 701–704 (2008)
S.L. Caudle, W.L.R. Gorr, K.E. Newcomer, Key information systems management issues for the public sector. MIS Q. 15(2), 171–188 (1991)
M. Ward, S. Mitchell, A comparison of the strategic priorities of public and private sector information resource management executives. Gov. Inf. Q. 21(3), 284–304 (2004)
MoSPI, Manual—infrastructure statistics CSO-MIS-2012 (Central Statistics Office and Programme Implementation Government of India, New Delhi, 2012)
M.N. Murty, K.K. Dhavala, R. Singh, Social cost-benefit analysis of Delhi (Report for Planning Commission, Government of India, Institute of Economic Growth, New Delhi, 2006)
F. Beckers, N. Chiara, A. Flesch, J. Maly, E. Silva, U. Stegemann, A risk-management approach to a successful infrastructure project. Mckinsey Working Paper on Risk. (52), 18 (2013)
M. Sambasivan, Y.W. Soon, Causes and effects of delays in Malaysian construction industry. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 25(5), 517–526 (2007)
S.O. Babatunde, A. Opawole, I.C. Ujaddughe, An appraisal of project procurement methods in the Nigerian construction industry. Civ. Eng. Dimens. 12(1), 1–7 (2010)
O. Motaleb, M. Kishk, An investigation into causes and effects of construction delays in UAE, in Annual Conference of the Association of Researchers in Construction Management (2010), p. 26
A.A. Aibinu, G.O. Jagboro, The effects of construction delays on project delivery in Nigerian construction industry. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 20(8), 593–599 (2012)
J.K. Lee, Cost overrun and cause in Korean social overhead capital projects: roads, rails, airports, and ports. J. Urb. Plan. Dev. 134(2), 59–62 (2008)
B. Flyvbjerg, M.K.S. Holm, S.L. Buhl, What causes cost overrun in transport infrastructure projects? Transp. Rev. 24(1), 3–18 (2004)
B. Flvbjerg, M.K.S. Holm, S.L. Buhl, How common and how large are cost overruns in transport infrastructure projects? Transp. Rev. 23(1), 71–88 (2003)
C.N. Doll, O. Balaban, A methodology for evaluating environmental co-benefits in the transport sector: application to the Delhi Metro. J. Clean. Prod. 58, 61–73 (2013)
N. Sharma, A. Singh, R. Dhyani, S. Gaur, Emission reduction from MRTS projects—a case study of Delhi metro. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 5(4), 721–728 (2014)
S.K. Jain, K. Varun, N. Ramakrishna, Economic analysis of Hyderabad metro rail project. Int. J. Technol. 5(2), 297–303 (2015)
D. Namiot, Z. Kutuzmanov, E. Fedorov, O. Pokusaev, On the assessment of socio-economic effects of the city railway. Int. J. Open Inf. 6, 92–103 (2018)
RITES, Integrated Multi-Modal Mass Rapid Transport System for Delhi: Economic Analysis for Modified First Phase (RITES, Gurgaon, 1995)
H. Bailly, P. Brinckerhoff, California life-cycle benefit/cost analysis model (Cal-B/C). (California Department of Transportation California, 1999)
T. Litman, ‘Vehicle Costs’-Transportation Cost and Benefit Analysis: Techniques and Implications (Victoria Transport Policy Institute, Victoria, 2009)
S. Polzin, X. Chu, S.R. Vishaka, Exploration of a Shift in Household Transportation Spending from Vehicles for Public Transportation (Centre for Urban Transportation Research- University of South Florida, Florida, 2008)
L.R. Kadiyali, Study for updating road user cost data, in Journal of Indian Roads Congress (1992)
A.K. Garg, S. Arya, The opportunity analysis of carbon credit trading for developing world—a case study. Int. J. Mark. Financ. Serv. Manag. Res. 4(2), 29–38 (2015)
MoSPI, 390th Flash Report on Central Sector Projects (Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation-Government of India, New Delhi, 2018)
E. Kula, Estimation of social rate of interest for India. J. Agric. Econ. 55(1), 91–99 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mittal, Y.K., Paul, V.K. & Sawhney, A. Methodology for Estimating the Cost of Delay in Architectural Engineering Projects: Case of Metro Rails in India. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 100, 311–318 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-019-00366-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-019-00366-y